2018-04
10
HART Multiplexer System KFD*-HM*-16
System Description
3 System Description
3.1 The Basic Principles of HART Communication
The HART protocol is supported by many conventional 4mAto20mA field devices that use it
to enable digital communication for configuration and maintenance purposes. Many of the
device parameters, and the measured value itself, can be digitally transferred to and from
the device. This digital communication runs in parallel to the 4 mA to 20 mA signal on the same
line. This is enabled via current modulation, which is superimposed on the desired signal.
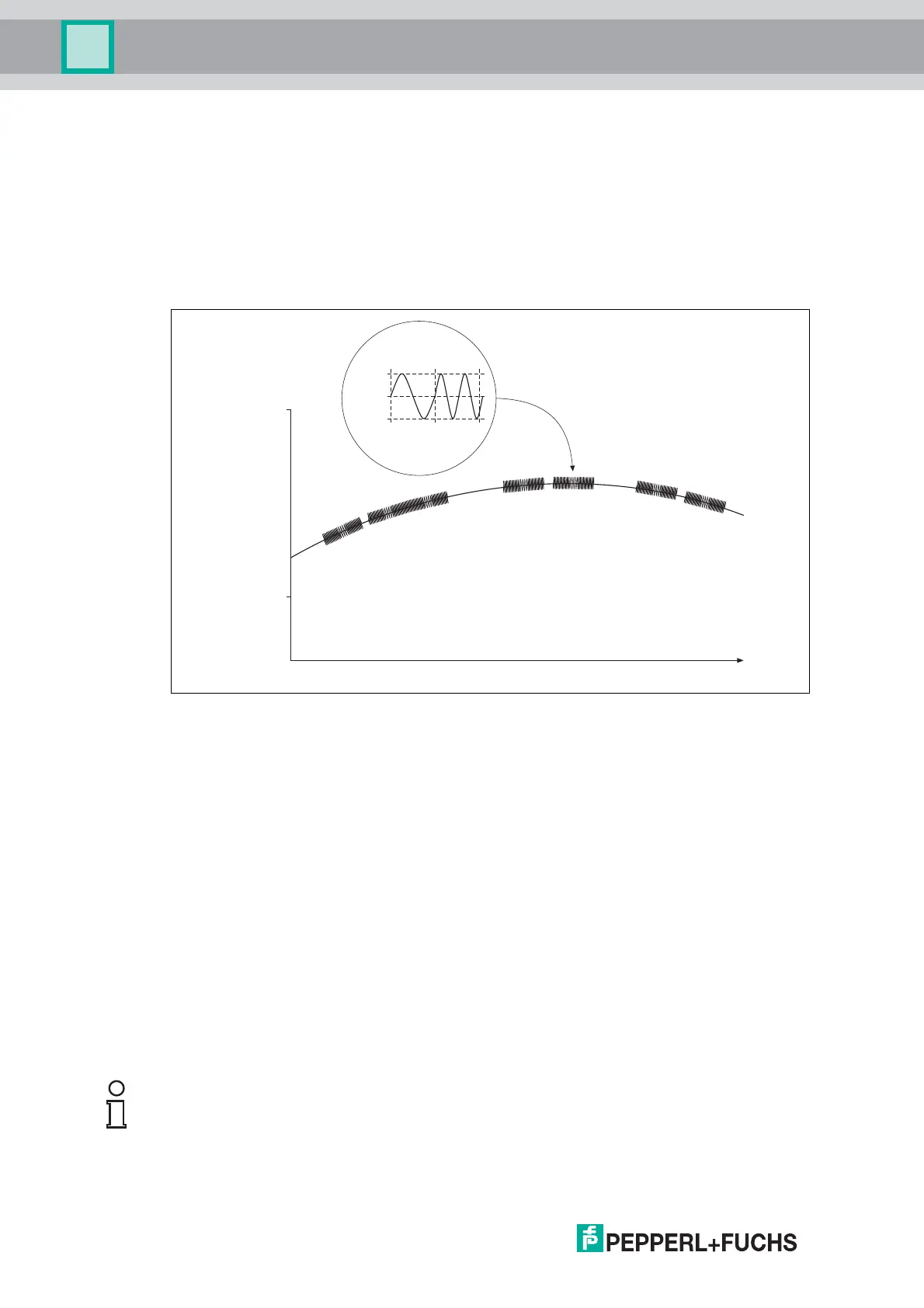
Figure 3.1
The high-frequency HART signal consists of the sine frequencies 1200 Hz and 2200 Hz.
The average value of the signal is 0 and can therefore be filtered through the standard circuit of
the analog input. This does not affect the analog signal.
The HART protocol is a master-slave protocol. This means that a field device responds only
when it is addressed. Burst mode is an exception. The message duration is a few hundred
milliseconds, meaning that two to three messages can be transferred per second.
The HART commands are divided into 3 groups:
• Universal commands
These commands must be supported by all field devices.
• Common practice commands
These commands correspond to common practice and are suitable for many field devices.
• Device-specific commands
These commands are only suitable for certain field devices.
All three types of commands are used in the HART multiplexer system. This document
includes a list of commands. See chapter 9.1.
+0.5 mA
-0.5 mA
0
1200 Hz 2200 Hz
"1"
"0"
20 mA
4 mA
Analog
signal
C = Command
R = Response
Time (seconds)
HART signal
C
R
C
R
C
R
Note!
Additional information can be found in /1/, /2/, /3/, see chapter 9.3.

 Loading...
Loading...