Supply water quality
Composition and pH value
The dosing unit adds acid or lye to the supply water to:
• regulate the pH value of the irrigation water;
• chemically mix (homogenise) the irrigation water in a optimum manner;
The pH value of the irrigation water must be between 5.2 and 6.2, depending on the crop and growing
medium.
Supply water consists of (a combination of) rain water, drinking water, well water, downstream mill
water, river water or reverse osmosis water, typically mixed with (disinfected) drain water. The variety
of chemical elements in the supply water determine not only the composition and the pH value of
the supply water but also whether or not the supply water can be used as irrigation water once
fertiliser and acid or lye have been added using the dosing unit.
Influence of bicarbonate
It is important that the quantity of bicarbonate (HCO
3
-
) in the supply water is established by means
of water analysis. Bicarbonate has a buffering effect on the pH value and affects the operation of
the acid dosing control in the dosing unit:
•
An optimum quantity of HCO
3
-
in the supply water helps to ensure that plants receive irrigation
water with a reliable and accurate pH value via the dosing unit. The correct pH value of the
irrigation water is necessary for the good take up of fertilisers by the plant.
•
An excessively low quantity of HCO
3
-
causes the pH control to become unstable.
•
An excessively high quantity of HCO
3
-
leads to the following problem: dosing acid neutralises
HCO
3
-
, with a quantity of carbon dioxide (CO
2
) being generated. Because the system is closed,
this CO
2
cannot escape from the irrigation water and therefore reaches the plants. There it will
be released into the ambient air, causing the pH to rise. In this case, the pH at the plants will not
therefore be the same as the pH that was set on the unit.
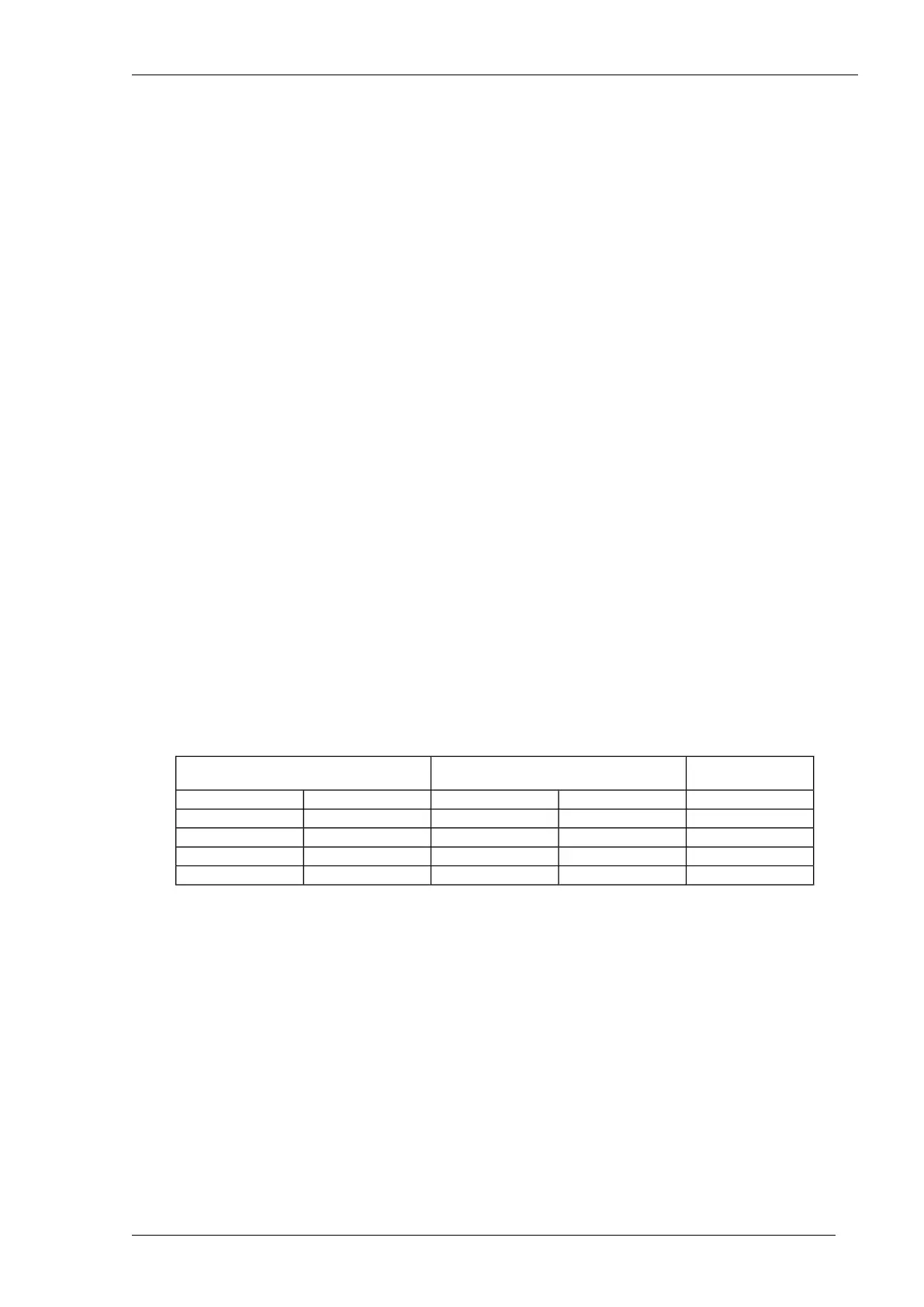
The table below shows the limit values for the quantity of HCO
3
-
and the qualification of the supply
water.
Bicarbonate limit values and supply water qualification
Supply water
qualification
Quantity of bicarbonate expressed as
calcium carbonate (CaCO
3
)
Quantity of bicarbonate (HCO
3
-
)
[mg/l] or [ppm][mmol/l][mg/l] or [ppm][mmol/l]
Too low< 5.0< 0.050< 6.1< 0.10
Optimum5.0 – 25.00.050 – 0.2506.1 – 30.50.10 – 0.50
High25.0 – 500.250 – 0.530.5 – 61.00.50 – 1.0
Too high≥ 50≥ 0.5≥ 61.0≥ 1.0
Pre-treat supply water
On the basis of the concentration of HCO
3
-
, it must be determined which measures or combinations
of measures should be taken to pre-treat the supply water.
Supply water with too low a concentration of bicarbonate:
When using reverse osmosis water, but in some cases rain water also, too low a quantity of HCO
3
-
(< 0.10 mmol/l) may be deemed to exist in the supply water. Dosing acid may give rise to an unstable
chemical reaction in the irrigation water.
NutriJet - user - 00.00240
Priva
 Loading...
Loading...