122 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor
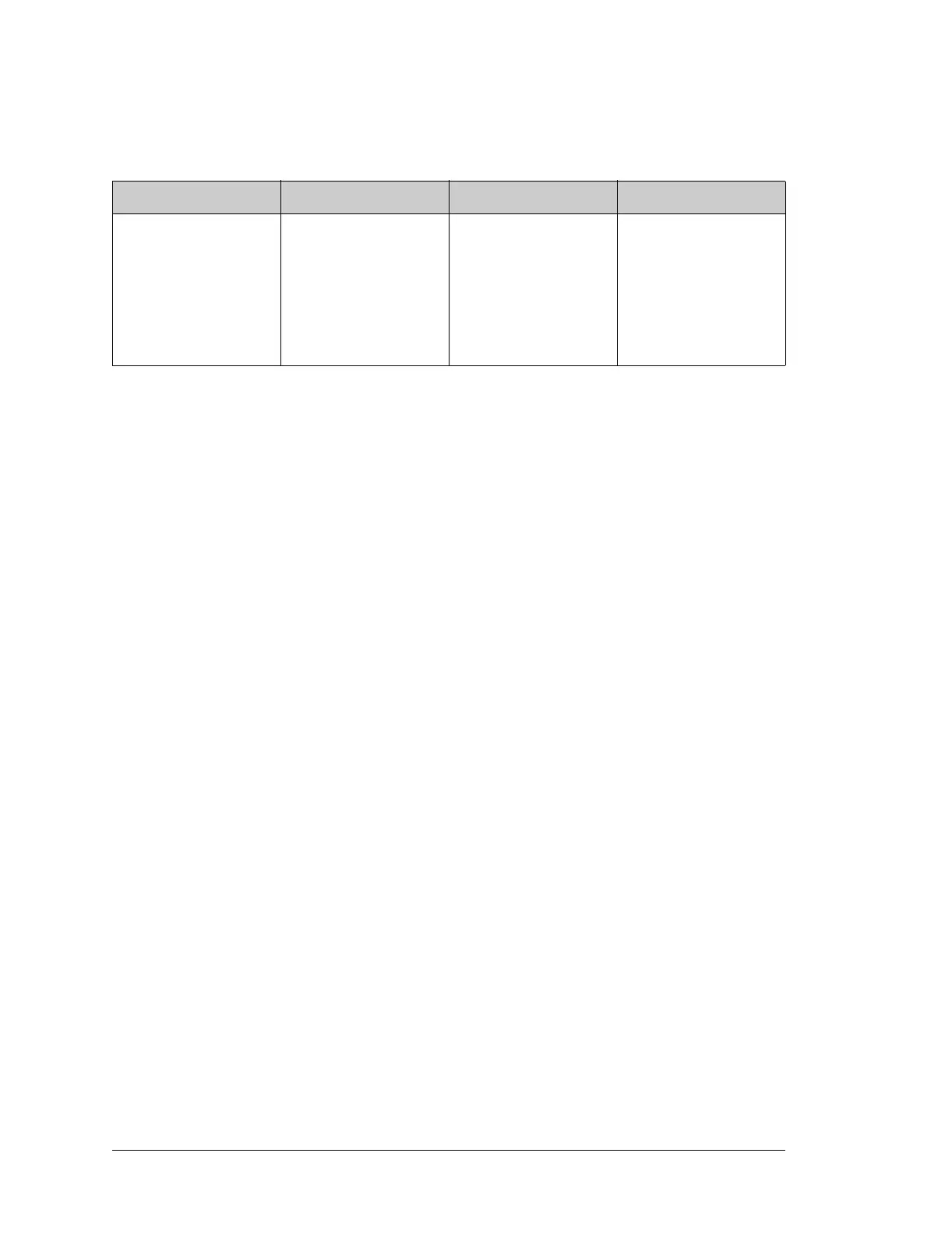
Table 12-3 describes the serial port control registers.
Bits 7,6—In asynchronous mode, always store zero in these bits. For Ports A and B, if the
clocked serial mode is enabled, store the code here to start an operation, either receive or
send. If the clock is internal, a burst of 8 clocks will drive the clock line. In external mode,
the receiver or transmitter waits for an externally supplied burst of 8 clocks.
Bits 5,4—This enables the standard or alternate pins for the ports. The parallel port output
function for the specified Tx pin becomes disabled when the port is enabled. The settings
in the parallel port C function register (PCFR) and the parallel port D function register
(PDFR) are used to enable the Port C and Port D serial outputs (see Section 9.3, “Parallel
Port C,” and Section 9.4, “Parallel Port D,” for more details).
Bits 3,2—This sets the mode of operation. Modes 10 and 11 apply only to Ports A and B.
Bits 1,0—These bits enable interrupts and set the interrupt priority.
Table 12-3. Serial Port Control Registers (adr = 11xx0100, xx = A,B,C,D)
Bit 7,6 Bit 5,4 Bit 3,2 Bit 1,0
00—no op
01—receive 1 byte
clocked mode (A,B)
10—send one byte
clocked mode (A,B)
11—reserved for future
use
00—use port C for serial
input
01—use port D for serial
input
1x—disable receiver
input
00—async mode, 8 bits
01—async mode 7 bits
10—clocked mode
external clock (A,B)
11—clocked mode
internal clock (A,B)
00—no interrupt
01— priority 1 interrupt
10—priority 2
11—priority 3
 Loading...
Loading...