0MNMHEM30RUENUB 00 pag. 11 / 57
2.3 Cooling of the premises
The recommended operating temperature for the lifetime of the UPS and of the batteries is between 20 and 25°C.
The lifespan of the battery depends on the operating temperature; with an
operating temperature of between 20°C and 30°C, the lifespan of the
batteries is halved. A heat dissipation system is required to keep the
temperature of the premises housing the equipment within the field 20÷25°C.
The heat dissipation needed for the correct operation of the UPS is brought
about by the air current made by the fans located inside the UPS (forced
convection) and by the air around the side panels (natural convection).
In order to ensure proper air circulation, and therefore the correct operation
of the UPS, measures must be taken during installation to avoid any
obstructions to the free circulation of air. These include the following:
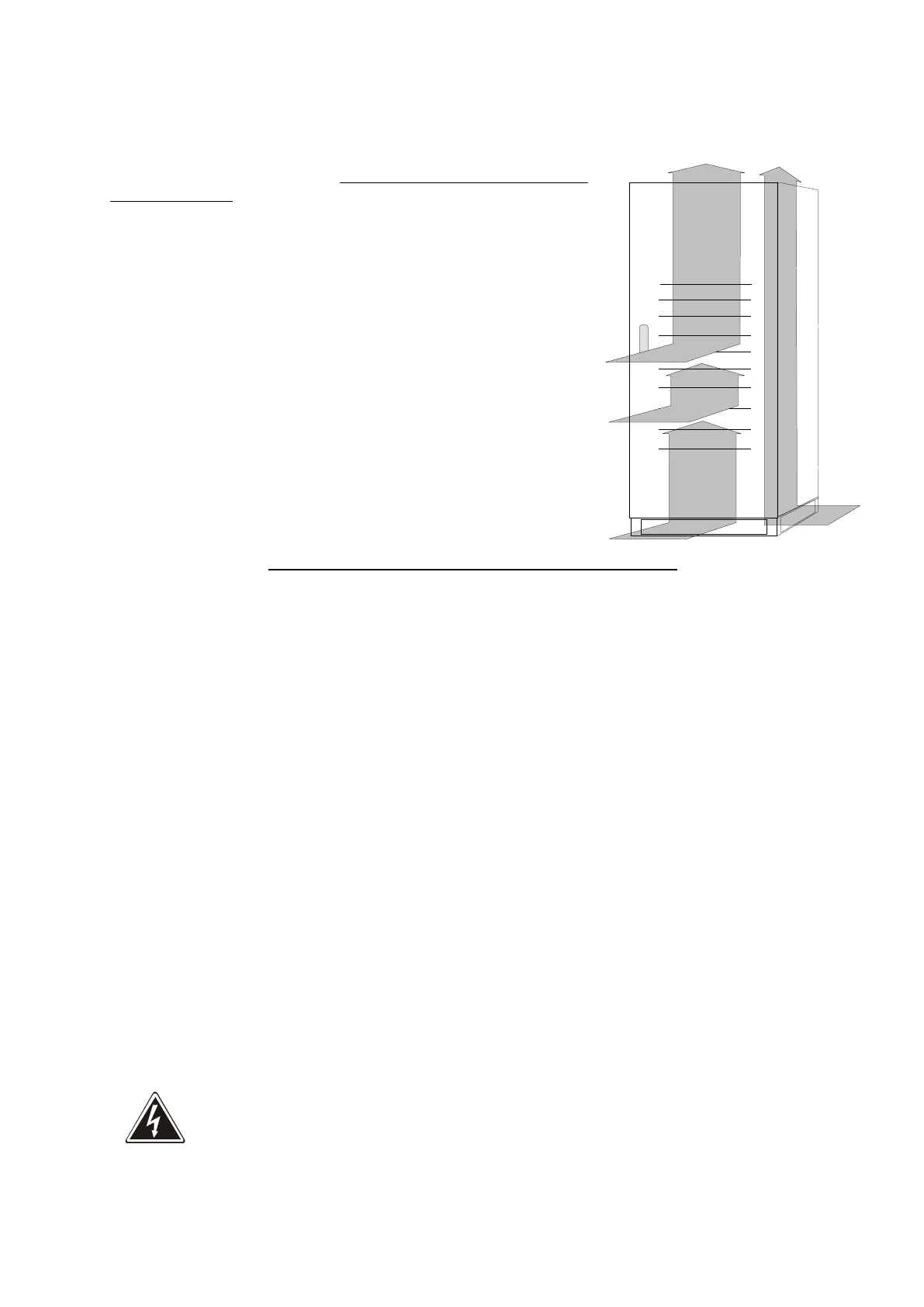
ensure a distance of at least 60 centimetres from the ceiling, so as not to
hinder air extraction,
leave a free space of at least one metre at the front of the equipment to
ensure both the circulation of the air and installation and maintenance
operations;
With natural convection the thermal load is dissipated to the outside
through the walls; thus a cabinet placed against a wall or in a hollow
dissipates less heat than one located in a free environment.
The following rule must be observed:
leave at least one of the three side walls free: right, left or back.
the side strips must not be mounted for installations where cabinets are placed side by side.
2.4 Air change for battery premises
The room in which the battery box is installed must be provided ventilated so as to keep the concentration of
hydrogen generated during charging within safe limits. The room should preferably be ventilated naturally; if it
cannot be, forced ventilation may be employed. Standard EN 50272-2 regarding air exchange provides that the
minimum aperture must satisfy the following equation:
A = 28 x Q = 28 x 0.05 x n x Igas x C10 (1/10³) [cm²]
where: A = surface free of air input/output opening; Q = air flow to be exhausted [m³/h];
n = number of battery elements; C10 = battery capacity in 10 hours [Ah];
Igas = gas producing current [mA//Ah]
according to the standard:
Igas = 1 in backup charging for VRLA type batteries (*); Igas = 8 in fast charging for VRLA type batteries (*)
(*) for open vessel or nickel batteries, contact the battery manufacture for details.
- example calculation
Type of battery: VRLA; Number of elements: 240 (40 mono-blocks)
Capacity: 120Ah; Igas (**): 8 (fast charging)
A = 28 x Q = 28 x 0.05 x n x Igas x C10=28 x 0.05 x 240 x 8 x 120 x 1/10³ = 322 cm
2
(**) to increase the safety margin, we take the fast charging condition, well aware that the battery mostly runs in
backup charging mode. Using the backup charging value for Igas would result in a value of one eighth of the above.
The air intake/outlet must be located so as to be most favourable to circulation, e.g.:
- openings on opposing walls;
- with a minimum distance of 2 m if both on the same wall.

 Loading...
Loading...