Rockwell Automation Publication 750-RM100A-EN-P - August 2019 89
Reference Motion Planners Chapter 9
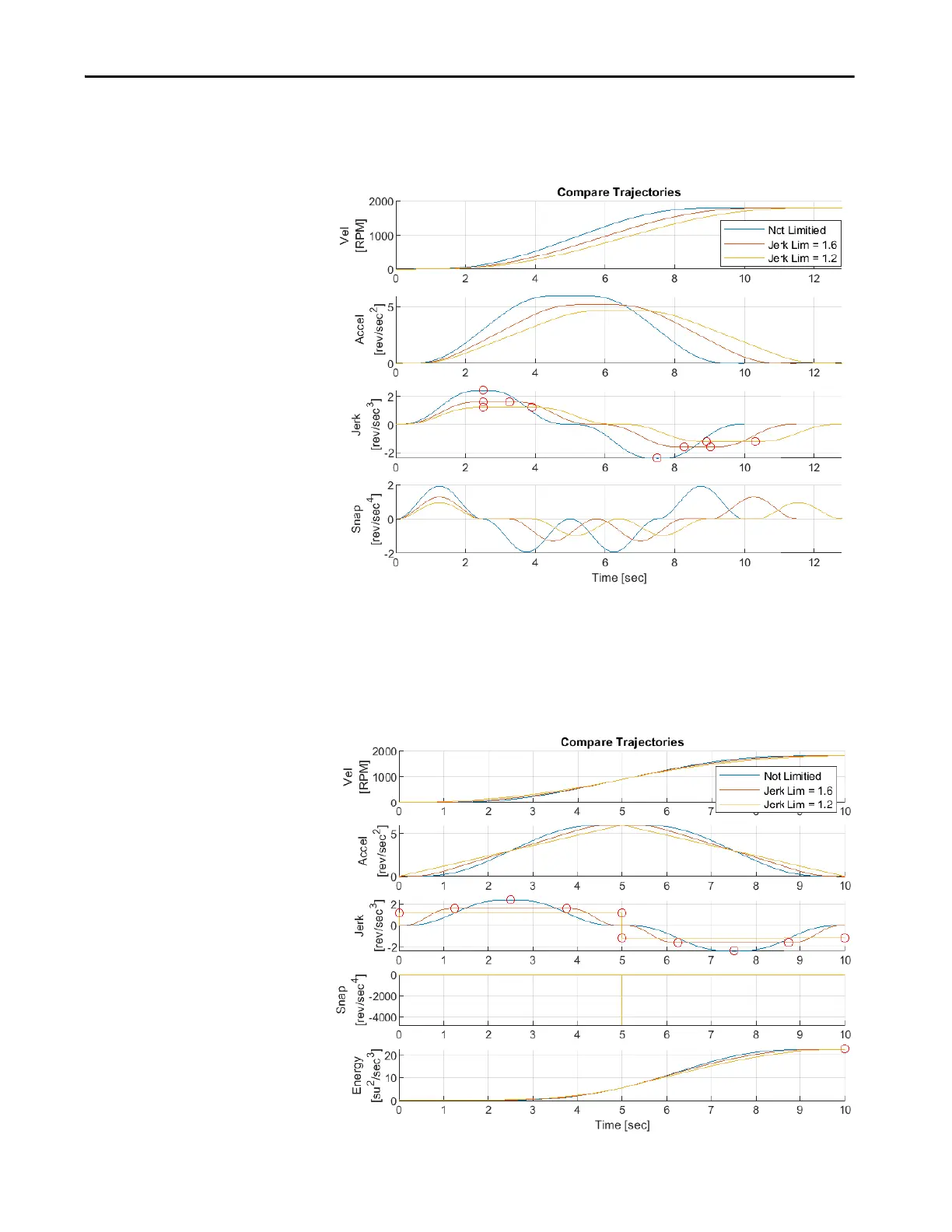
The following example shows what happens when minimum and maximum jerk limits
are lowered below what is required by an unconstrained 10 second move.
Figure 32 - Jerk Limiting
Acceleration and deceleration times can be readjusted to make up for the added dwell
time if required. However, times quickly go to zero when the limit approaches about half
the required maximum jerk because the area under the curve becomes square. Any further
lowering of the limit beyond this point forces an acceleration-dwell to be added, which
increases acceleration and deceleration times.
Figure 33 - Jerk Limiting with Adjusted Times

 Loading...
Loading...
















