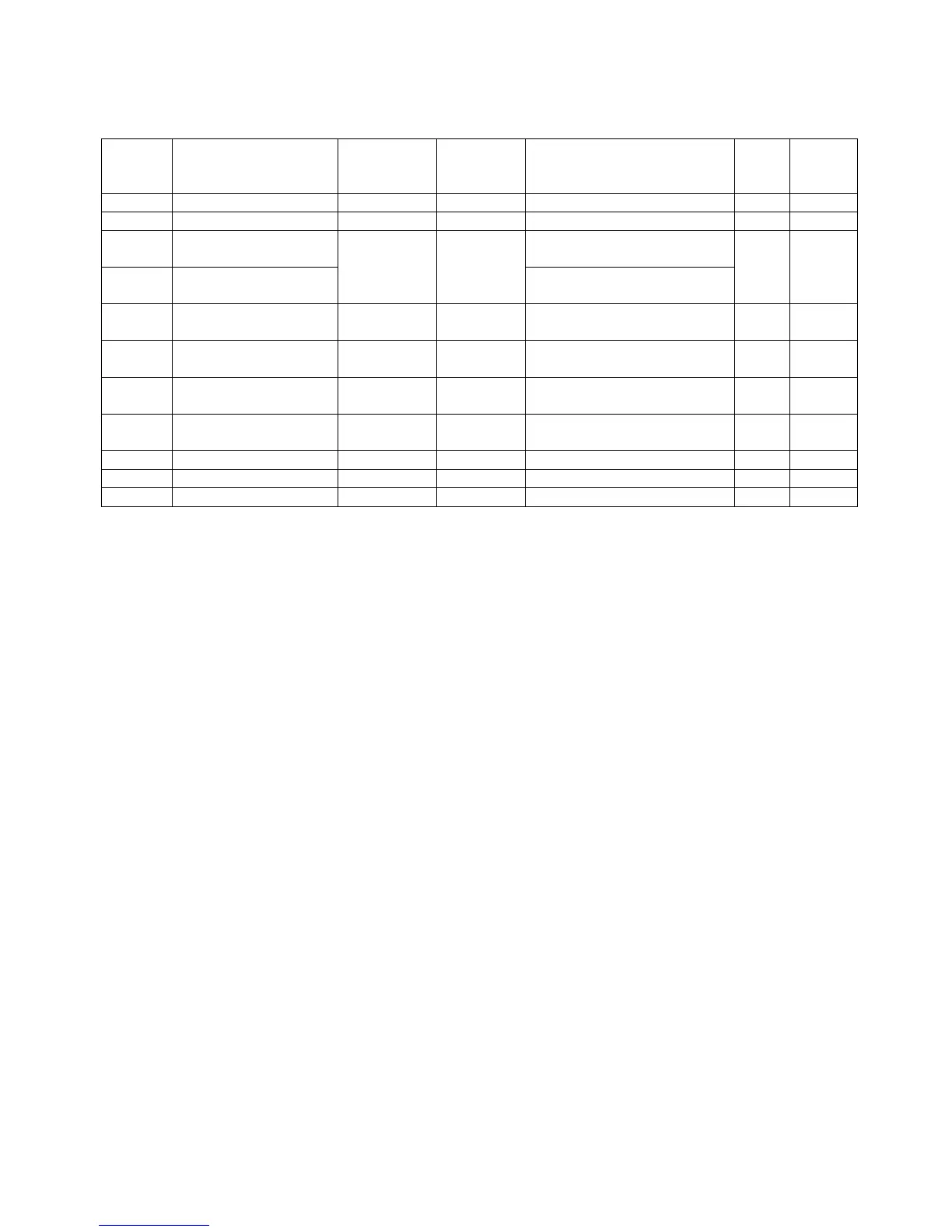
Remark:
In the late 1980’s there was a shift in the meaning of the RTS-signal:
Originally the DTE (computer) requests the DCE (modem) for permission that the DTE
may send data - and the DCE “answeres” via CTS. But this protocol is asymmetric
because the DTE has no means to notify the DCE to wait for internal computations when
the DCE sends data. For this reason “Request To Send” was re-claimed: The DTE
requests the DCE to send data – or in other words, the DTE is “Ready To Receive”
(RTR). RTR and CTS are now independent of each other and the protocol between DTE
and DCE is symmetric. But in most cases the name “Request To Send” (RTS) was kept,
hence it is fairly ambiguous.
The PC-G850V(S) implements the newer, symmetric RTR-semantics (but the signal
name RTS has been kept). This is in contrast to the preceding pocket computer model
PC-E500(S), which implements the original RTS meaning and therefor needs the
XON/XOFF-protocol in addition, when it reads data/programs from a PC. The PC-
G850V(S) sets the DTR-signal to HIGH, when the SIO-interface is active, but it does not
care about the DSR-input. So there is no DTR/DSR-handshake. The RTS/CTS-
handshake, or alternatively the XON/XOFF-protocol can be configured in the
TEXT/Sio/Format-submenue by the item "flow".
!
&
 Loading...
Loading...