RF300 system planning
4.6 EMC Directives
SIMATIC RF300
4-48 System Manual, Release 04/2006, J31069 D0166-U001-A2-7618
Interference sources
In order to achieve a high level of electromagnetic compatibility and thus a very low level of
disturbance in a plant, it is necessary to recognize the most frequent interference sources.
These must then be eliminated by appropriate measures.
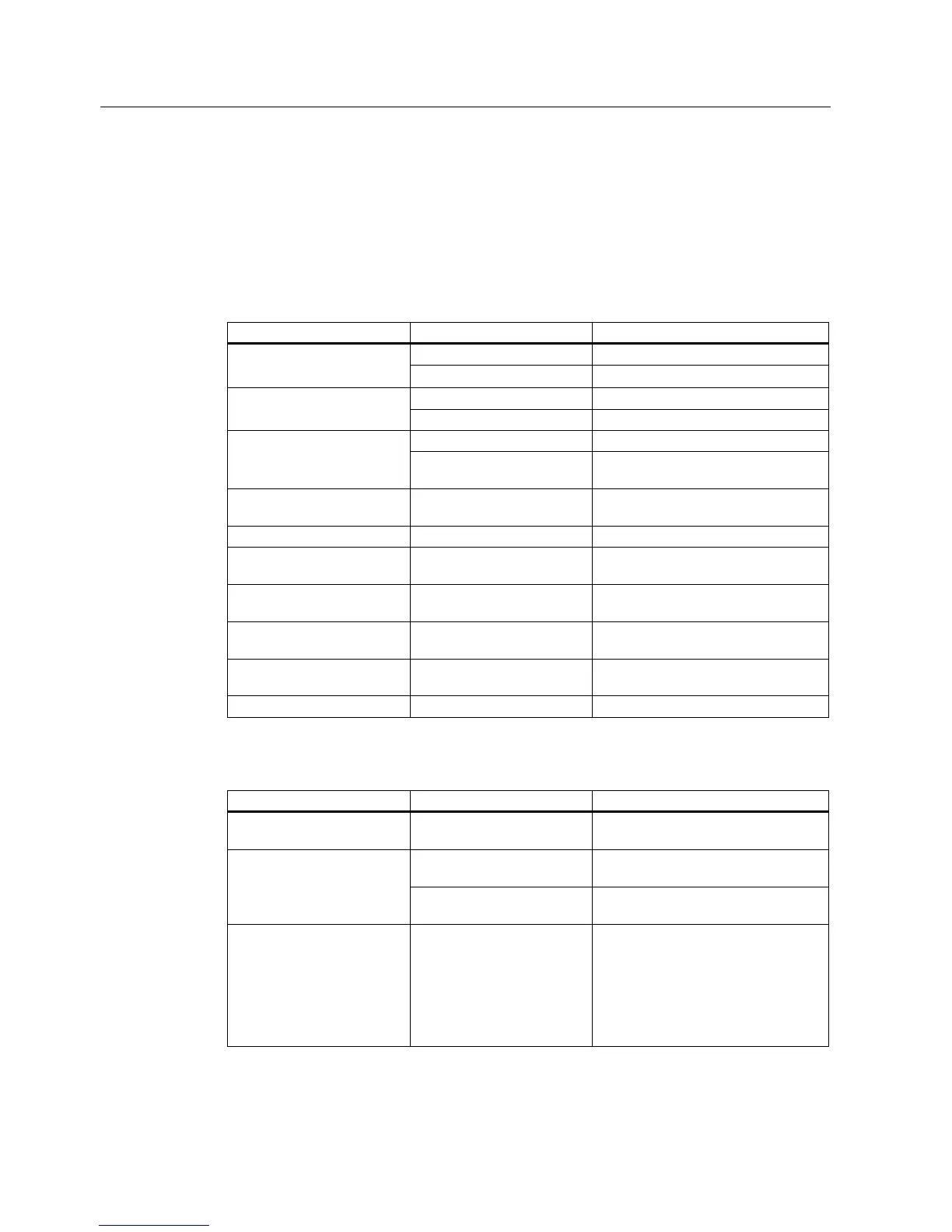
Table 4-9 Interference sources: origin and effect
Interference source Interference results from Effect on the interference sink
Contacts System disturbances Contactors,
electronic valves
Coils Magnetic field
Collector Electrical field Electrical motor
Winding Magnetic field
Contacts Electrical field Electric welding device
Transformer Magnetic field, system disturbance,
transient currents
Power supply unit, switched-
mode
Circuit Electrical and magnetic field, system
disturbance
High-frequency appliances Circuit Electromagnetic field
Transmitter
(e.g. service radio)
Antenna Electromagnetic field
Ground or reference potential
difference
Voltage difference Transient currents
Operator Static charge Electrical discharge currents, electrical
field
Power cable Current flow Electrical and magnetic field, system
disturbance
High-voltage cable Voltage difference Electrical field
What interference can affect RFID?
Interference source Cause Remedy
Switched-mode power supply Interference emitted from the
current infeed
Replace the power supply
Cable is inadequately
shielded
Better cable shielding Interference injected through
the cables connected in
series
The reader is not connected
to ground.
Ground the reader
HF interference over the
antennas
caused by another reader
• Change the operating mode of the
reader.
• Position the antennas further
apart.
• Erect suitable damping materials
between the antennas.
• Reduce the power of the readers.
 Loading...
Loading...











