Instructions
9.4 PID basic functions
PID control
486 Function Manual, 03/2017, A5E35300227-AC
Input parameters TCONT_CP
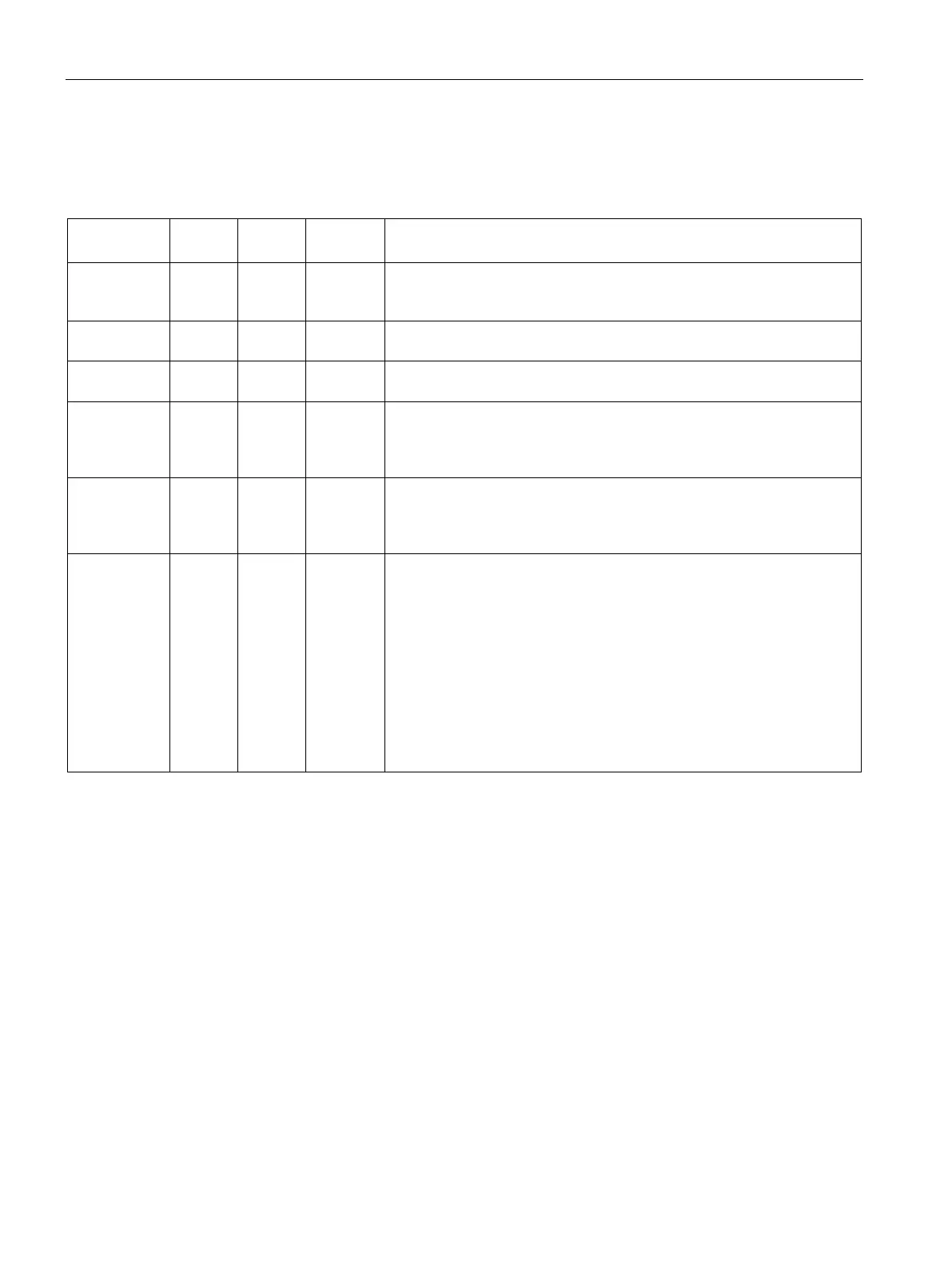
Table 9- 19 Input parameters TCONT_CP
PV_IN 0.0 REAL 0.0 At the "Process value input" you can assign parameters to a commis-
sioning value or you can interconnect an external process value in float-
ing-point format. The valid values depend on the sensors used.
PV_PER 4.0 INT 0 The process value in I/O format is interconnected with the controller at
the "Process value I/O" input.
DISV 6.0 REAL 0.0
For feedforward control, the disturbance variable is interconnected to the
"Disturbance variable" input.
INT_HPOS 10.0 BOOL FALSE The output of the integral action can be held in the positive direction. For
this, the input INT_HPOS must be set to TRUE. In a cascade control,
INT_HPOS of the primary controller is connected to QLMN_HLM of the
INT_HNEG 10.1 BOOL FALSE The output of the integral action can be held in the negative direction.
For this, the input INT_HNEG must be set to TRUE. In a cascade con-
trol, INT_HNEG of the primary controller is connected to QLMN_LLM of
the secondary controller.
SELECT 12.0 INT 0 If the pulse shaper is on, there are several ways of calling the PID algo-
rithm and pulse shaper:
• SELECT = 0: The controller is called in a fast cyclic interrupt priority
class and the PID algorithm and pulse shaper are processed.
• SELECT = 1: The controller is called in OB1 and only the PID algo-
rithm is processed.
• SELECT = 2: The controller is called in a fast cyclic interrupt priority
class and only the pulse shaper is processed.
• SELECT = 3: The controller is called a slow cyclic interrupt priority
class and only the PID algorithm is processed.
Operating principle of the pulse generator (Page 481)
Block diagram TCONT_CP (Page 484)

 Loading...
Loading...






















