Programming principles
1.3 Axis movements
Turning Part 2: Programming (Siemens instructions)
38 Programming and Operating Manual, 05/2012, 6FC5398-5DP10-0BA0
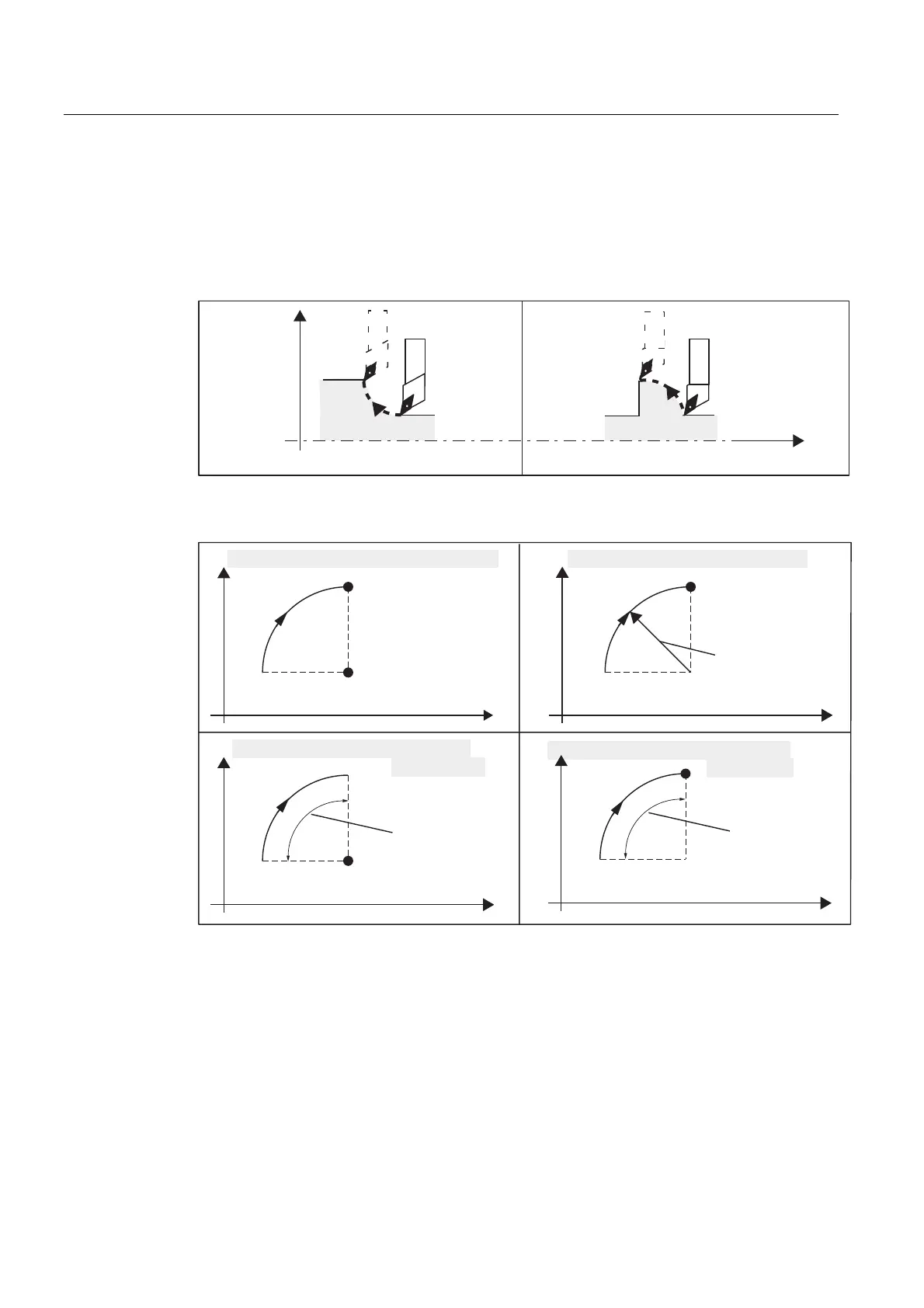
1.3.4 Circular interpolation: G2, G3
Functionality
The tool moves from the starting point to the end point along a circular path. The direction is
determined by the G function:
&ORFNZLVH
*
*
&RXQWHUFORFNZLVH
Figure 1-9 Definition of the circular direction of rotation
The description of the desired circle can be given in various ways:
(QGSRLQW;=
;
HJ*;=,.
&HQWHUSRLQW,.
6WDUWLQJSRLQW;=
=
(QGSRLQW;=
;
HJ*;=&5
&LUFOHUDGLXV&5
6WDUWLQJSRLQW;=
=
;
HJ*$5,.
&HQWHUSRLQW,.
6WDUWLQJSRLQW;=
=
$QJOH$5
;
HJ*$5 ;=
(QGSRLQW;=
6WDUWLQJSRLQW;=
=
$QJOH$5
**DQGFHQWHUSRLQWSDUDPHWHUHQGSRLQW
**DQGUDGLXVSDUDPHWHUHQGSRLQW
**DQGVSHFLILFDWLRQRIDSHUWXUHDQJOH
FHQWHUSRLQW
**DQGVSHFLILFDWLRQRIDSHUWXUHDQJOH
HQGSRLQW
Figure 1-10 Option for circular path programming with G2 G3 with G2 as an example
G2/G3 remains active until canceled by another instruction from this G group (G0, G1, ...).
The path velocity is determined by the programmed F word.
Programming
G2/G3 X... Y... I... J... ; Center and end points
G2/G3 CR=... X... Y... ; Circle radius and end point
G2/G3 AR=... I... J... ; Opening angle and center point
 Loading...
Loading...




















