6-2
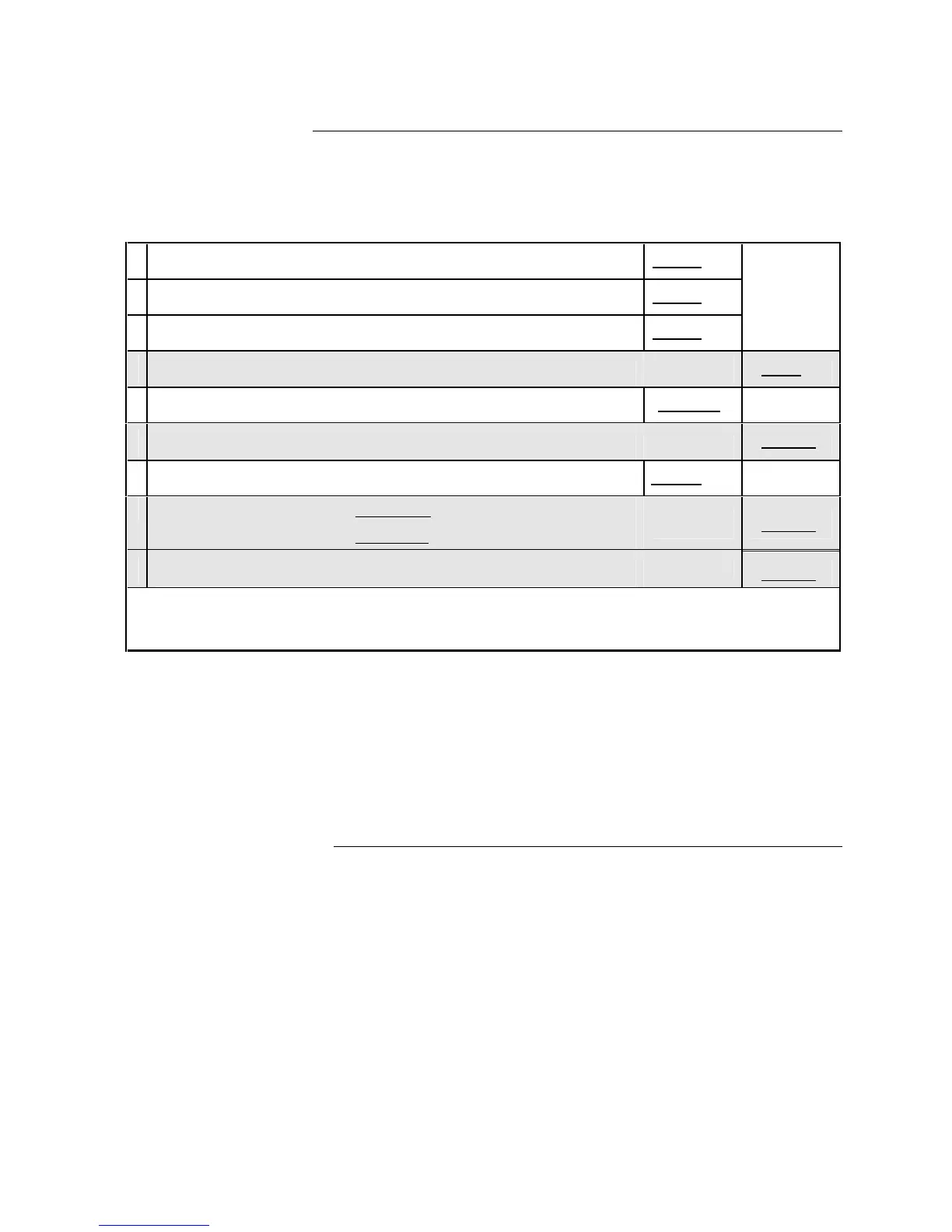
Table 4. Battery Selection Calculation
1
Enter total supervisory current from all cards in system (See Table 3)
Amps
2
Enter total Auxiliary power current draw in standby (See Note 1, below)
Amps
3
Enter total two-wire detector current draw in standby (See Note 2, below)
Amps
4
ADD lines [1], [2], and, [3] (Total standby current)
= Amps
5
Enter the required hours of standby
Hr
6
MULTIPLY line [4] by line [5]
= Ah
7
Enter the total NAC/AUX alarm current
Amps
8
MULTIPLY line [7] by .083 for five minutes of alarm
–or– line [7] by .167 for ten minutes of alarm
= Ah
9
ADD lines [6] and [8]
= Ah
• If the total in line [9] is less than or equal to 5.1, use 2081-9272 6.2 Ah batteries.
• If the total in line [9 is greater than 5.1 and less than or equal to 8.3, use 2081-9274 10 Ah batteries.
• If the total in line [9 is greater than 8.3, the 4004 charger is not capable of charging larger capacity batteries.
Consider using the 4004 with a 4009 NAC Power Extender or a 4005 Fire Alarm Control Panel.
Notes:
1. All Auxiliary loads subtract from the total 4.0 Amps of power available on the 4004. As an example:
Total Available NAC power = 4.0 Amps
Total Available AUX power = 2.0 Amps
Total COMBINED power = 4.0 Amps
2. Standby current is listed on Detector Data Sheets. Maximum standby current draw on the “low current” IDC is
2 mA per zone. Maximum standby current draw on the “high current” IDC is 3 mA per zone. Refer to UL's
two-wire detector compatibility listing for compatible models and maximum quantity of two-wire detectors per
zone.
Battery Selection Calculation
 Loading...
Loading...