14169000-IG, Edition 11.0
January 2018, Original document
32
Network Topology
Every time a PTPv2 packet passes through a switch - jitter is potentially added. Therefore, the num-
ber of switches between all base stations must be kept low. Because every individual base station
can assume the role as PTPv2 master or slave regardless of its position in the network topology, a
worst case position of master and slave must be considered when deploying the base stations in the
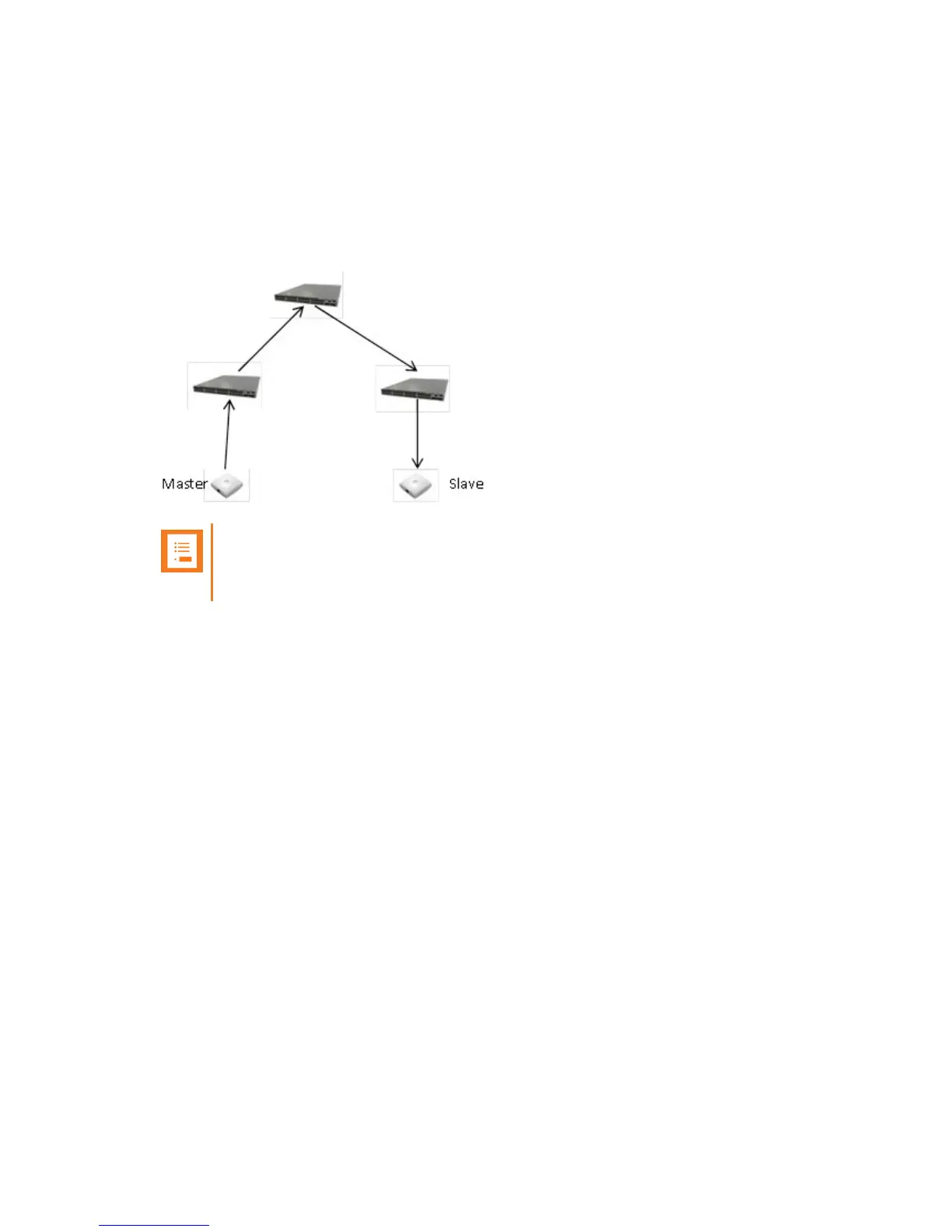
network. The figure below illustrates this with a core switch with two access switches connected.
Here the worst case path length is three switches.
Note:
In the lab, the IP-DECT base stations have successfully been synchronized with 5 enter-
prise LAN switches between master and slave.
Traffic Load
The traffic load on the switches will also affect the jitter. High traffic load and especially a large num-
ber of large packets will increase the jitter. For example, a 1500 bytes data packet introduces an
immediate 120 usec delay on a 100 Mbps link.
It is recommended that the core network links provides higher bandwidth than the access links, i.e. if
the access links are 100 Mbps, the uplink and core network should be at least 1 Gbps. This will alle-
viate the probability of traffic saturating the network path used for the base station synchronization.
If the traffic load causes problems for the base station synchronization, it may be necessary to sep-
arate the base stations from the data network. Be aware that separation via VLAN may not help as it
is still using the same physical link.
Spectralink IP-DECT Server 400/6500 and DECT Server 2500/8000 Synchronization and Deployment Guide
 Loading...
Loading...




