50 Series 4180 Powerhead
: Push the test flange (1)
1119 850 4201 into position.
: Fit the sleeves (2)
0000 963 1008 and secure them
with the nuts (3).
: Seal the impulse hose (4) with a
suitable plug (5).
– Loosen the muffler mounting
screws.
: Fit the sealing plate (1)
0000 855 8106 between the
muffler and cylinder exhaust port
– the sealing plate must
completely cover the opening in
the muffler.
– Tighten down the screws firmly.
Vacuum test
Oil seals tend to fail when subjected
to a vacuum, i.e. the sealing lip lifts
away from the crankshaft during the
piston's induction stroke because
there is no internal counterpressure.
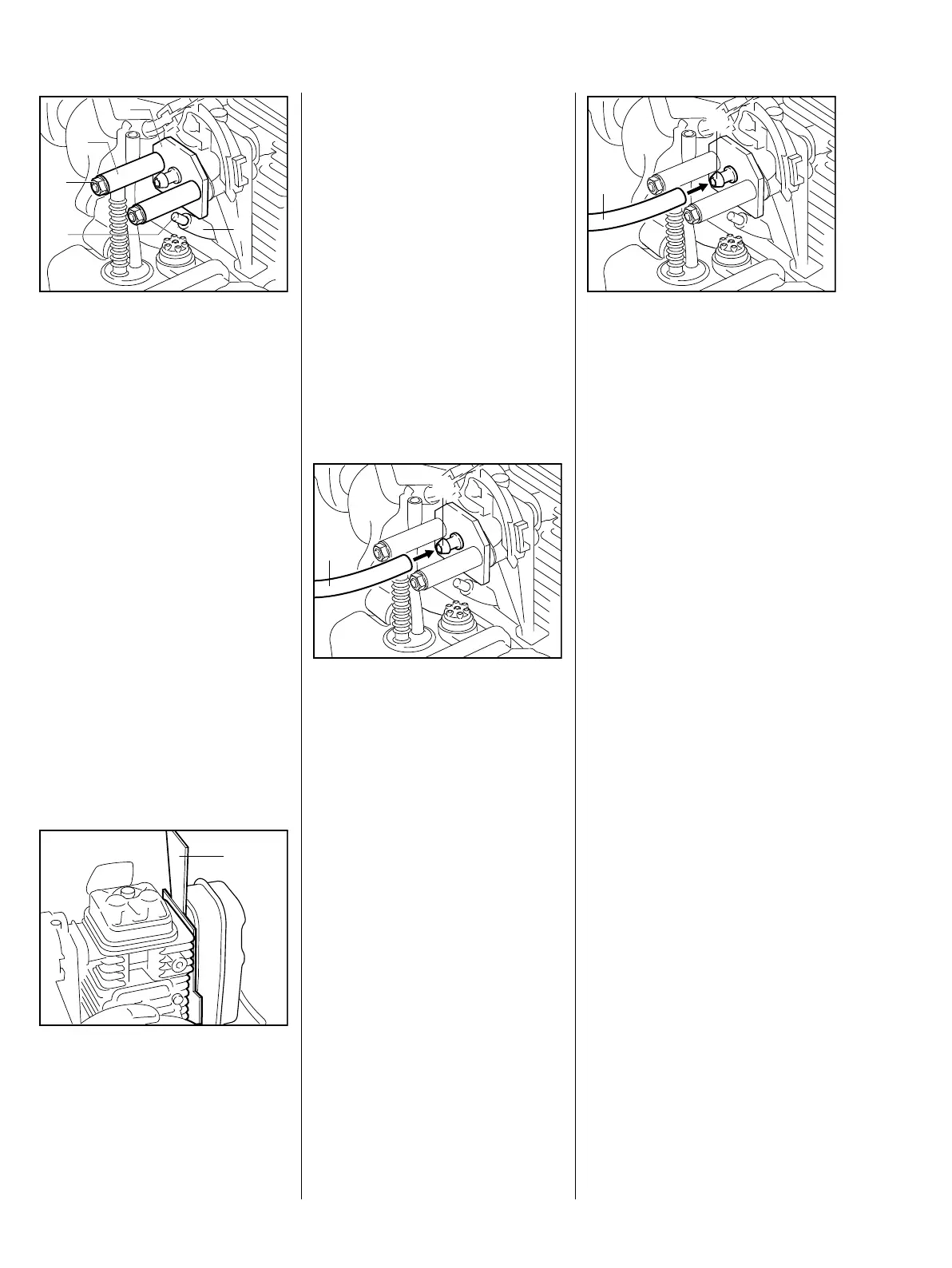
: Connect suction hose (1) of
vacuum pump 0000 850 3501 to
the nipple (2).
– Close the vent screw on the
pump.
– Operate the vacuum pump until
the pressure gauge indicates a
vacuum of 0.5 bar.
If the vacuum reading remains
constant, or drops to no more than
0.3 bar within 20 seconds, it can be
assumed that the oil seals are in
good condition.
If the vacuum drops to less than 0.3
bar within 20 seconds, the oil seals
are defective and have to be
replaced, b 7.8.1.
Pressure test
: Connect pressure hose (1) of
tester 1106 850 2905 to the
nipple (2).
– Close the vent screw on the
rubber bulb.
– Operate the pump bulb until the
pressure gauge indicates a
pressure of 0.5 bar.
If this pressure remains constant for
at least 20 seconds, the engine
housing is airtight.
If the pressure drops, the leak must
be located and the faulty part
replaced.
– To find the leak, coat the suspect
area with oil and pressurize the
crankcase. Bubbles will appear if
a leak exists.

 Loading...
Loading...