12
FB BRAKE ASSEMBLY – INSPECTION,
ADJUSTMENT & MAINTENANCE
2. Construction and Operating Principles
a. Construction
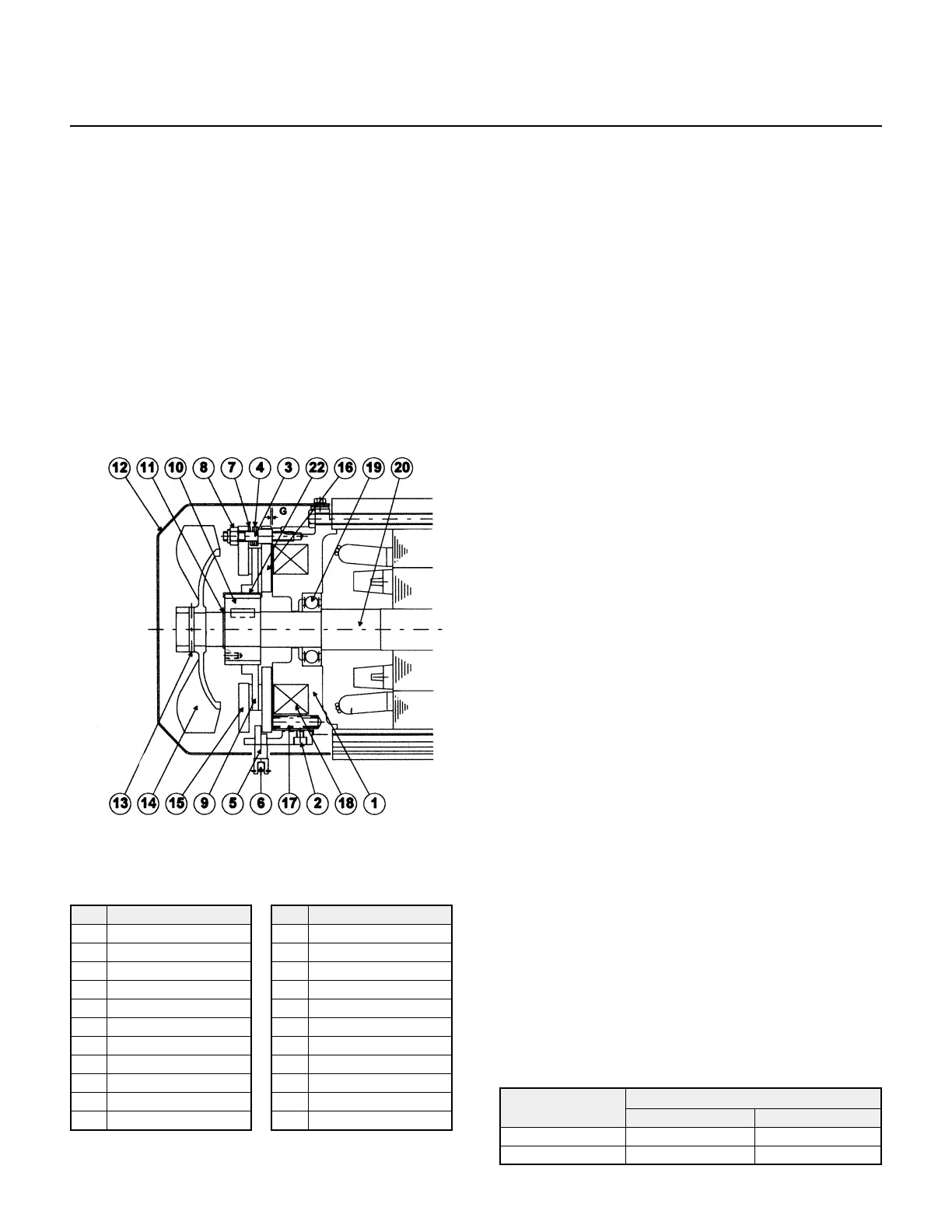
Fig. 19 illustrates the construction of the brake.
Among the brake parts, the stationary core (1),
solenoid coil (18), and stud bolt (3) constitute an
integral subassembly unit. The stud bolt (3) keeps
the armature plate (16) from rotating, but the plate
moves axially by electromagnetic attraction and the
tension of the pressure spring (17). The adjusting
washer (4) and spring washer (7) hold the brake
shoe (15) against the nut (8) at all times. The brake
lining (9) is fit to the hub (10), which is secured to the
motor shaft with a key.
No. Part Name
1 Stationary Core*
2 Brake Release Support
3 Stud Bolt*
4 GAP Adjusting Washer*
5 Shifting Pin
6 Brake Release Lever
7 Spring Washer*
8 Nut*
9 Brake Lining*
10 Hub*
11 Retaining Ring
No. Part Name
12 Fan Cover
13 Fan Set Screw or Pin
14 Fan
15 Brake Shoe*
16 Armature*
17 Pressure Spring*
18 Solenoid Coil*
19 Fan Side Bearing
20 Motor Shaft
21 Bearing Cover
22 Leaf Spring*
*These parts are included in a complete brake kit.
Table 17 FB-5B, -8B Parts
Fig. 19 FB-5B, FB-8B Models
b. Operating Principles
The brake is a (fail-safe type) spring actuated type
brake that releases the brake mechanism when the
solenoid coil is energized and engages when the
solenoid coil is not energized.
When power is applied to the unit, the solenoid coil
and electric motor become energized and the
energized coil attracts the armature plate (16)
against the tension of the pressure spring (17). As a
result, the brake lining (9) disengages and the motor
starts to run.
When the power is disconnected, the solenoid coil
and electric motor are not energized. This causes
the pressure spring (17) to actuate the armature
plate (16), which in turn presses the brake lining (9)
against the brakeshoe (15) and brings the motor to a
quick stop.
3. Inspection
a. At regular intervals, check that:
• the unit is operating normally.
• the brake lining is not excessively worn (or gap
G is normal).
• all the mounting screws are securely tightened.
b. Manual brake release procedure
FB-5B, -8B brakemotors are equipped with a one-
touch release mechanism. To manually release
the brake with power to the unit turned off, pull the
brake release lever out from its holder and push it
forward toward the reducer. Releasing the lever
will re-engage the brake.
4. Gap Inspection
The brake lining will wear after the unit has been
used for a long period of time. Regularly check that
gap G (Fig. 18) is at an acceptable value. If gap G
becomes too large, the solenoid coil may fail to pull
in the armature plate, and hence cannot release the
brake, resulting in the unit remaining in a
continuously braked condition. Follow these steps to
inspect the brake gap:
a. Remove the cover (12).
b. Insert a gap gage into the space between the
stationary core (1) and armature plate (16).
Measure the gap size at three appropriate
circumferential points.
c. The gap needs to be adjusted if the values are
close to the allowable limit listed in Table 18.
Brake Type
Gap value G (in)
Spec. value Allowable limit
FB-5B 0.016 ~ 0.020 0.039
FB-8B 0.016 ~ 0.020 0.039
Table 18 Brake Gap Size

 Loading...
Loading...