Appendix
0
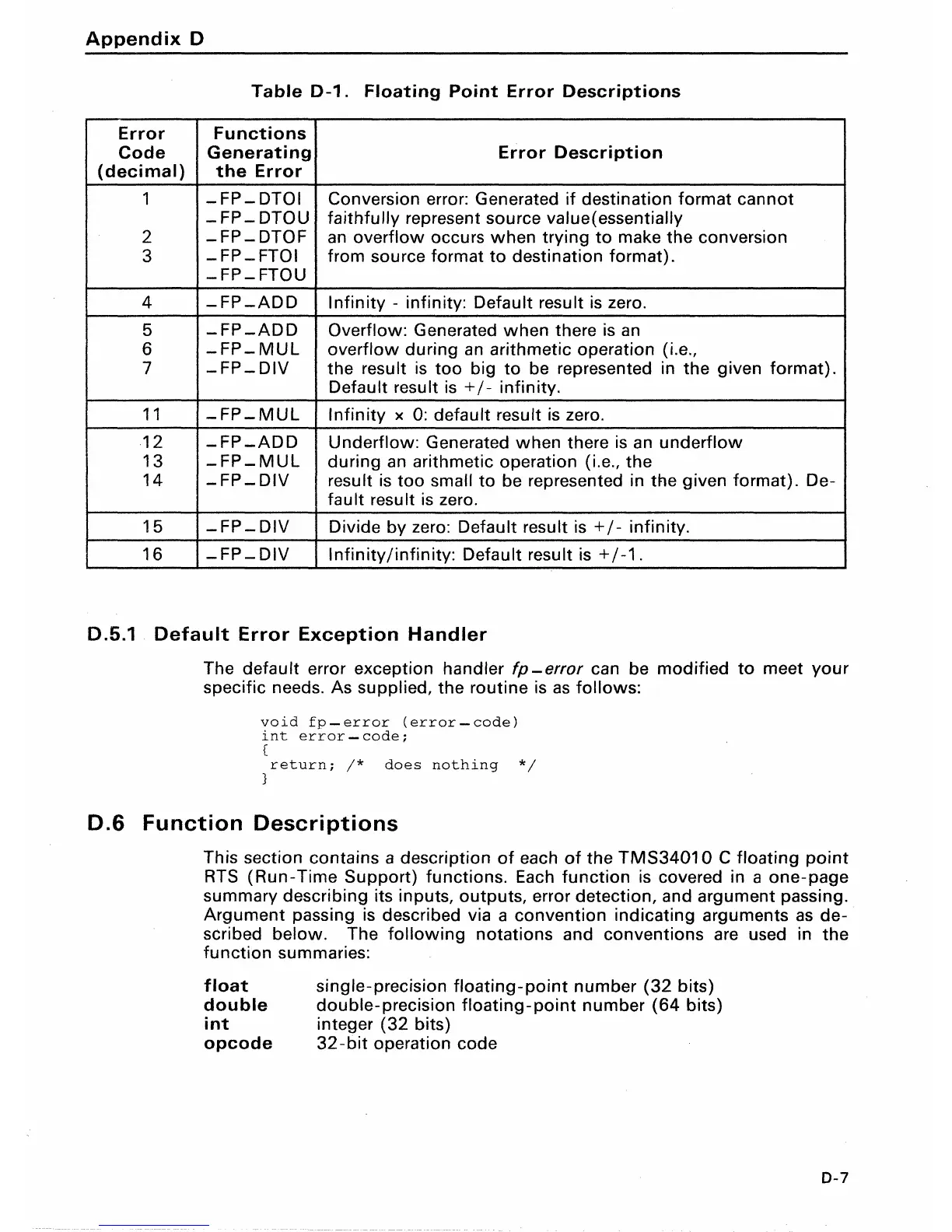
Table
0-1.
Floating
Point
Error
Descriptions
Error
Functions
Code
Generating
Error
Description
(decimal)
the
Error
1
-FP-DTOI
Conversion error: Generated
if
destination format cannot
-FP-DTOU
faithfully represent source value(essentially
2
-FP-DTOF
an
overflow occurs
when
trying
to
make the conversion
3
-FP-FTOI
from source format
to
destination format).
-FP-FTOU
4
-FP-ADD
Infinity
- infinity: Default result
is
zero.
5
-FP-ADD
Overflow: Generated
when
there
is
an
6
-FP-MUL
overflow
during
an
arithmetic operation (i.e.,
7
-FP-DIV
the result
is
too
big
to
be represented in the given format).
Default result
is
+ / - infinity.
11
-FP-MUL
Infinity
x 0: default result
is
zero.
12
-FP-ADD
Underflow: Generated
when
there
is
an
underflow
13
-FP_MUL
during
an
arithmetic operation (Le., the
14
_FP_DIV
result
is
too
small
to
be represented in the given format). De-
fault result
is
zero.
15
-FP-DIV
Divide by zero: Default result
is
+ / - infinity.
16
-FP-DIV
Infinity/infinity:
Default result
is
+/-1.
0.5.1
Default
Error
Exception
Handler
The default error exception handler
fp-error
can be modified
to
meet
your
specific needs. As supplied, the routine
is
as
follows:
void
fp-error
(error_code)
int
error
-
code;
[
return;
/*
does
nothing
*/
}
0.6
Function
Descriptions
This section contains a description
of
each
of
the TMS3401 0 C floating
point
RTS
(Run-Time Support) functions.
Each
function
is
covered in a one-page
summary describing its inputs, outputs, error detection, and argument passing.
Argument passing
is
described via a convention indicating arguments
as
de-
scribed
below. The
following
notations and conventions
are
used in the
function
summaries:
float
double
int
opcode
single-precision
floating-point
number
(32
bits)
double-precision
floating-point
number
(64
bits)
integer
(32
bits)
32-bit
operation code
0-7
 Loading...
Loading...











