Basi
nsta
at
on and Operat
on G
de
T
Ser
es D
ta
olid
tate
o
t
tarters 1
1250A
65 | Page
Appendix 1 - Ramp Profile Details
The TE Series offers four different types of starting ramp profiles. Simply
select the one that best matches your motor / load requirements. In
addition, two separate ramps are available that can be selected via
contact closure (see section 4.2.5.a), and each one can be set up for any
ramp type as shown in the table below.
Following are descriptions of the four types of Ramp Profiles
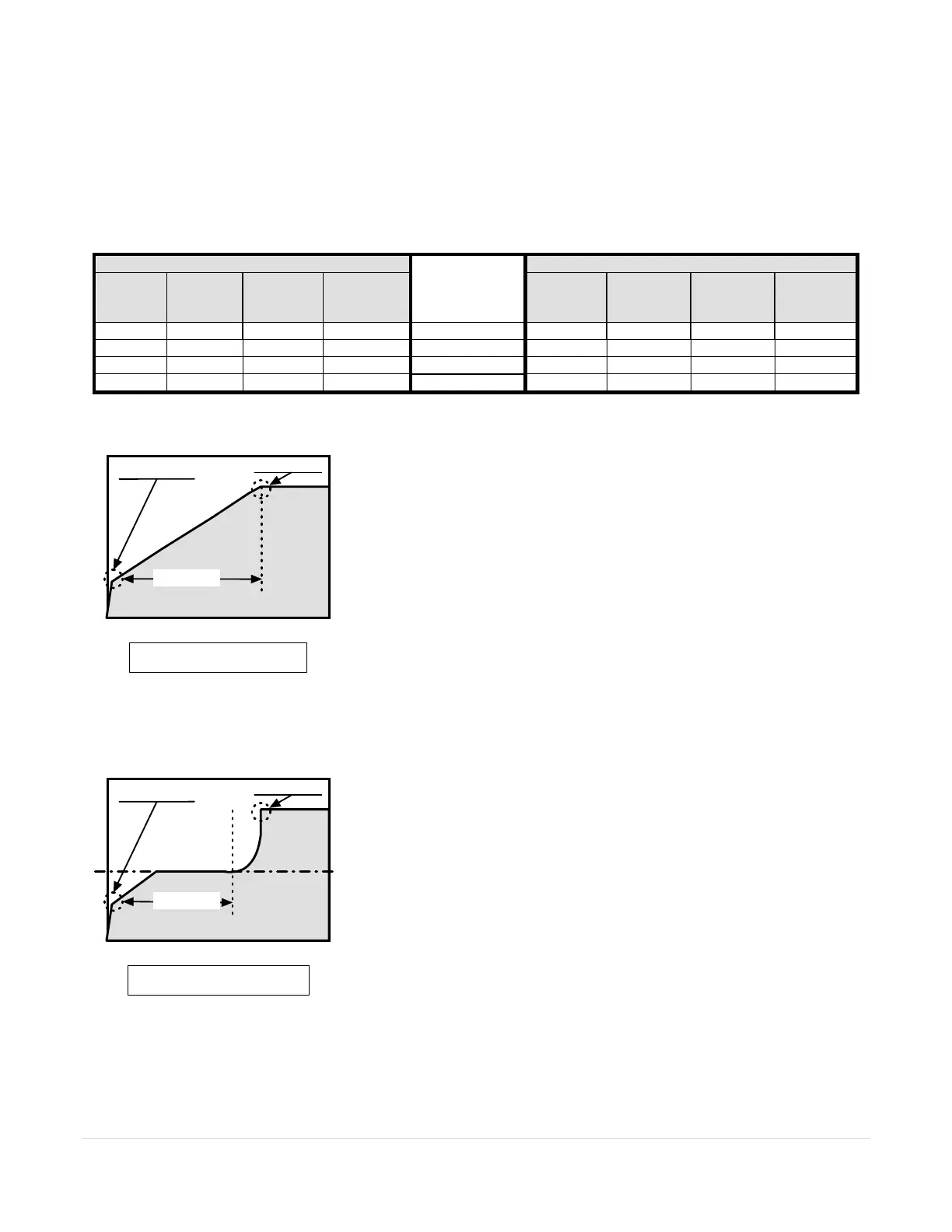
1. Voltage Ramping is the most reliable starting method, due to the fact
that at some point the starter will reach an output voltage high enough to
allow the motor to draw full current and develop full torque. This method
is useful for applications where the load conditions change frequently
and significantly enough to require different levels of starting torque.
Examples where this is effective are:
Material handling conveyers
Positive displacement pumps
Drum mixers, grinders etc.
Voltage is increased from a starting point (Initial Torque) to full voltage
over an adjustable time period (Ramp Time). To achieve Voltage
Ramping, set the Ramp Profile (F010) to 0001 or 0003 (Voltage Ramp),
and the Maximum Current Limit setting (F014) to maximum (600%).
Since this is essentially Locked Rotor Current on most motors, there will
be little or no Current Limit effect on the Ramp profile. Initial Torque
setting comes from the Initial Voltage function F011.
2. Voltage Ramping with Current Limit works similar to mode 1, except
this mode adds an adjustable maximum current output. Voltage is
increased gradually until the motor current reaches the Maximum
Current Limit setting (F014) . The motor current is held at this level until
the motor accelerates to full speed. When the motor current drops below
the limit setting the output voltage is automatically increased to maximize
torque until the TE Series is At-Speed. This may be necessary in
applications where the electrical power is limited. Examples would be:
Portable or emergency generator supplies
Utility power near the end of a transmission line or other starting
power demand restrictions.
Using Current Limit will override the Ramp Time setting if necessary, so
use this feature when acceleration time is not critical. The Ramp Time
setting however still determines the slope of the ramp up to the Current
Limit setting to apply the softest possible acceleration. To achieve
Voltage Ramping with Current Limit, set the Ramp Profile (F010) to 0001
or 0003 (Voltage Ramp), and the Maximum Current Limit setting (F014)
to a desired lower setting, as determined by your application
requirements.
Ramp 1 Settings
“Ramp Type
Selection”
from F010
Ramp 2 Settings
Ramp
Type
Initial
Torque
from…
Ramp
Time
from…
Current
Limit
from…
Ramp
Type
Initial
Torque
from…
Ramp
Time
from…
Current
Limit
from…
Voltage F011 F013 F014 1 Voltage F015 F017 F018
Current F012 F013 F014 2 Current F016 F017 F018
Voltage F011 F013 F014 3 Current F016 F017 F018
Current F012 F013 F014 4 Voltage F015 F017 F018
Table APP 1.1: Ramp Selection Choices and Settings
Initial Torque
Full Speed
Voltage
Time
Figure APP 1.2:
Voltage Ramp with Current Limit
Ramp Time
Current
Limit Setting
Initial Torque
Full Speed
Voltage
Time
Figure APP 1.1:
Voltage Ramp w/o Current Limit
Ramp Time
Buy: www.ValinOnline.com | Phone 844-385-3099 | Email: CustomerService@valin.com

 Loading...
Loading...