6F8C0904 7
1.4 Basic Functionality
1
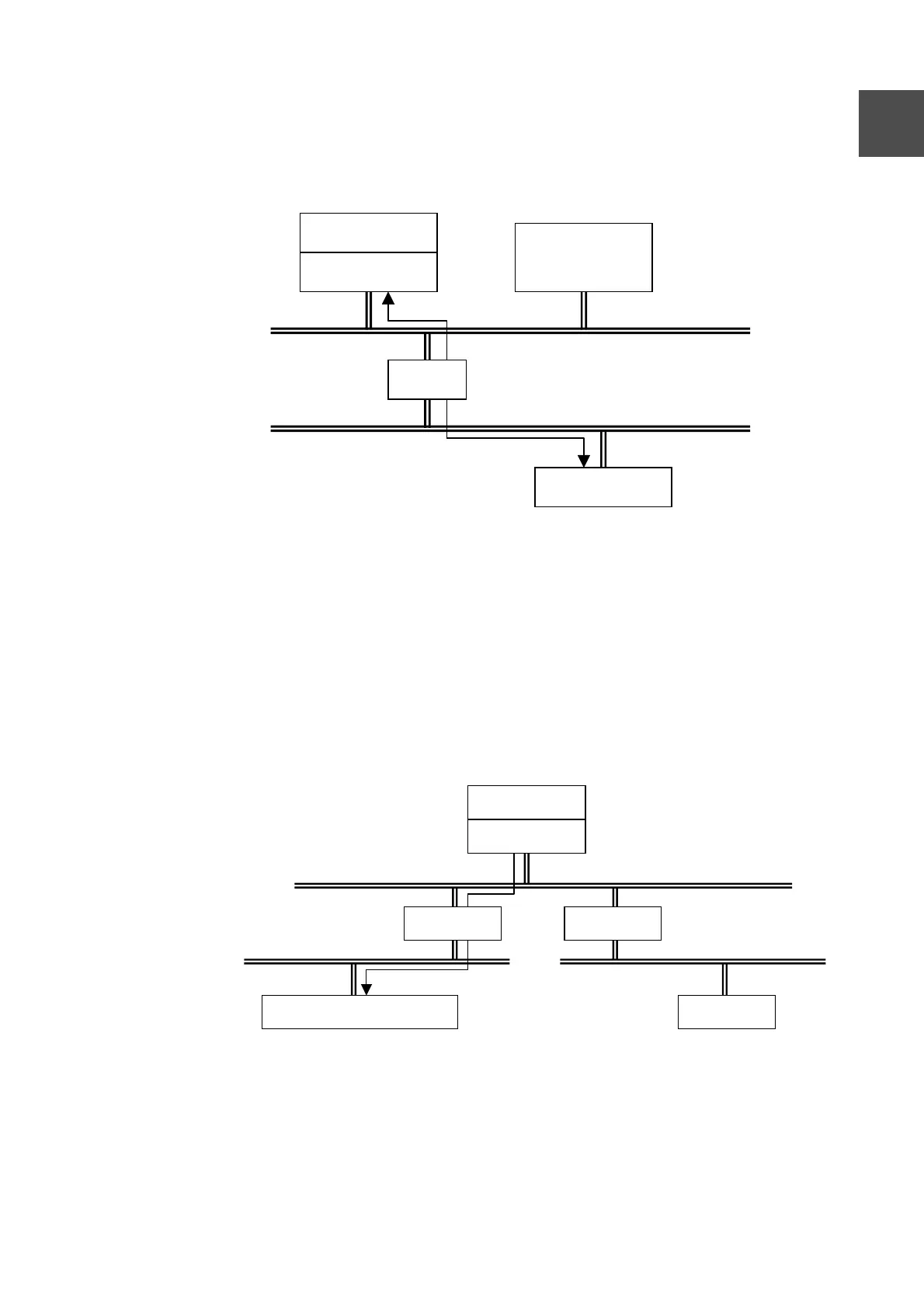
(4) Routing feature support
In order to exchange data between an EN311 on Network A which supports routing
feature and a PC on Network B, the EN311 should pass the transmission data to the
router. This is called an indirect routing and is supported by EN311.
Figure 1-5 Routing feature
The indirect routing supported by EN311 is the default routing method. In this
method, if the destination of the data is not on the same network, the transmission
data is routed to the default router.
One address (IP address) per router can be registered into EN311. The destination
network must exist over this router. To send data from an EN311 on Network A to a
workstation on Network B, the IP address of Router A should be registered into the
EN311. If Router A is the EN311 router, the EN311 cannot send data to any PCs on
Network C. To send data to PCs on Network C, put the EN311 into the standby
mode, register Router B as the router, then put it into the run mode.
Figure 1-6 Router setting
S controller
EN311
Workstation
PC
Router
Network A
Network B
Network A
Network C Network B
S controller
EN311
Router B Router A
PC Workstation router B

 Loading...
Loading...











