Ubee Interactive Using the WLAN Option
Ubee EVW32C Advanced Wireless Voice Gateway Subscriber User Manual • March 2017 47
6.3.5.2 Estimating Wireless Cable Modem to Wireless Client Distances
The information in this section helps you to determine how far a wireless access point (the
EVW32C) can be placed from wireless client devices. Environmental variances include
the capabilities of wireless clients and the types of material through which the wireless
signal must pass. When the EVW32C and wireless clients reach the distance threshold
between each other, network performance degrades.
To determine wireless cable modem placement:
1. Connect a wireless client to the EVW32C. Refer to Connecting Devices to the Network
on page 15 if needed.
2. Place the wireless client at around one meter (three feet) away from the EVW32C.
3. Obtain the RSSI value for the connected client. Refer to Using the Access Control
Option on page 44. This value is used in the formula further below.
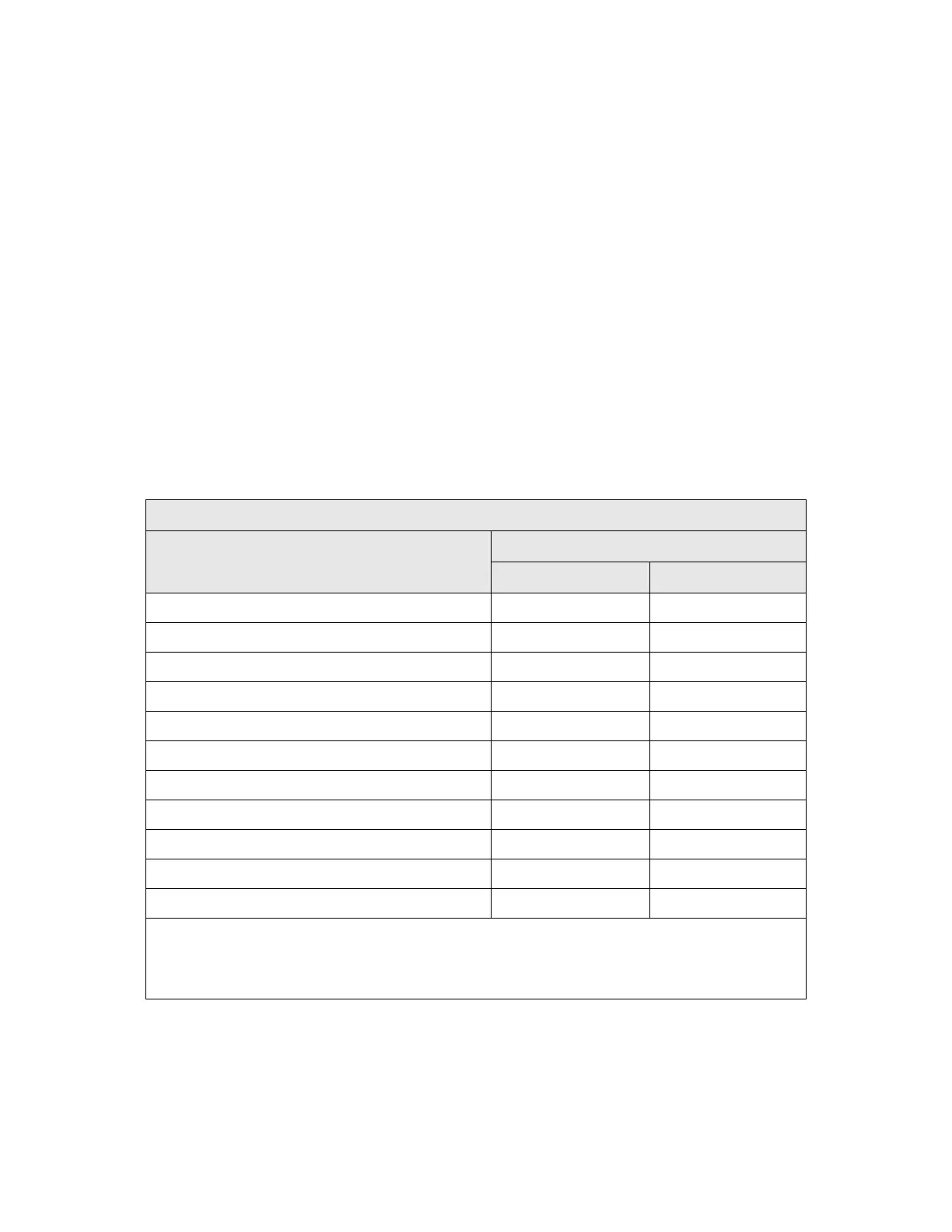
4. Use the following table to determine what materials the wireless signal must travel
through to reach the desired wireless coverage distance.
Attenuation Considerations
Material
Attenuation
2.4GHZ 5GHz
Free Space 0.24dB / foot 0.3dB / foot
Interior Drywall 3dB to 4dB 3dB to 5dB
Cubicle Wall 2dB to 5dB 4dB to 9dB
Wood Door (Hollow/Solid) 3dB to 4dB 6dB to 7dB
Brick, Concrete Wall (Note 1) 6dB to 18dB 10dB to 30dB
Glass Window (not tinted) 2dB to 3dB 6dB to 8dB
Double Pane Coated Glass 13dB 20dB
Bullet Proof Glass 10dB 20dB
Steel / Fire Exit Door 13dB to 19dB 25dB to 32dB
Human Body 3dB 6dB
Trees (Note 2) 0.15dB / foot 0.3dB / foot
Note 1: Different types of concrete materials are used in different parts of the world and the thickness
and coating differ depending on whether it is used in floors, interior walls, or exterior walls.
Note 2: The attenuation caused by trees varies significantly depending upon the shape and thickness
of the foliage.
 Loading...
Loading...