HOW THE LIFT TRUCK WORKS?HOW THE LIFT TRUCK WORKS?
1-161-16
The load center is determined by the distance fromThe load center is determined by the distance from
the face of the forks (or the front face of the loadthe face of the forks (or the front face of the load
backrest) to the center of gravity of the load. Thebackrest) to the center of gravity of the load. The
maximum load is the maximum weight allowablemaximum load is the maximum weight allowable
with that nominal load center.with that nominal load center.
The Load Chart, showing the relationship betweenThe Load Chart, showing the relationship between
the load center and the maximum permissible load,the load center and the maximum permissible load,
is attached to is attached to the truck as the truck as a decal. a decal. When the loadWhen the load
center moves closer toward the tips of the forks, thecenter moves closer toward the tips of the forks, the
combined center of gravity also moves further to thecombined center of gravity also moves further to the
rear, which reduces the rear, which reduces the truck’s lifting capacity.truck’s lifting capacity.
■■
ACCELERATING, DECELERATING ANDACCELERATING, DECELERATING AND
TURNINGTURNING
Inertia refers to the principle that a stationary objectInertia refers to the principle that a stationary object
remains stationary as long as there is no externalremains stationary as long as there is no external
force acting to move it, and that a moving objectforce acting to move it, and that a moving object
continues moving at a constant speed as long ascontinues moving at a constant speed as long as
there is no external force acting to stop it.there is no external force acting to stop it.
When the lift truck starts to move there is aWhen the lift truck starts to move there is a
momentary backward force (resistance to moving)momentary backward force (resistance to moving)
due to inertia, and when it stops there is adue to inertia, and when it stops there is a
momentary forward force (resistance to stopping).momentary forward force (resistance to stopping).
As a result, if As a result, if the brakes are applied the brakes are applied suddenly whilesuddenly while
the truck is traveling in reverse, the backward forcethe truck is traveling in reverse, the backward force
will become strong enough to tip the truck overwill become strong enough to tip the truck over
backward. Likewise, when the truck is turning therebackward. Likewise, when the truck is turning there
is a centrifugal force that pulls it outward from theis a centrifugal force that pulls it outward from the
turning center. This force can cause the truck to tipturning center. This force can cause the truck to tip
over sideways. Since the zone of sideways stabilityover sideways. Since the zone of sideways stability
is especially narrow, it is necessary to slow down ais especially narrow, it is necessary to slow down a
lot when turning, in order to prevent the truck fromlot when turning, in order to prevent the truck from
tipping.tipping.
When the load is elevated the combined centerWhen the load is elevated the combined center
of gravity is raised, increasing the danger that theof gravity is raised, increasing the danger that the
truck will tip over backward or sideways.truck will tip over backward or sideways.
■■
MAXIMUM LOAD (LOAD WEIGHT AND MAXIMUM LOAD (LOAD WEIGHT AND LOAD CENTER)LOAD CENTER)
50005000
66000 0 880000
1000 1000
FRSB16-8FRSB16-8
16001600
12701270
10501050
(1,600kg)(1,600kg)
600mm600mm
(1,050kg)(1,050kg)
1,000mm1,000mm
mmmm
mmmm
kgkg
When the load is raised higher, or the load’s center of
When the load is raised higher, or the load’s center of
gravity is moved further backward (toward the trailinggravity is moved further backward (toward the trailing
wheels), the allowable load iwheels), the allowable load is reduced accordingly.s reduced accordingly.
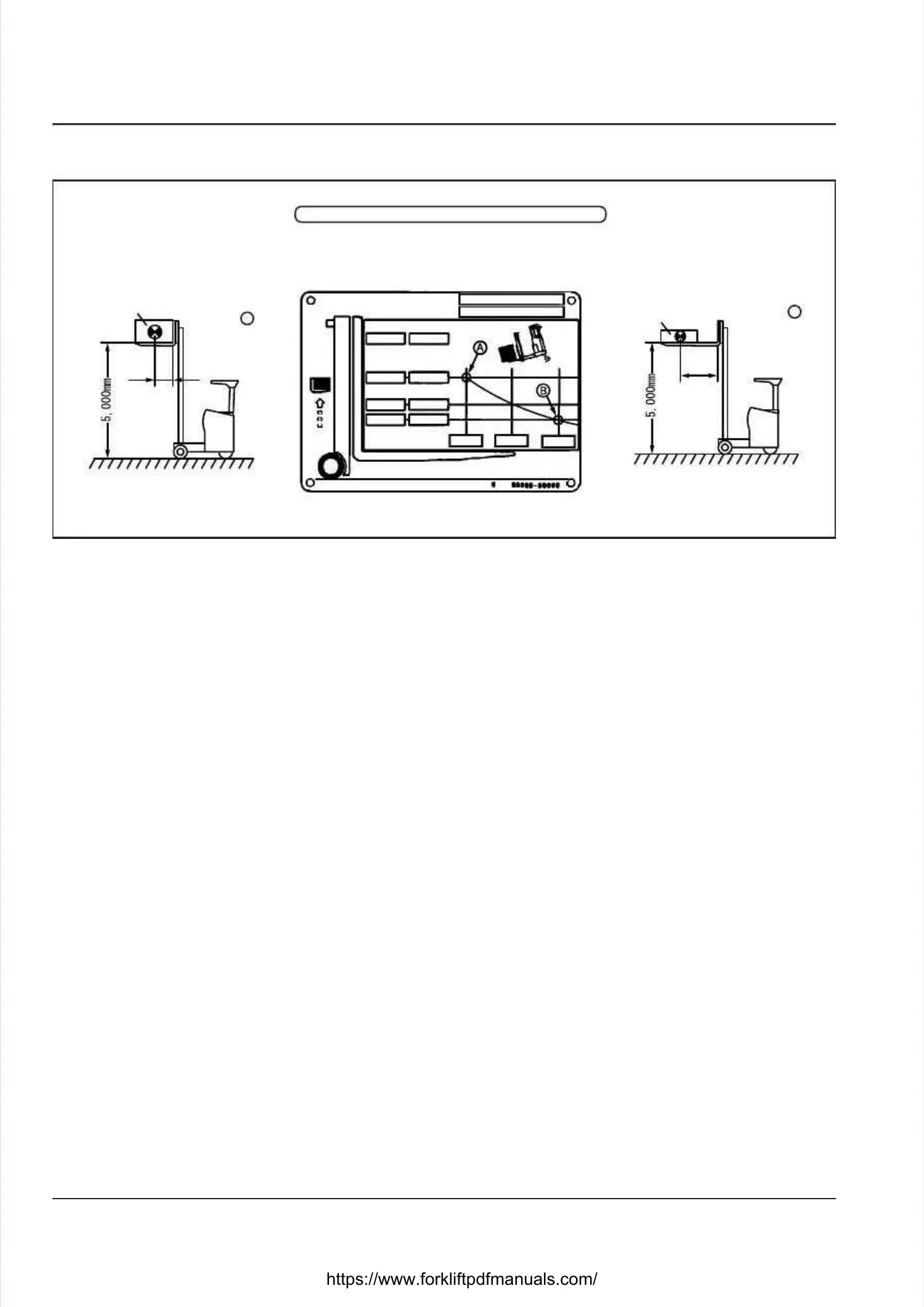
HOW TO READ THE LOAD CHARTHOW TO READ THE LOAD CHART
PointPoint
AA
PointPoint
BB
LOAD CENTERLOAD CENTER
ACTUAL ACTUAL CAPCAPACITYACITY
MAX. FORK HEIGHTMAX. FORK HEIGHT
 Loading...
Loading...


