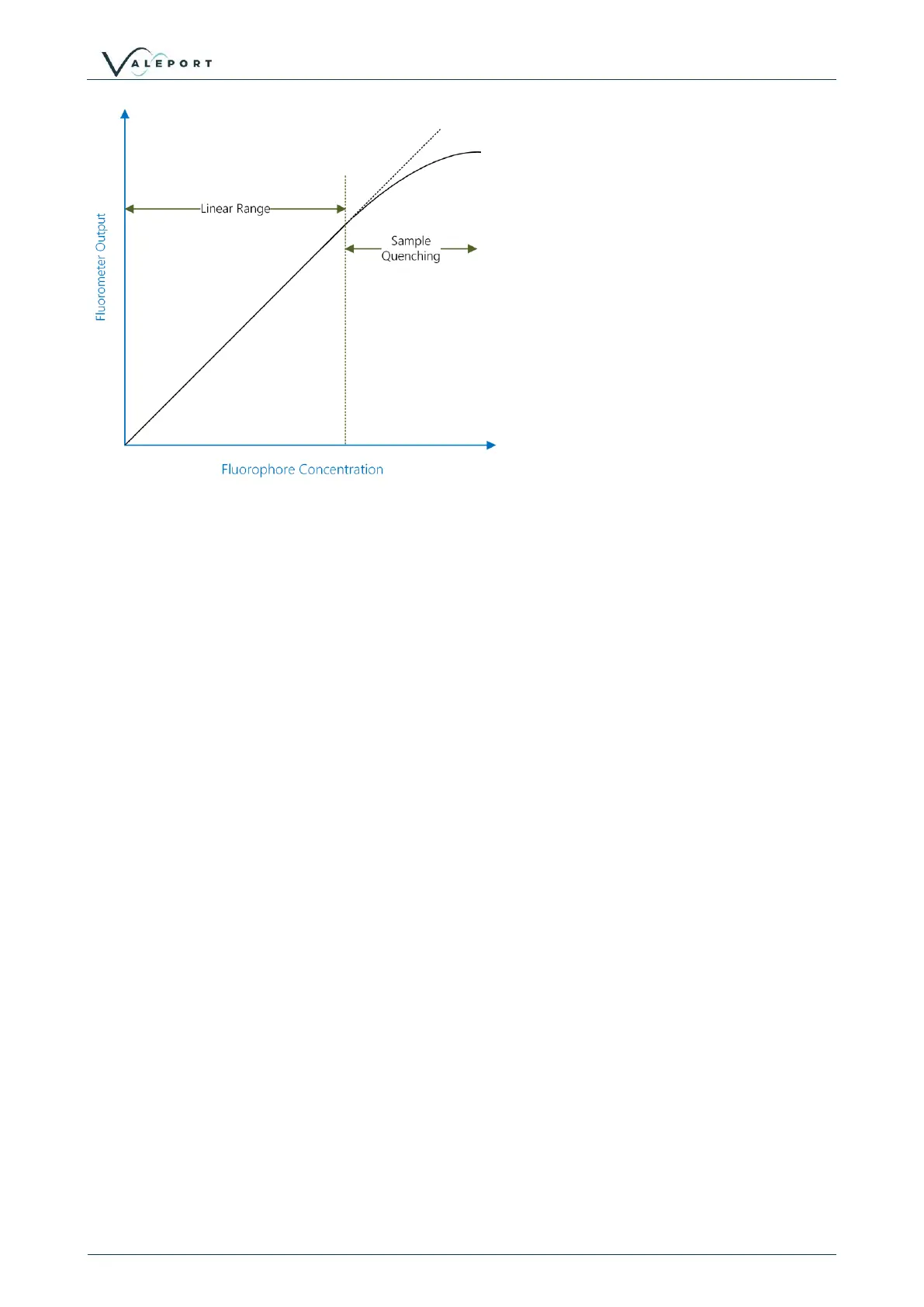
To perform a quick linearity check, dilute a sample of dye 1:1 with RO water. If the reading
decreases by 50%, the sample is in the linear range. If the reading decreases by less than 50% or
even increases, the sample is above the linear range.
3.5.1.7.1 Quenching
Quenching refers to the reduction in fluorescence of a fluorophore. Several processes can result
in quenching:
Chloride is known to quench quinine sulphate and Fluorescein. It is, therefore, advisable to
prepare any fluorophore solutions with Reverse Osmosis (RO) or De-Ionised (DI) water.
Temperature quenching - as the temperature of the sample increases, the fluorescence decreases,
that is, fluorescence is sensitive to temperature. In order to improve accuracy, measure the
sample at different temperatures and derive corrections for changes in temperature.
Photo-bleaching (or fading) is the (permanent) degradation of a fluorophore molecule by light
resulting in lower signal levels. Photo-bleaching is dependent on exposure (intensity of light and
duration) and wavelength (UV is more damaging than longer wavelengths). Use of more robust
fluorophores is recommended to avoid photo-bleaching.
 Loading...
Loading...