Induction Cooktop
Electronic Control
3-4
PRINCIPLES OF INDUCTION (continued)
Operational Principles
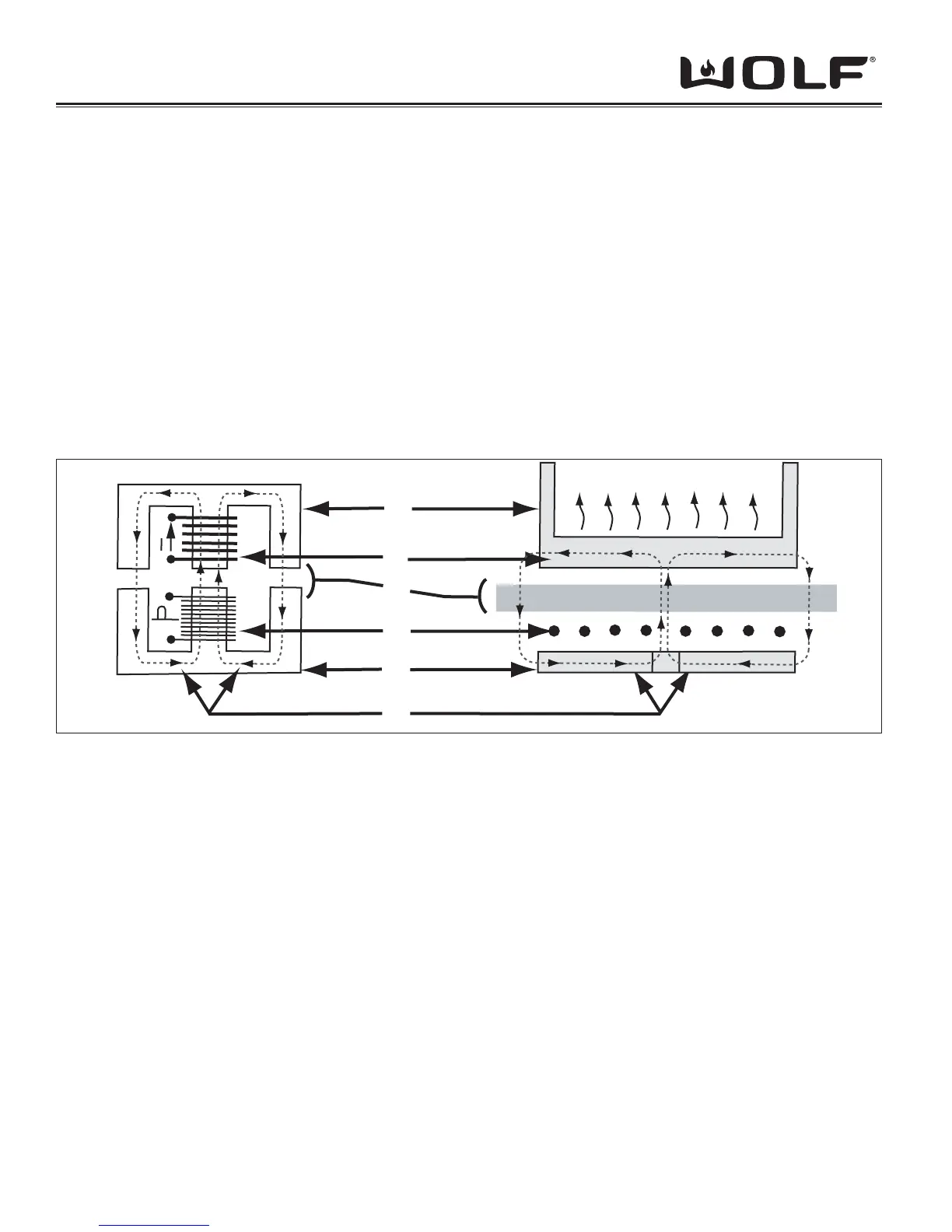
An induction cooktop operates thanks to the electromagnetic properties of most containers used on the traditional
cooktop.
You can compare this cooktop with a transformer of which the secondary winding would be shorted. A signifi cant
internal current arises and causes quick heating.
The saucepan can be compared with a shorted set of concentric coils whose internal resistance is not zero.
From the function keys, you can control the electrical power supply to the transformer primary winding that generates a
magnetic fi eld. This fi eld induces currents at the bottom of the container placed on the cooking zone. These induced
currents immediately heat the container, which transmits the produced heat to the food contained inside. Cooking is
performed practically without any loss of energy.
TRANSFORMER INDUCTION UNIT
Magnetic Conductor 1 Saucepan
Secondary Winding 2 Saucepan
Gap 3 Glass-Ceramic Plate
Primary Winding 4 Inductor (Element)
Magnetic Conductor 5 Ferrite
Magnetic Field 6 Magnetic Field
 Loading...
Loading...