Induction Cooktop
Electronic Control
3-3
PRINCIPLES OF INDUCTION
Introduction
There are two techniques of glass-ceramic heating:
• Infrared.
• Induction.
The difference is only obvious once the cooking zones are turned on. Induction has no visible indication of operation.
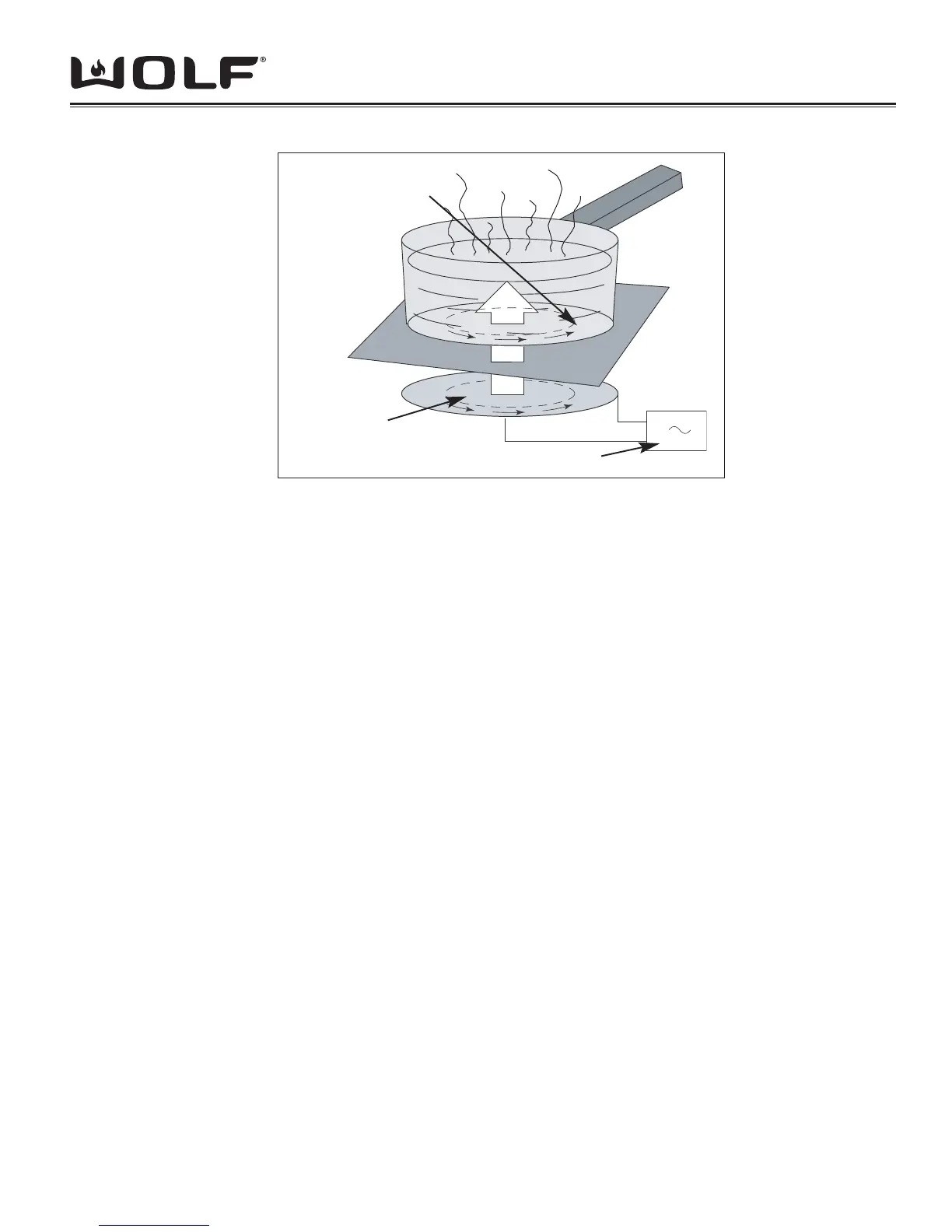
The Infrared is provided with radiant or halogen sources that transmit heat by radiation or conduction. Induction
Cooktops produce a magnetic fi eld which passes through the glass ceramic to the pan. When ferro magnetic cookware
is used, this magnetic fi eld excites the molecules in the pan, causing them to vibrate at a very high frequencies,
producing heat.
The principle of heating by induction is a natural phenomenon discovered in the 19th century by several physicists,
among them Leön Foucault. He discovered the induced currents that are named eddy currents.
Eddy currents are caused by a conductor (such as a pot or pan) intersecting a varying magnetic fi eld (created by the
inductor hob). These currents transform electromagnetic energy into heat. The glass surface then remains relatively
cool and the cooking response time is very quick.
The fl exibility of the quick response time and increased safety due to the glass staying cool are not the only advantages
to the induction cooktop. The energy effi ciency of an induction cooktop is up to 90% and cleaning is easy due to the
glass cooking surface staying cool.
+
-
Induced “eddy” currents
Electronic circuit
Induction coil
 Loading...
Loading...