Xerox® Security Guide for Entry Production Color Class Products
March 2019 Page 6-24
Network Authentication
When configured for network authentication, user credentials are validated by a remote authentication
server.
Versant 80 Press, Versant
180 Press
Versant 2100 Press,
Versant 3100 Press
Color 800/1000 Presses,
Color 800i/1000i Presses
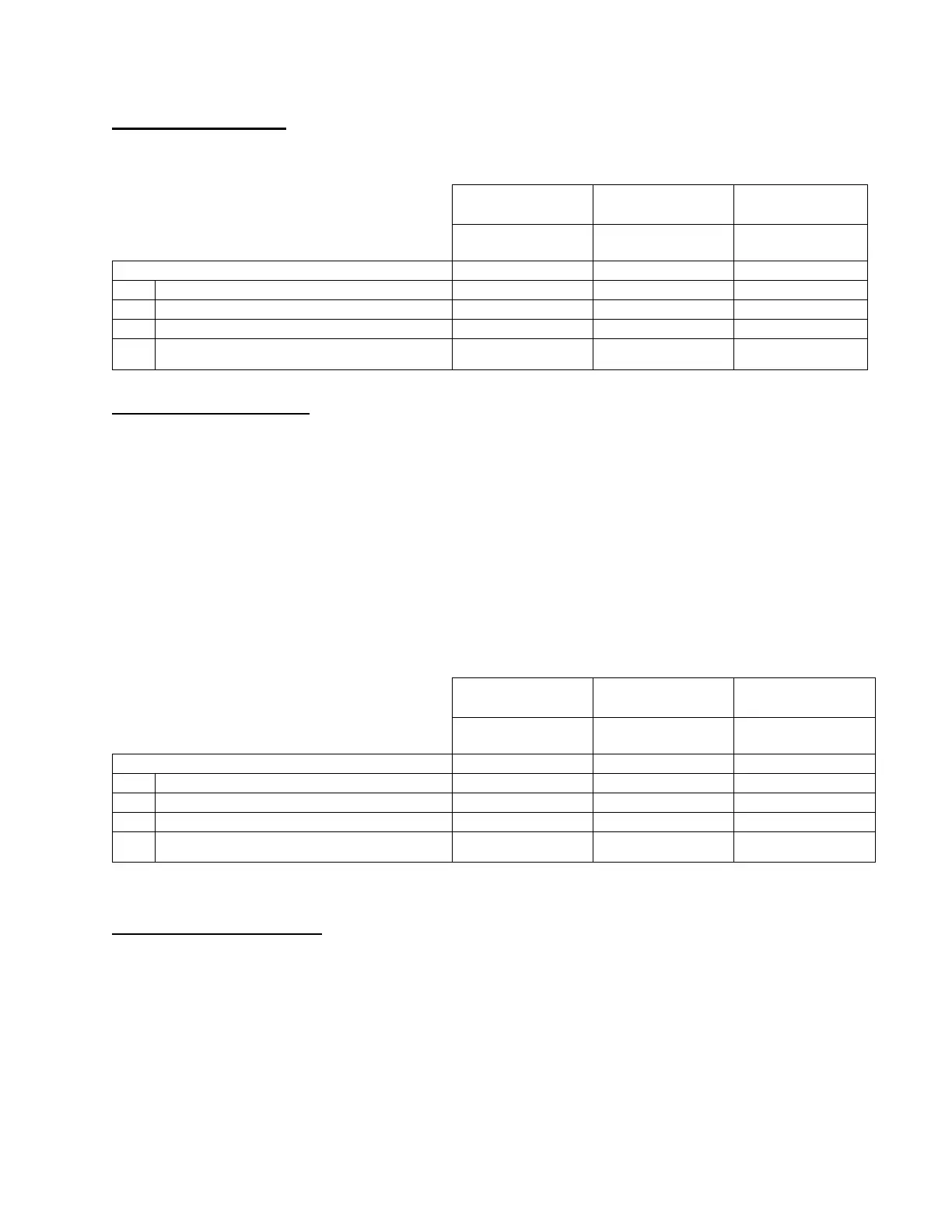
Network Authentication Providers
Kerberos (Microsoft Active Directory)
SMB NTLM Versions Supported
Version 3 (including TLS
1.2)
Version 3 (including TLS
1.2)
Version 3 (including
TLS 1.2)
Smart Card Authentication
Two-factor security - Smart Card plus User Name/Password combination, requires optional card reader
hardware and software plugin. Authentication is handled by a remote server. Supported remote
authentication methods include Kerberos, SMB and LDAP.
Smart Card authentication is considered very secure due to the nature of the Smart Card architecture and
potential levels of encryption of data on the card itself.
Support for the SIPR network is provided using the XCP Plug-in architecture and a Smart Card
authentication solution created by 90meter under contract for Xerox.
Details regarding 90meter can be found online here: http://www.90meter.com/
Other Smart Card authentication solutions are offered including support for CAC/PIV and .NET
compatible cards leveraging XCP Plug-ins.
Versant 80 Press, Versant
180 Press
Versant 2100 Press,
Versant 3100 Press
Color 800/1000 Presses,
Color 800i/1000i Presses
Net (Gemalto .Net v1, Gemalto .Net v2)
(Not Currently
Supported)
(Not Currently
Supported)
(Not Currently
Supported)
Convenience Authentication
Convenience authentication offloads authentication to a third-party solution which may offer more or less
security than native security implementations. Users swipe a pre-programmed identification card or key
fob to access the device.
For example, employees may be issued key fobs for access to facilities. Convenience mode may be
configured to allow an employee to authenticate using their fob or require the fob in a multi-factor manor.
The level of security provided is dependent upon the chosen implementation.
Some examples of third party convenience authentication providers include:

 Loading...
Loading...














