VESDA Pipe Network Installation Guide VESDA by Xtralis
20 www.xtralis.com
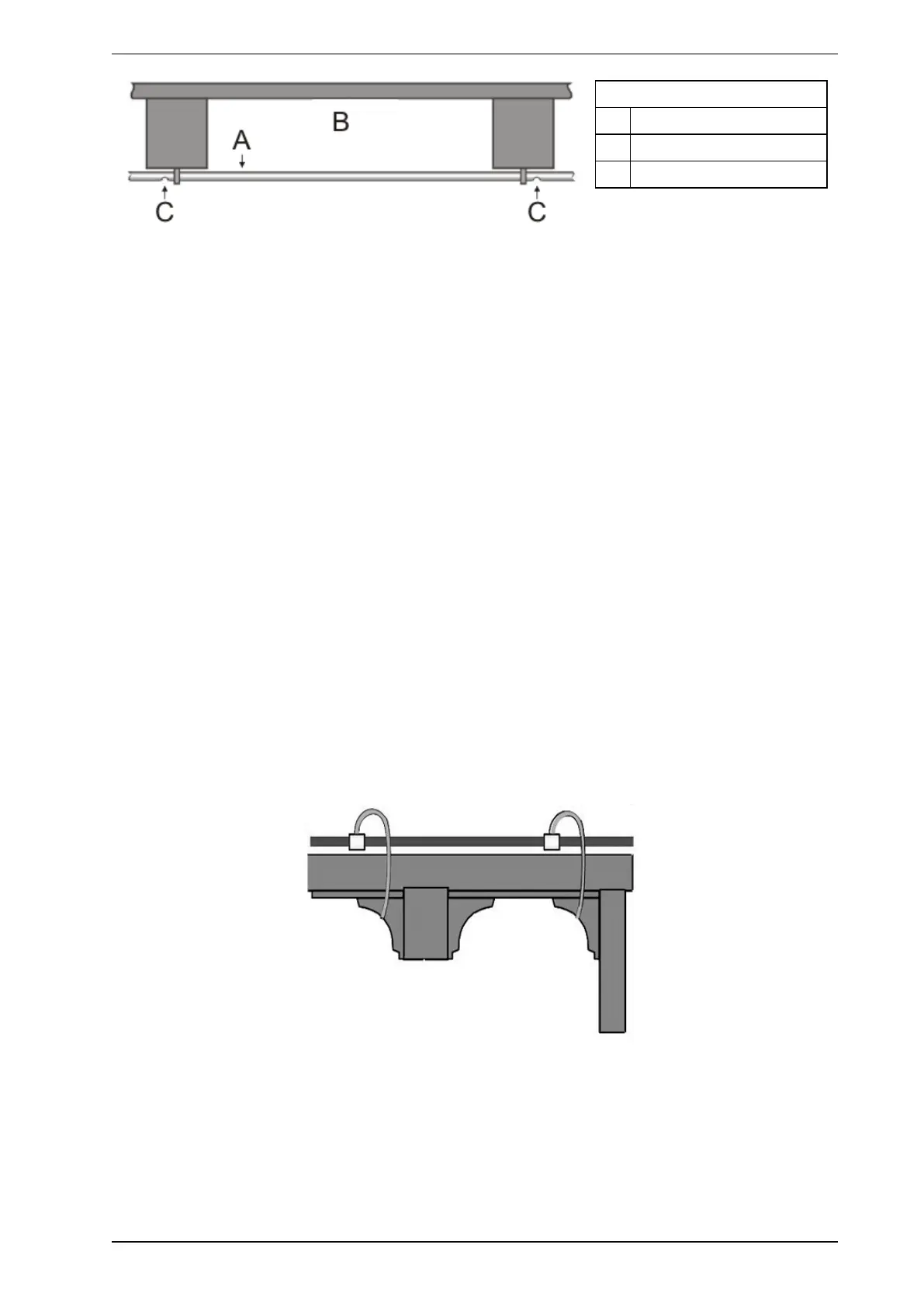
Legend
A Sampling Pipe
B Beam Pockets
C Sampling holes
Figure 5-6: Inter-beam sampling
5.1.5 Capillary Tubes and Drop Pipes Installation
Capillary tubes and drop pipes are used to monitor the environment from areas away from the sampling pipe.
Capillary tubes and drop pipes are typically used for Concealed and In-Cabinet sampling.
Guidelines for Capillary and drop pipes:
1. Install the sampling pipe using Tee adaptors where the capillary tubes or drop pipes need to be
attached.
2. Fix appropriate sized reducing connection to the Tee
3. Connect capillary tube or drop pipe to the reducing connector
4. Run the capillary or the drop pipe to the required sampling point
5. Attach sampling point fitting
Note: Microbore only requires steps 4 and 5.
5.1.6 Concealed Sampling
Concealed sampling is used when there is a requirement for aesthetics or for security. Capillary tubes and
drop pipes are normally used for concealed sampling. The ceiling void is used to lay the sampling pipe.
Capillary tubes are routed to the required location and penetrate the ceiling, generally using something to hide
the tube. The end of the tube is either restricted with a capillary cap or left fully open.
In situations where discreet sampling is required to maintain the aesthetics of the protected area, the capillary
tube can be concealed behind a ceiling rose, wound down a chandelier support chain or can sit flush with the
ceiling cornice. The sampling holes can be concealed by using a flush sampling point or a sampling point
inserted inside the end of the sampling pipe.
1. Follow the guidelines in Section 5.1.2 on page 18.
2. Then follow the guidelines in Section 5.1.5 on page 20.
Figure 5-7: Concealed sampling points
 Loading...
Loading...











