34 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
VLAN serves as a logical workgroup with no physical
barriers, and allows users to share information and
resources as though located on the same LAN.
You can use the Switch to create VLANs to organize
any group of ports into separate broadcast domains.
VLANs confine broadcast traffic to the originating group
and help eliminate broadcast storms in large networks.
This also provides for a more secure and cleaner
network environment.
Using the Switch, you can create up to 64 VLANs, add
specific ports to a chosen VLAN (so that the port can
only communicate with other ports on the VLAN), or
configure a port make it a member of all VLANs.
Communication between different VLANs can only take
place if they are all connected to a router or layer 3
switch.
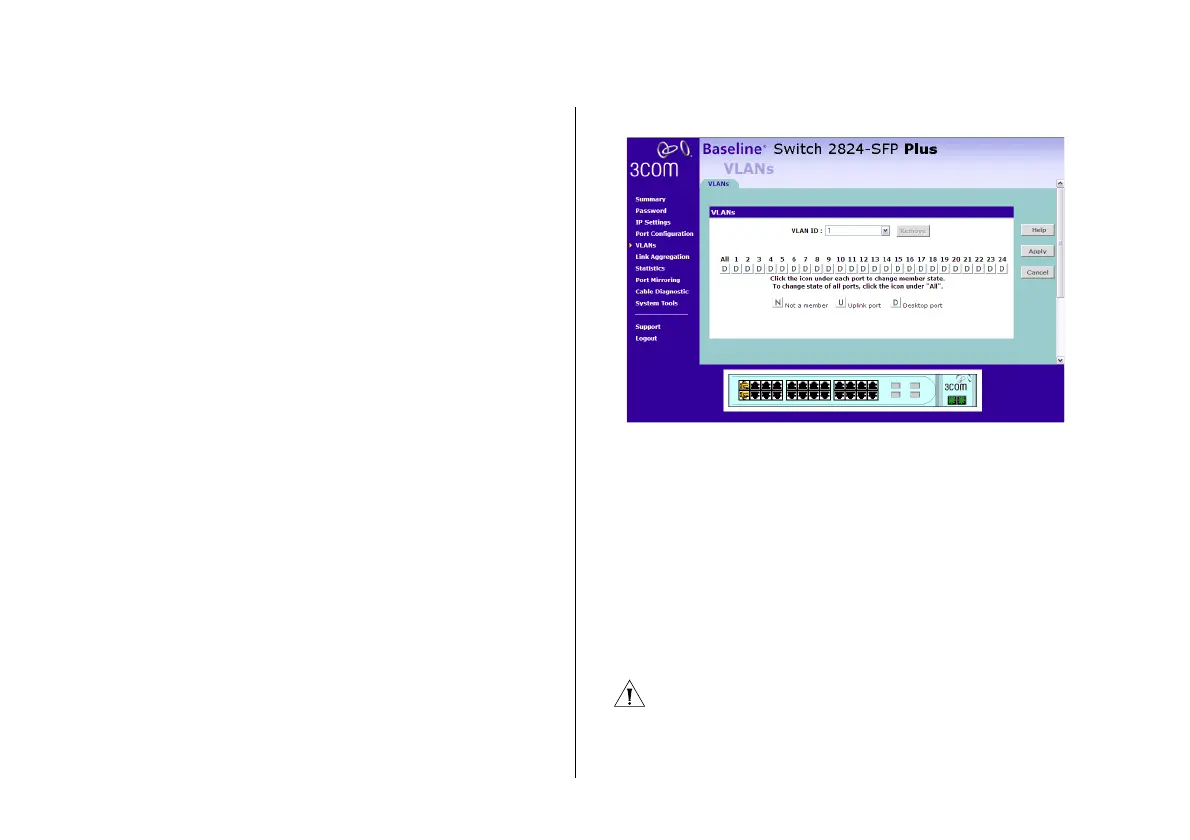
Creating a VLAN
Use the VLANs page to create VLANs on the Switch. To
propagate information about VLAN groups used on this
Switch to external devices, you must specify a VLAN ID
for each VLAN.
Figure 14 VLANs Page
Ports belonging to a VLAN must be set to either U
(uplink) or D (desktop). Desktop VLAN ports can only be
members of one VLAN at any time. Setting a port as an
uplink (tagged) VLAN port forwards all VLAN traffic
from the other ports on the Switch to this port. Use the
uplink port function to connect the Switch to the
backbone of the network. Traffic from all the VLANs on
the switch is automatically forwarded to the uplink port
or ports.
By default, all ports belong to VLAN 1.
CAUTION: At least one port must always be a member
of VLAN 1 (the management VLAN). If you choose to
connect all ports to VLANs other than VLAN 1, you will
no longer be able to access the Web interface. If this
 Loading...
Loading...











