Condenser Flooding
In order to maintain head pressure in the
refrigeration system, liquid refrigerant is
kept in the condenser to reduce condenser
surface. The following chart shows the
percentage that a condenser must be flooded
in order to function properly at the given
ambient temperature.
During higher ambient temperatures the
entire condenser is required to condense
refrigerant. During these higher ambient
temperatures, a receiver tank is used to
contain the refrigerant that was required to
flood the condenser during low ambient
operation. The receiver is factory-sized to
contain all of the flooded volume. Without a
receiver there would be high head pressures
during higher ambient conditions.
Table 8 - Condenser Flooding
PERCENTAGE OF CONDENSER TO BE
FLOODED
Evaporating Temperature (°F)
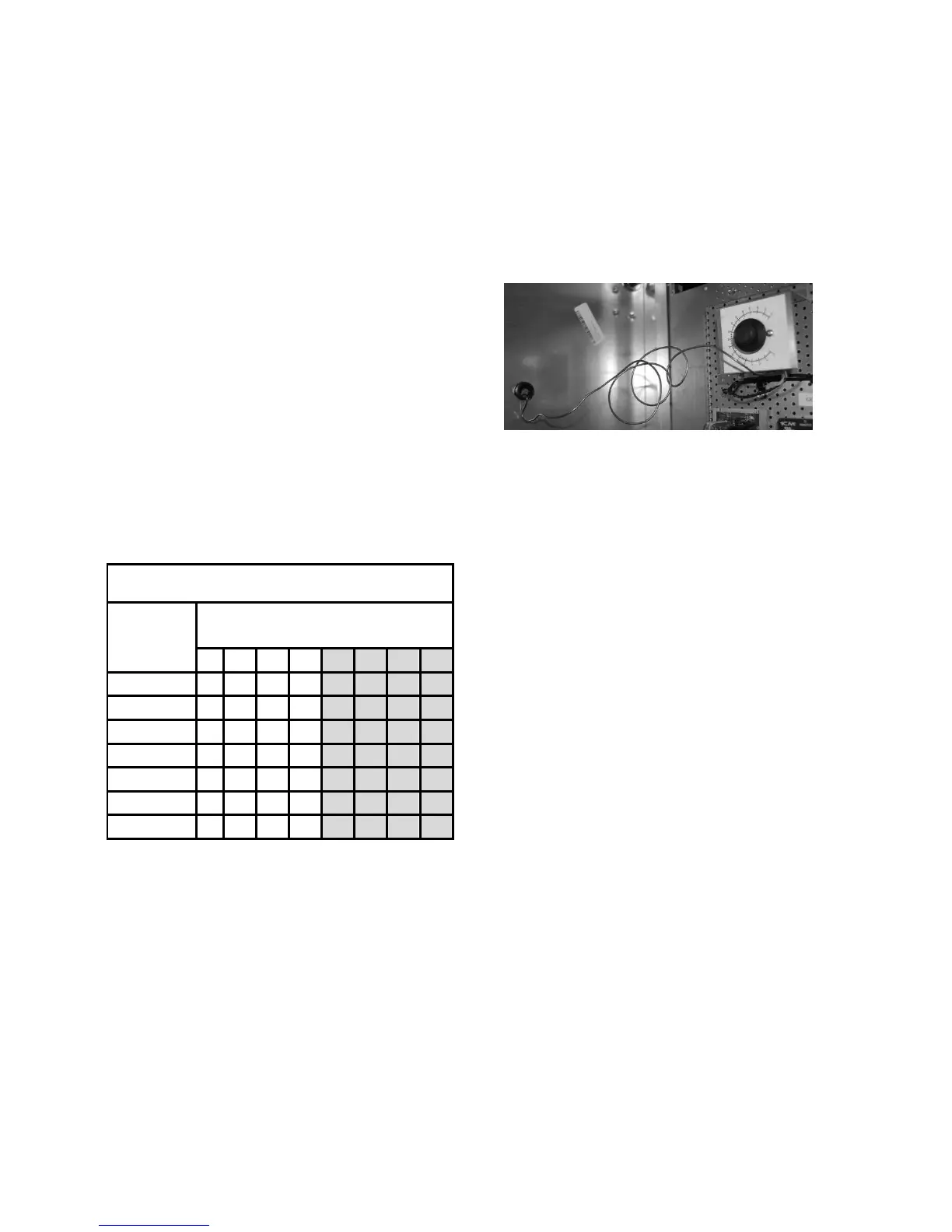
Compressor Lockouts
Some units include adjustable compressor
lockouts. The compressor lockout in the
picture below can be set to any temperature
between -10°F and 70°F. The ambient
temperature sensor hangs right outside the
unit with a cover.
Figure 11 - Adjustable compressor lockout
Heat pump units include a non-adjustable
compressor lockout for the cooling mode set
to 55°F, and an adjustable compressor
lockout for the heating mode that can be set
between 20°F to 95°F. If a heat pump is
selected with the compressor lockout
feature, the adjustable compressor lockout
will change to the -10°F to 70°F range.

 Loading...
Loading...