Polarization is defined as the orienta-
tion of the electric field as radiated from
the transmitting antenna. Polarization
is determined by the position of the
antenna or cable with respect to the
earth. If a cable leak is parallel to the
earth, it radiates horizontal signal
waves. If a cable leak is at a right angle
to the earth, it radiates vertical signal
waves (See diagram above). If cross
polarization occurs, there will be inade-
quate detection of many signal deci-
bels. Therefore, if a leak is coming from
the cable in the horizontal position,
your antenna must be held in the hori-
zontal position in order to obtain the
most accurate level reading. The same
principle should be applied to a vertical
leak, hold the antenna in a vertical posi-
tion. In simple terms, you should point
your antenna in the same directional
position as your leak.
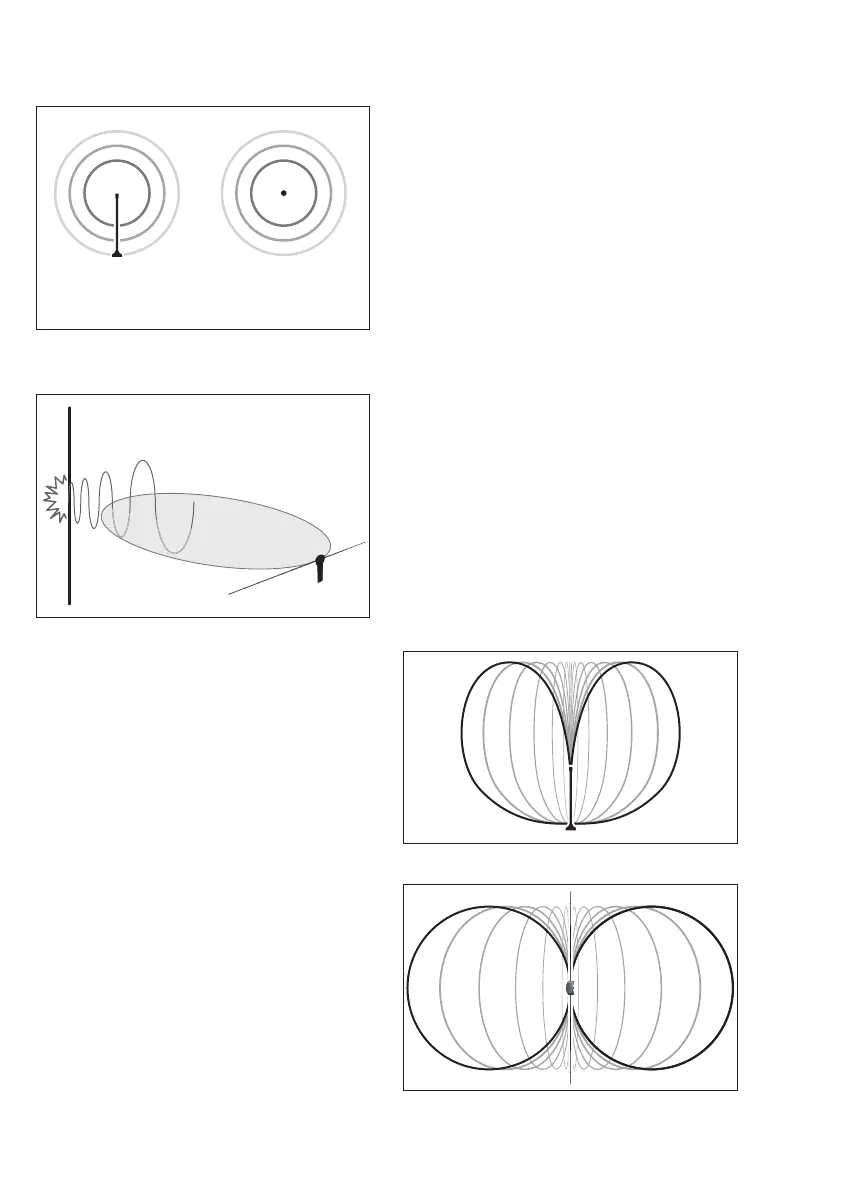
The two types of antennas that we will
discuss in this manual are the mono-
pole and the dipole. The diagrams pro-
vided below indicate the radiation pat-
tern emitted by each of the antenna
types. As you can see, the radiation
pattern of the monopole is parallel to
the antenna. In comparison, the radia-
tion pattern of the dipole looks like a
figure 8 pattern that is perpendicular to
the center of the antenna. Compare
the gain and polarization of both types
of antennas. Which type of antenna will
provide the field technician with a high-
er degree of flexibility and accuracy
when checking for cable leakage? Why?
3-16
 Loading...
Loading...