Appendix E
Appendix E RS-485 Network E
-3
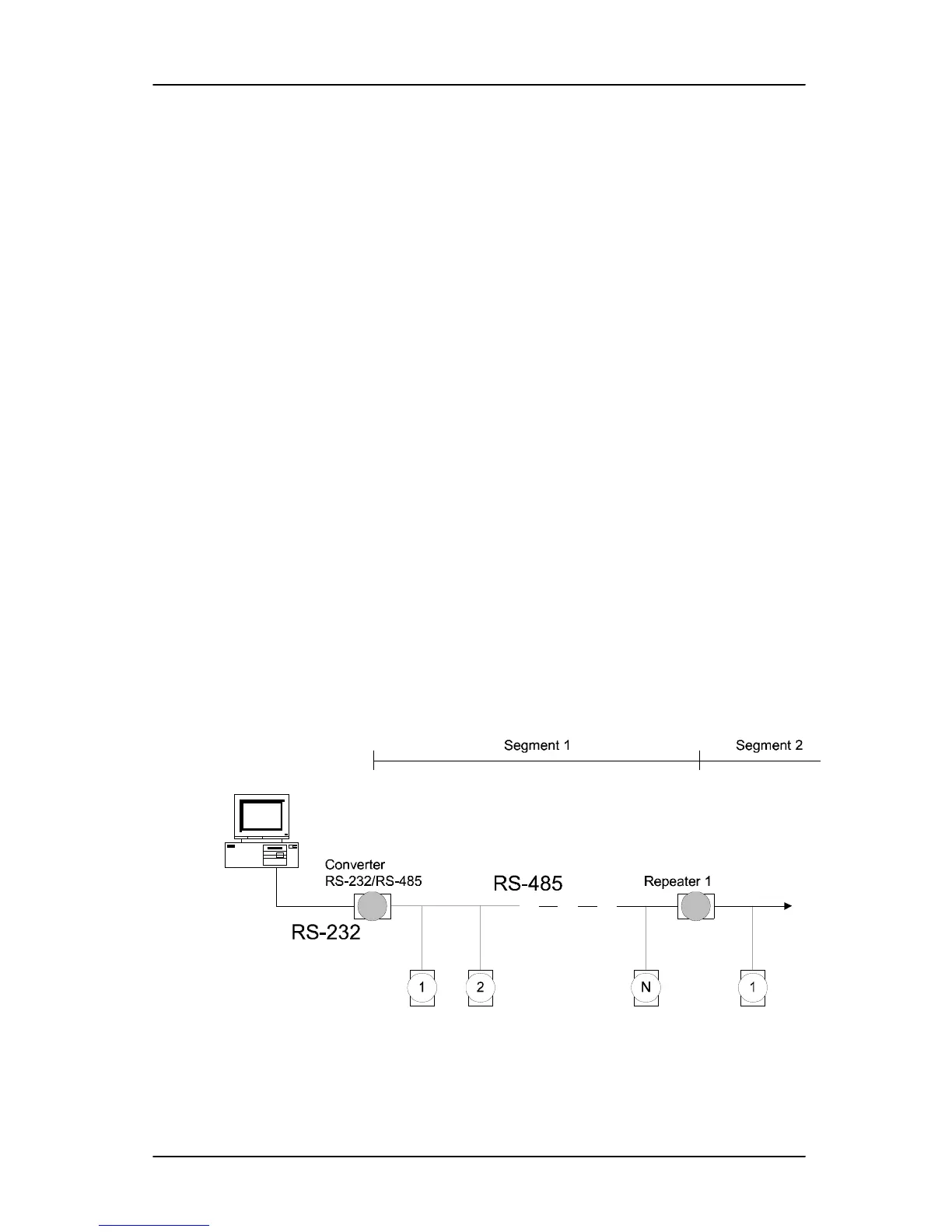
E.1 Basic Network Layout
Multi-drop RS-485 implies that there are two main wires in a segment.
The connected modules are connected by the so called drop cables, and
all the connections are in parallel. As a result, connecting or
disconnecting of a node doesn’t affect the network as a whole. Since
ADAM modules use the RS-485 standard with an ASCII-based
commands set, they can connect and communicate with all the ASCII-
based computers and terminals. The basic layouts that can be used for
an RS-485 network are:
Daisychain
The last module of a segment is a repeater, and it is directly connected
to the main-wires. Therefore, it acts as a medium which repeats the
signals between two segments. However, there is a limitation towards
this topology. It can only sustain up to 32 addressable modules. If more
modules per segment are used, the IC driver current will rapidly
decrease which may cause communication errors. Furthermore, the
entire network can only hold up to 256 addressable modules because of
the limitation of two numbered hexadecimal representation. The
maximum representation of two numbered hexadecimal representation
is 256. The ADAM converter, repeaters and the host computer are non
addressable units; therefore, they are not included in these numbers.
Figure E-1 Daisychaining
 Loading...
Loading...