Chapter 5 295
Concepts
Analog Modulation Concepts
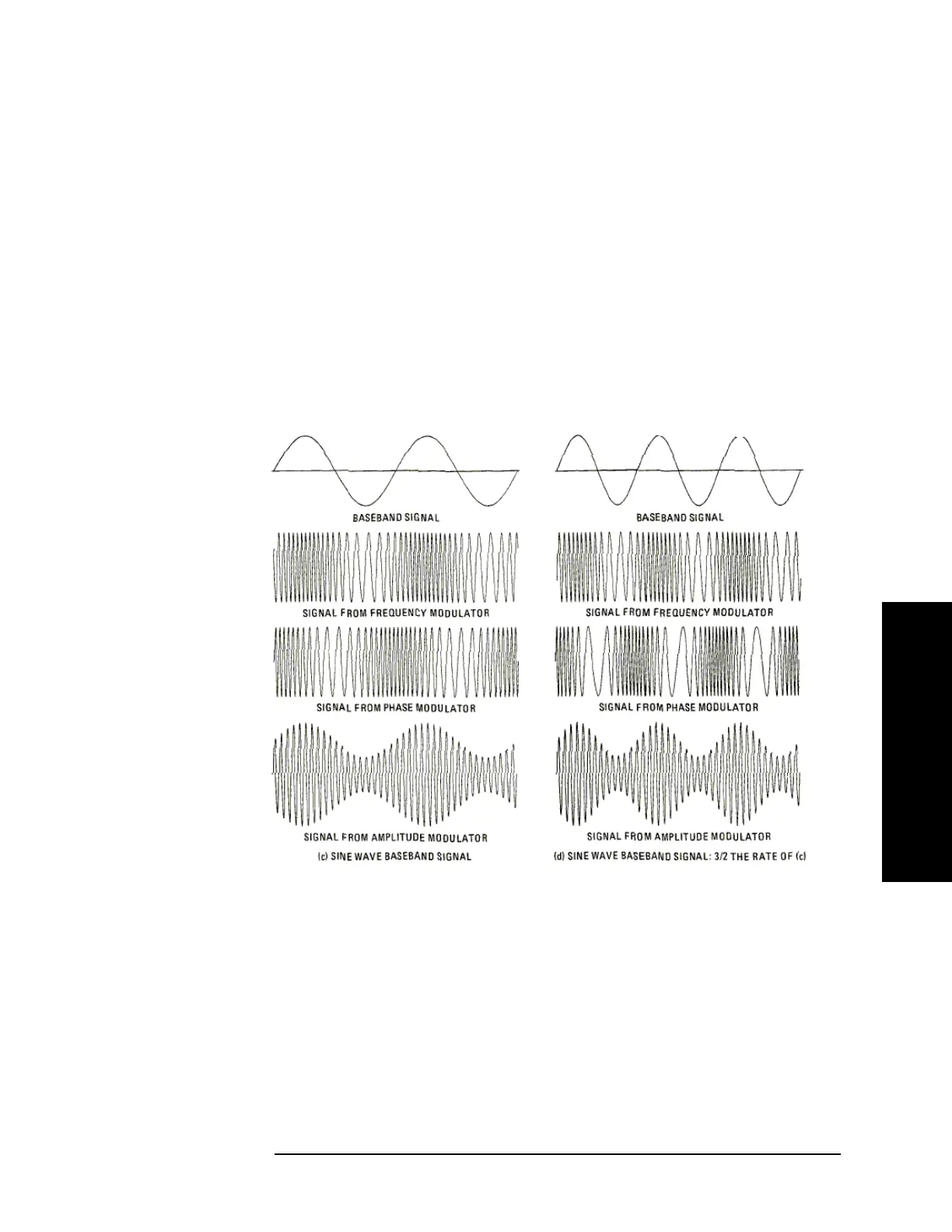
between two. For the frequency modulated signal, the frequency is highest when
the baseband signal is most positive and lowest when most negative. For the phase
modulated signal, the frequency is highest when the slope of the baseband signal is
steepest in a positive direction. This occurs at the positive-going zero crossing.
Similarly, the frequency is lowest when the slope is most negative.
If in the last example, the rate, but not the amplitude, of the baseband signal is
increased, the highest and lowest frequencies of the signal form the frequency
modulator stay the same- they just occur more often. However, for the signal form
the phase modulator, not only do the frequency peaks occur more often, but the
excursions are large because the slopes of the baseband signal are steeper at the
zero crossings. See Figure 5-9 on page 295.
Figure 5-9 Signals from Frequency, Phase and Amplitude Modulators for Various
Baseband Signals (Sine Waves)
Other Considerations
In practice, it is difficult to produce an FM or ΦM signal which does not also have
a small amount of AM- called incidental AM or AM-on-FM. Likewise, an AM
signal usually contains a small amount of incidental FM and ΦM. In order to
accurately measure this incidental modulation, the Measuring Receiver itself must
not contribute to it. This contribution is specified as AM rejection and FM
rejection.
A typical CW signal also contains a small amount of residual AM,FM, and ΦM.
The residual modulation is generated by such things as line hum, noise, and
 Loading...
Loading...