114 Rockwell Automation Publication 20A-UM001N-EN-P - July 2013
Appendix C Application Notes
Operation below 100% current causes the temperature calculation to account for
motor cooling.
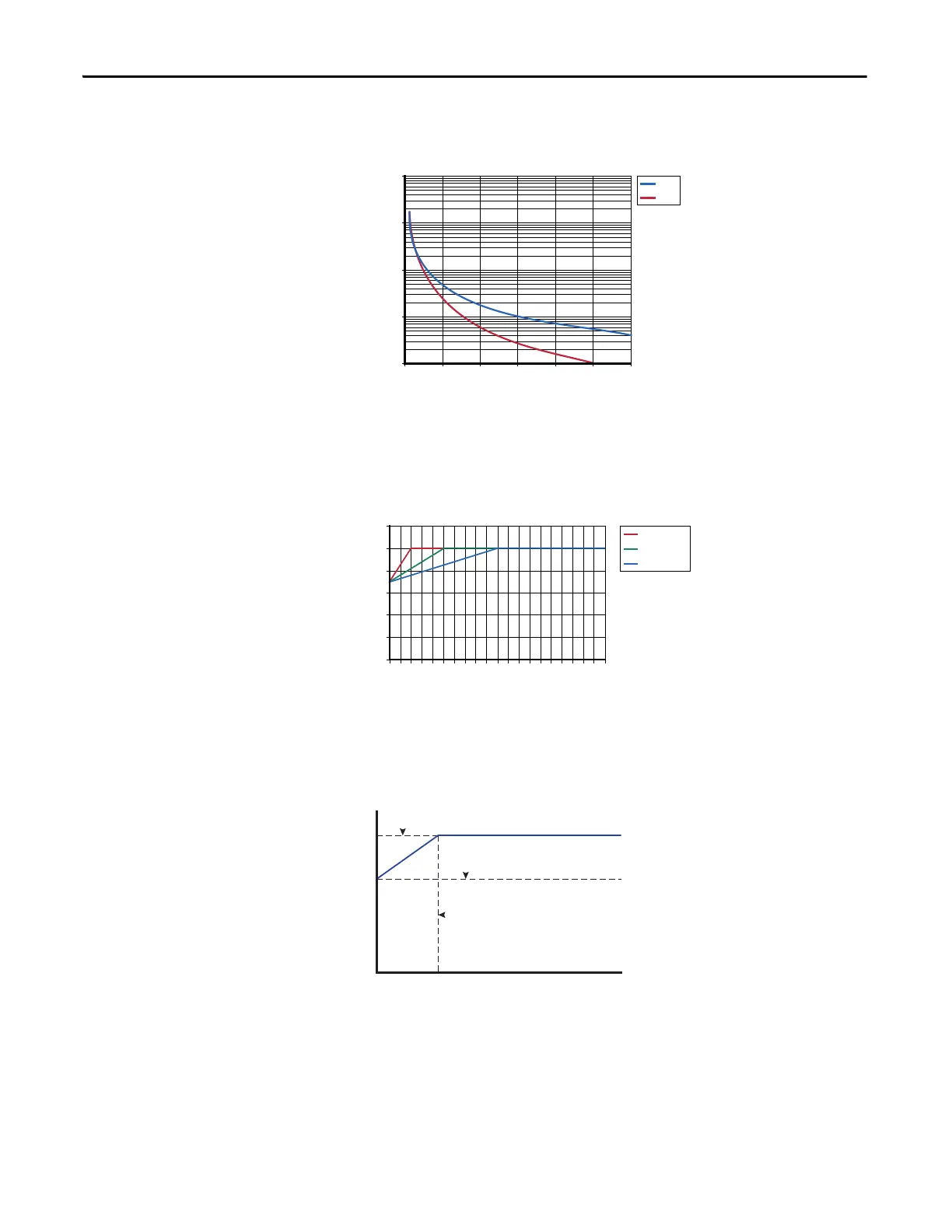
[Motor OL Hertz] defines the frequency where motor overload capacity derate
begins. The motor overload capacity is reduced when operating below [Motor
OL Hertz]. For all settings of [Motor OL Hertz] other than zero, the overload
capacity is reduced to 70% at an output frequency of zero.
[Motor NP FLA] is multiplied by [Motor OL Factor] to select the rated current
for the motor thermal overload. This can be used to raise or lower the level of
current that causes the motor thermal overload to trip. The effective overload
factor is a combination of [Motor OL Hertz] and [Motor OL Factor].
The motor overload, if enabled, enables continuous operation at or below the
line. Above the line, the overload trips after a time delay. The further above the
line, the shorter the trip time.
Motor Overload Curve
100 125 150 175 200 225 250
Full Load Amps (%)
Trip Time (Sec)
Cold
Hot
10
100
1000
10000
100000
Changing Overload Hz
0102030405060708090100
% of Base Speed
Continuous Rating
OL Hz = 10
OL Hz = 25
OL Hz = 50
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
Trip Amps = P42 [Motor NP FLA] x P48 [Motor OL Factor]
P1 [Output Freq] (Hz)
P3 [Output Current] (Amps)
0.7 x Trip Amps
P47 [Motor OL Hertz]

 Loading...
Loading...















