Rockwell Automation Publication 20A-UM001N-EN-P - July 2013 121
Application Notes Appendix C
Voltage Tolerance
This section describes voltage tolerances for the different drive ratings.
Example:
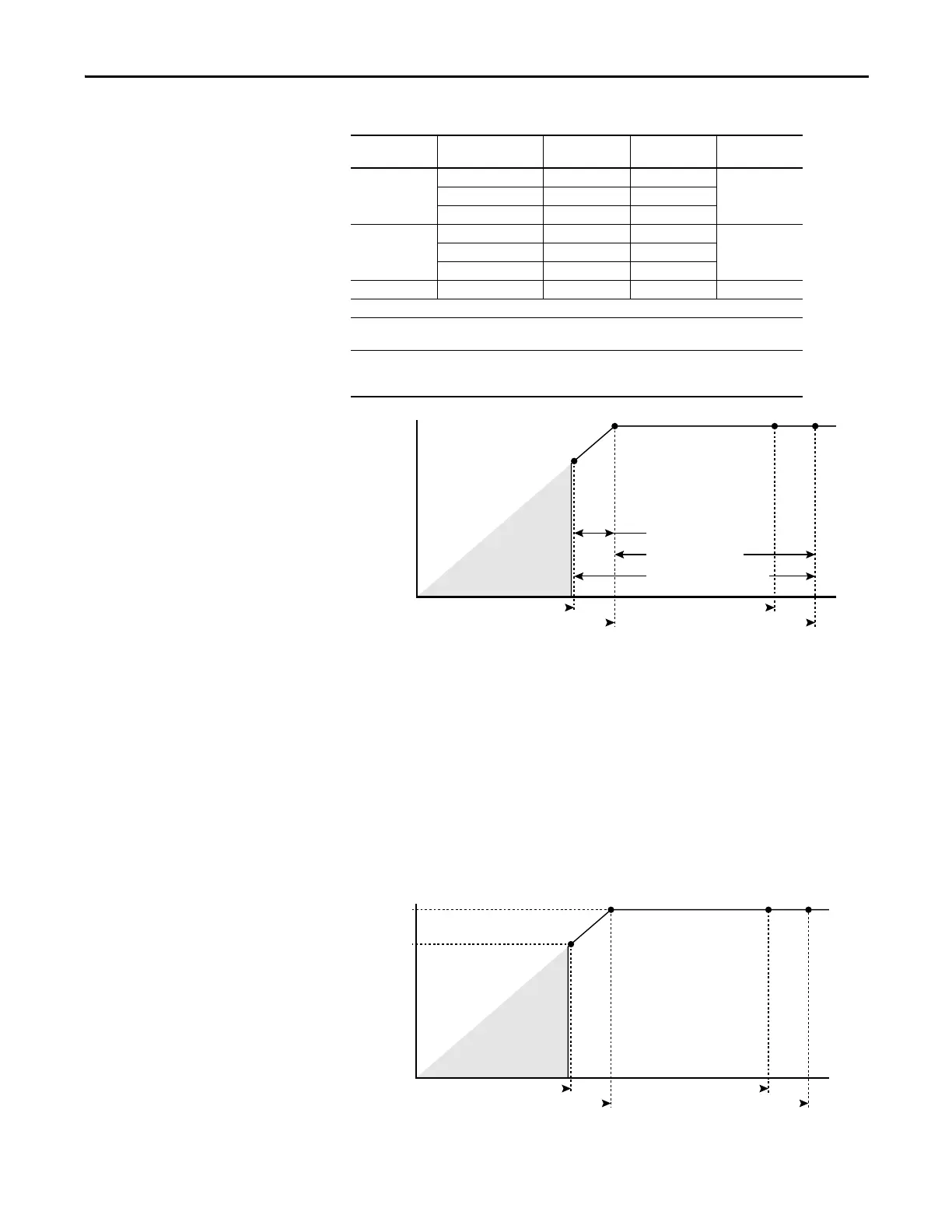
Calculate the maximum power of a 5 Hp, 460V motor connected to a 480V rated
drive supplied with 342V Actual Line Voltage input.
• Actual Line Voltage / Nominal Motor Voltage = 74.3%
• 74.3% × 5 Hp = 3.7 Hp
• 74.3% × 60 Hz = 44.6 Hz
At 342V Actual Line Voltage, the maximum power the 5 Hp, 460V motor can
produce is 3.7 Hp at 44.6 Hz.
Drive Rating Nominal Line
Voltage
Nominal Motor
Voltage
Drive Full Power
Range
Drive Operating
Range
200…40 200 200† 200…264 180…264
208 208 208…264
240 230 230…264
380…400 380 380† 380…528 342…528
400 400 400…528
480 460 460…528
500…600 600 575† 575…660 432…660
Drive full power range = Nominal motor voltage to drive rated voltage + 10%.
Rated current is available across the entire drive full power range
Drive operating range = Lowest nominal motor voltage - 10% to drive rated voltage + 10%.
Drive output is linearly derated when the actual line voltage is less than
the nominal motor voltage.
HP @ Motor (Drive Output)
Actual Line Voltage (Drive Input)
Full Power Range
Drive Operating Range
Nominal Motor Voltage -10%
Nominal Motor Voltage
Derated Power Range
No Drive
Output
Drive Rated Voltage
Drive Rated Voltage +10%
5 HP
3.7 HP
HP @ Motor (Drive Output)
Actual Line Voltage (Drive Input)
342V
460V
No Drive
Output
480V
528V

 Loading...
Loading...















