Page 28
User GuideLSPHD Linescanner Head
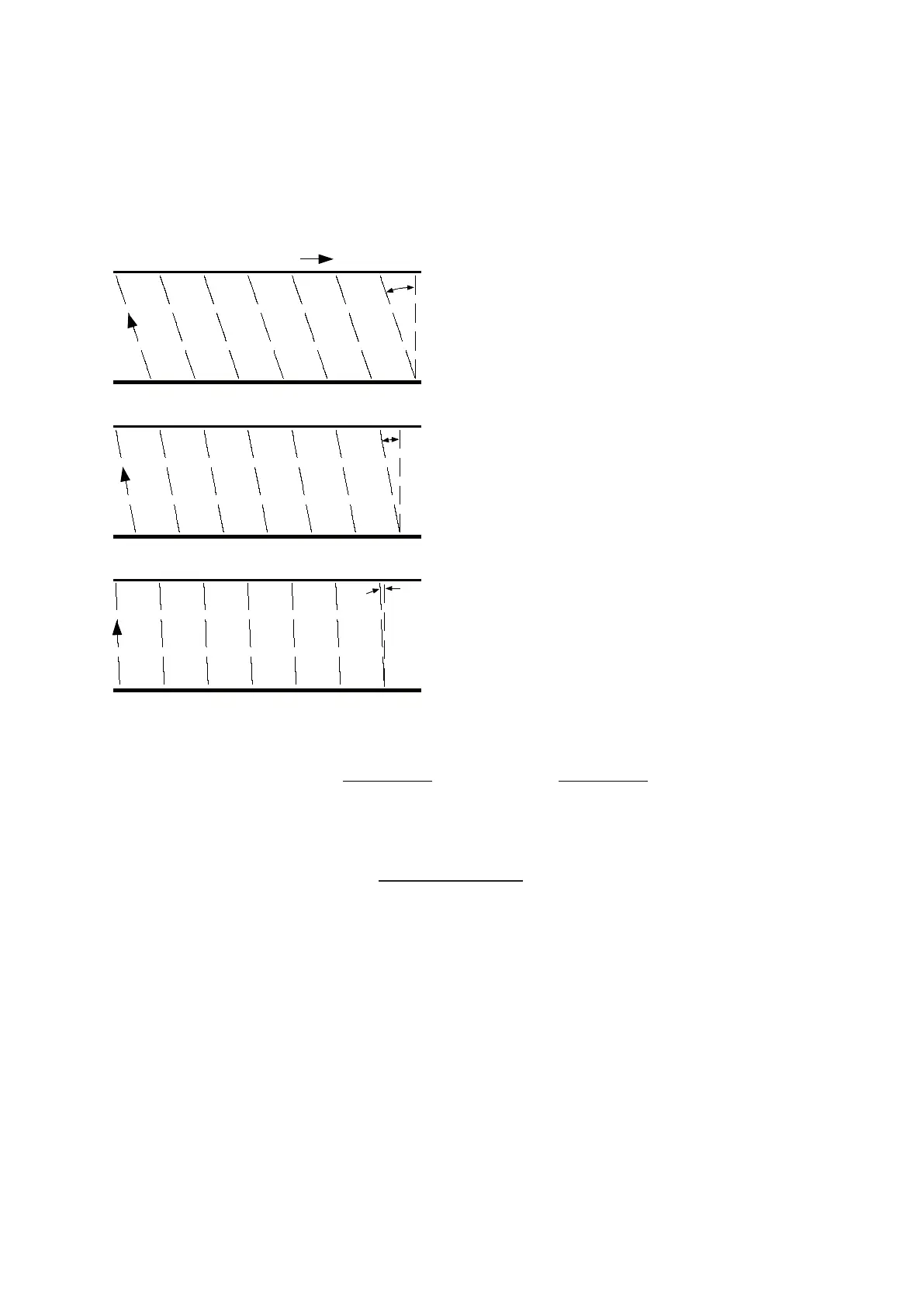
Example 1-Agreaterskewangle
iscreatedwhenhighproduct
speedsarecombinedwithlowscan
frequencies.
Note:Duringproductwidth
calculations,theapparentwidthis
displayedgreaterthantheactual
width.
Example 2-Whenhighproduct
speedsarecombinedwithmedium
scanfrequencies,theskewangleis
reducedwhencomparedtoExample1.
Example 3-Whenhighproduct
speedsarecombinedwithhigh
scanfrequencies,theskewangle
isnegligiblewhencomparedto
Example 1.
The scan skew angle is given by:
e.g. At a scan frequency of 50Hz, a target distance (D) of 2m and product speed of 10m/s ......... θ = 0.91°
Apparent (measured) product width = actual product width (ignoring edge correction errors)
Cos θ
6.5 Skew Angle
When a linescanning thermometer is scanning across a moving product travelling along
aline,settingthescanfrequencytoolowmaycausethescanlinetobeexcessively
tilted,or'skewed'.Whentheproductspeedishighandthescanfrequencyislow,the
skewismoreapparent,andresultsinaninaccurateindicationofproductwidth.
Product movement
Scan line
Skew angle
θ
θ
θ
−−
speedscan
TAN
frequencyscan 2
TAN
11
d
π

 Loading...
Loading...