Appendix A: Marshalling Protocol
217
NetLinx Programming Language Reference Guide
Marshalling Protocol (Variables)
The protocol assumes that every logical field (variable) is identified with a name or index, type/size
information and the actual data. For example, if there is a 4 byte long integer field within a structure, the
XML stream representing that field would consist of 3 tags: A name tag specifying the name of the
variable, a type tag specifying a 4 byte unsigned value, and the data. This concept is extended to all
primitive, structure and array types. The type of a field is always stored using W3C standard type
declarations. The type of the field is optional, as the data will be "stuffed" into whatever type matches the
name of the parameter. The specific formats of all the supported types are described below.
Marshalled Stream format
The following table describes the byte format of the various types supported in the XML marshaller.
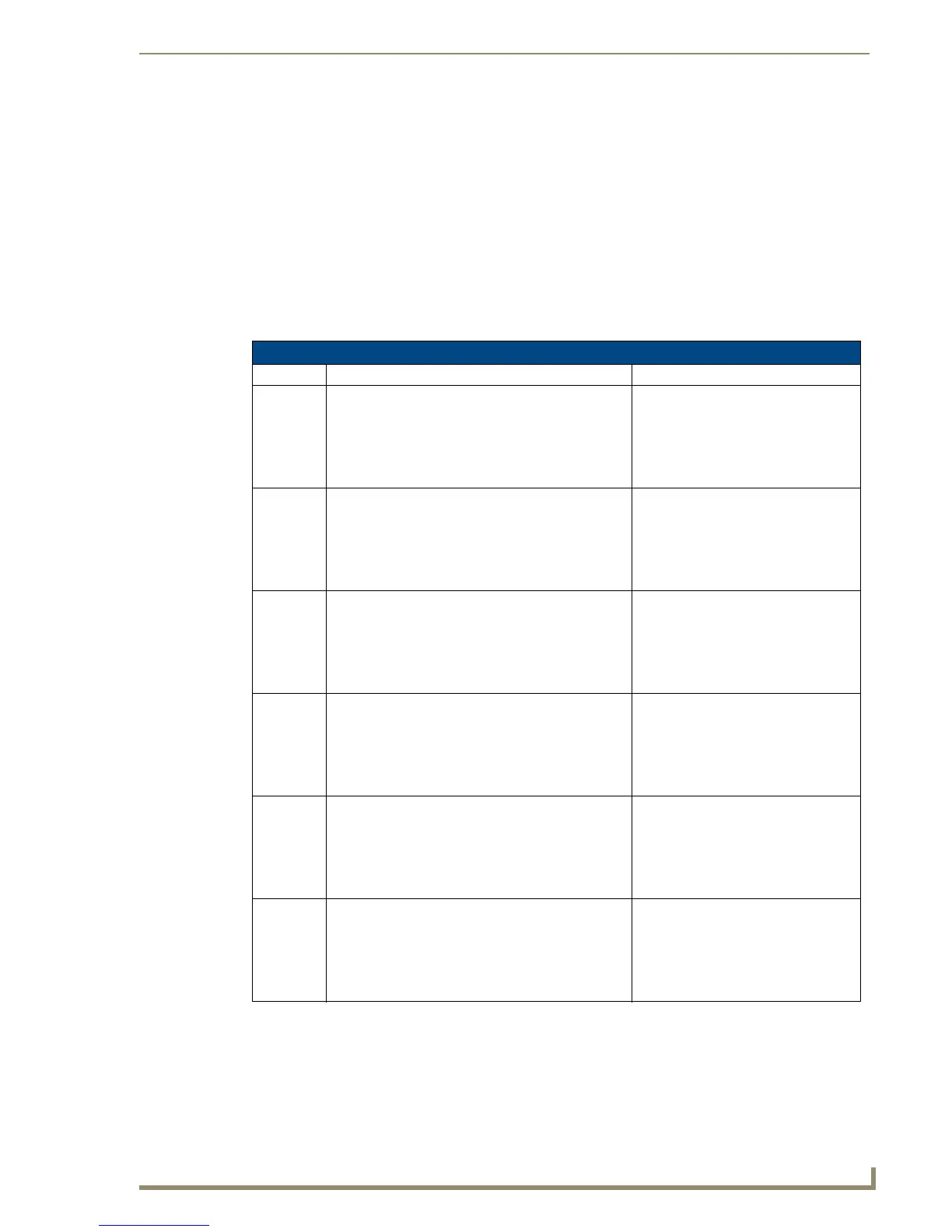
Types Supported in the XML Marshaller
Type Description Stream Format
BYTE Unsigned char/byte value. If var is an element of an
array, name is replaced with <index></index>. The
index value, and the type are optional. Typically, only
<var><data>Data</data></var> is needed.
<var>
<name>MyName</name>
<type>ui1</type>
<data>255</data>
</var>
UWORD Unsigned short value. If var is an element of an array,
name is replaced with <index></index>. The index
value, and the type are optional. Typically, only
<var><data>Data</data></var> is needed.
<var>
<name>MyName</name>
<type>ui2</type>
<data>65535</data>
</var>
WORD Signed short value. If var is an element of an array,
name is replaced with <index></index>. The index
value, and the type are optional. Typically, only
<var><data>Data</data></var> is needed.
<var>
<name>MyName</name>
<type>i2</type>
<data>-32767</data>
</var>
ULONG 4-byte unsigned value. If var is an element of an array,
name is replaced with <index></index>. The index
value, and the type are optional. Typically, only
<var><data>Data</data></var> is needed.
<var>
<name>MyName</name>
<type>ui4</type>
<data>4294967295 </data>
</var>
LONG 4-byte signed value. If var is an element of an array,
name is replaced with <index></index>. The index
value, and the type are optional. Typically, only
<var><data>Data</data></var> is needed.
<var>
<name>MyName</name>
<type>ui4</type>
<data>-2147483647 </data>
</var>
FLOAT 4-byte IEEE 754 float value. If var is an element of an
array, name is replaced with <index></index>. The
index value, and the type are optional. Typically, only
<var><data>Data</data></var> is needed.
<var>
<name>MyName</name>
<type>float.IEEE.754.32</type>
<data>1.23</data>
</var>

 Loading...
Loading...