Technical Reference
POWERmini USB User Guide 12 2.0
TECHNICAL REFERENCE
Battery Types
For best results you should be sure to set the charge and cut-off parameters to suit the battery chemistry
that you are going to use. POWERmini allows you to save settings for the maximum and minimum battery
voltages separately for two different types of batteries, Lithium ion and Lead Acid.
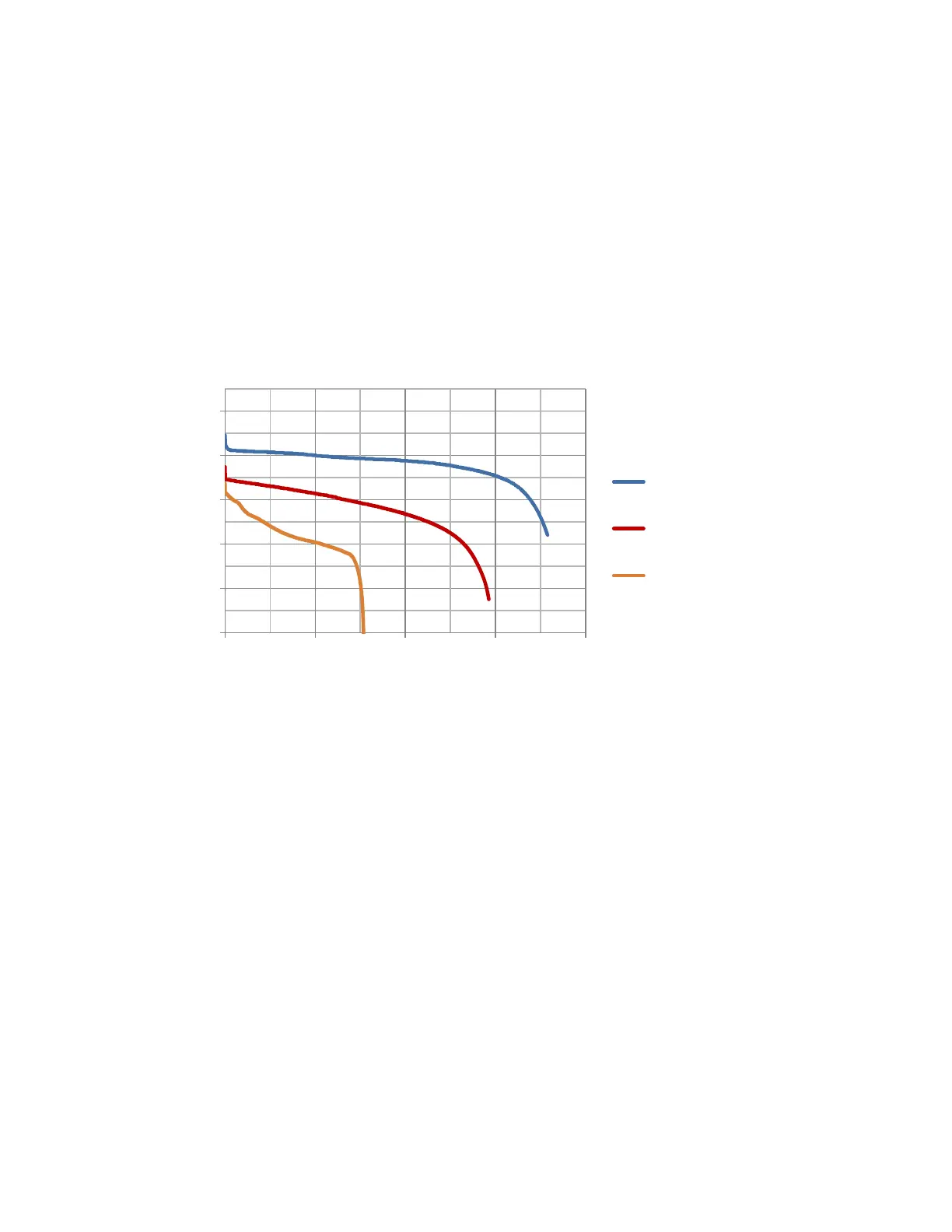
Different types of battery chemistry have different voltage vs capacity characteristics. The characteristic
Capacity (Ah) vs voltage curves of three popular battery types are shown in Figure 10 below.
Figure 10 Comparison of battery characteristics for different battery chemistry
The three types of batteries are Lithium Iron Phosphate (4 cell), Lead Acid (6 cell) and Lithium Polymer (3
cell). Notice that the curves are similar in shape but have very different values for the fully charged and
depleted states.
The Lithium Iron Phosphate battery has a higher maximum voltage (100% charge level) and a relatively
flat discharge curve.
The Lead Acid battery has a lower maximum voltage, more slope to the discharge curve and a lower cut-
off voltage.
The Lithium Polymer (3 cell) battery has an even lower maximum voltage and a lower cut-off voltage. It
should be noted that this type of battery is frequently used as a car jump start battery and cell phone
charger. The low terminal voltage of this battery is problematic for radios, many of which require a
battery voltage of over 12V to function normally.
The Battery Type setting shows the POWERmini which type of battery you are using. The Maximum
Charge Voltage and Low Voltage Limit (minimum battery voltage) are saved separately for Lead Acid and
Lithium ion batteries. First choose the battery type you want to use and then set the Maximum Charge
Voltage and Low Voltage Limit voltage for that type of battery. Then if you plan to use a different type of
battery chemistry repeat the process selecting the new battery type and storing values for Max Charge
 Loading...
Loading...