33
Esempio 4:
Si abbiano le seguenti specifiche di progetto: al fine di ottimiz-
zare il rendimento invernale di una caldaia di un circuito di riscalda-
mento domestico, si può prevedere una temperatura di esercizio
(St1) di 70°C per temperature esterne superiori a 15°C. Quando la
temperatura esterna si fa più rigida, quella di esercizio della caldaia
deve aumentare in modo proporzionale, fino ad arrivare ad una tem-
peratura massima di 85°C prevista per una temperatura esterna
minore o uguale di 0°C.
Soluzione: si potrà utilizzare un regolatore Infrared con la sonda
principale NTC1 sul circuito dell’acqua, Modo 2 (riscaldamento),
set-point St1=70 e differenziale P1=4. Sarà inoltre necessario uti-
lizzare una sonda NTC2 posta all’esterno, abilitare la compensa-
zione ’INVERNALE’ (C19=3) con St2=15 in modo che intervenga
solo nel caso di temperature esterne inferiori a 15°C. Per il calco-
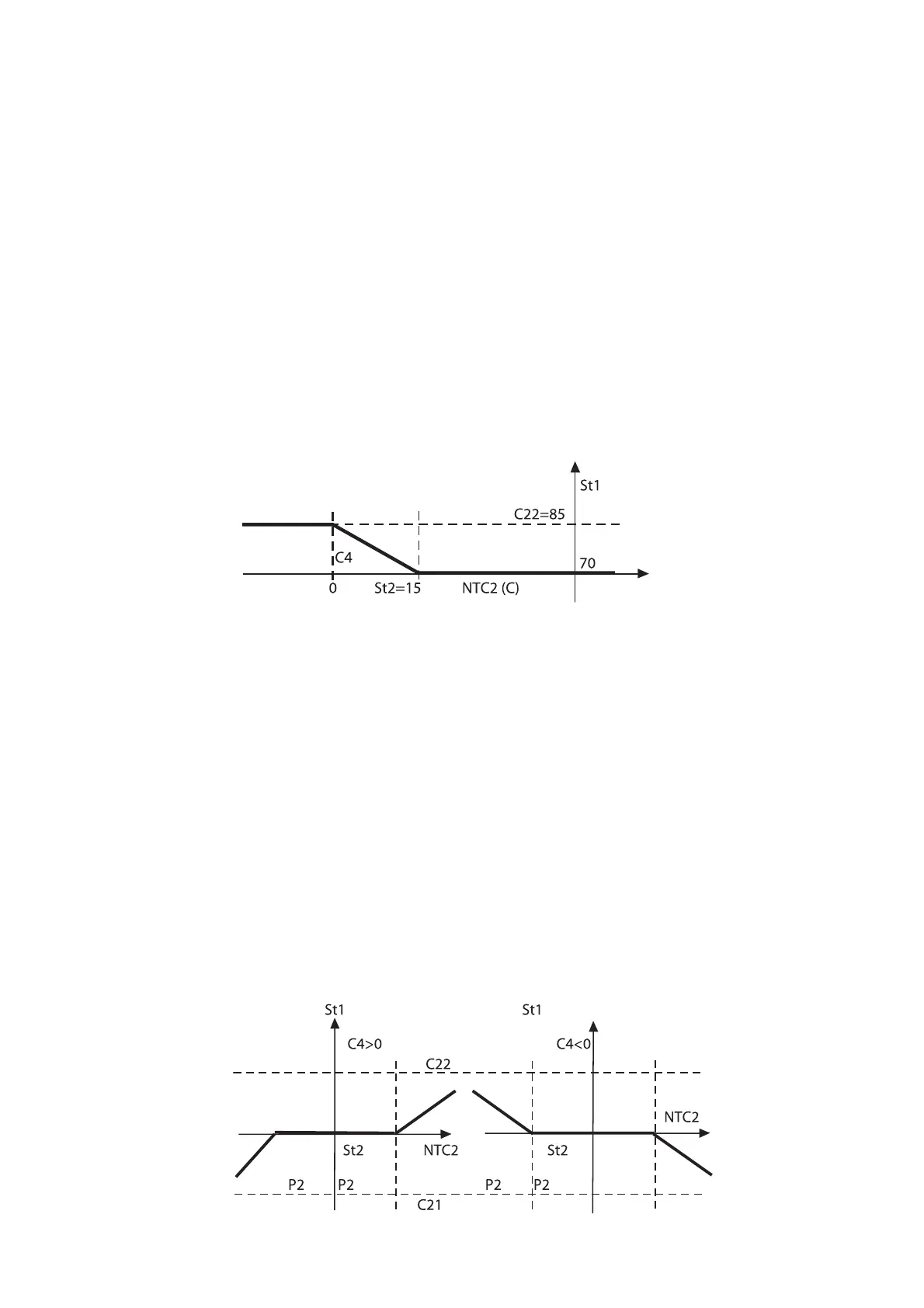
lo dell’autorità si consideri che a fronte di una variazione di NTC2
di -15°C (da +15 a 0°C) St1 deve variare di +15°C (da 70 a 85°C),
ne consegue che C4= -1.
Infine dovrà essere fissato il limite massimo del St1,
selezionando C22=85. Il grafico di figura 23 mostra come varia
St1 al diminuire della temperatura esterna NTC2.
Descrizione C19=4 – COMPENSAZIONE CONTINUA:
la compensazione di St1 è attiva per valori di NTC2 diversi da St2:
Con questo valore di C19 si può sfruttare il parametro P2 per
definire una zona neutra attorno a St2 in cui la compensazione
non è attiva, ovvero quando NTC2 assume valori compresi tra
St2-P2 ed St2+P2, viene esclusa la compensazione e St1 non
viene modificato:
se NTC2 è superiore a (St2+P2),
St1 effettivo = St1+ [NTC2-(St2+P2)]*C4
se NTC2 è compreso tra (St2-P2) e (St2+P2), St1effettivo=St1
se NTC2 è inferiore a (St2-P2),
St1effettivo = St1+ [NTC2-(St2-P2)]*C4
Nota: la compensazione ottenuta con C19=4 è l’azione combi-
nata della compensazione estiva e di quella invernale viste in
precedenza. Nei diagrammi seguenti è rappresentata la compen-
sazione continua per valori di C4 positivi e negativi. Tralasciando
l’effetto di P2, se C4 è positivo St1 aumenta quando NTC2>St2 e
diminuisce per NTC2<St2. Viceversa, se C4 è negativo St1 dimi-
nuisce per NTC2 > St2 e aumenta per NTC2 inferiori a St2.
Example no. 4
In order to optimize the efficiency of a domestic boiler, suppose
an operating temperature of 70°C (St1) with outdoor temperatu-
res above 15°C. When the outdoor temperature falls, the tempe-
rature of the boiler has to rise in a proportional way up to max.
85°C in response to external temperatures equal or below 0°C.
Solution: use an Infrared controller and locate the main sen-
sor NTC1 on the water circuit. Set Mode 2 (heating), set-point
St1=70 and differential P1=4. Use a second sensor (NTC2) to
be located outside and set winter offset (C19=3) and St2=15.
As for the authority, consider that for any variation of NTC2 of
-15°C (from +15 to 0°C), St1 must increase of +15°C (from 70 to
85°C). Therefor C4=-1. Finally set the max. St1 limit: C22=85. The
diagram below shows how St1 changes as the outdoor tempera-
ture measured by NTC2 falls.
C19=4, CONTINUOUS OFFSET
The offset of St1 takes place when the temperature measured
by NTC2 deviates from St2. When C19=4, you can enjoy the
benefits of P2 that allows you to create a neutral zone around
St2 in which offset does not occur (that is, when NTC2 detects
values ranging between St2-P2 and St2+P2). Therefore St1 will
not change.
If NTC2 rises above (St2+P2), then: actual
St1=St1+ [NTC2-(St2-P2)]*C4
If NTC2 ranges between (St2-P2) and (St2+P2), then: actual
St1=St1
If NTC2 falls below (St2-P2), then:
actual St1 = St1+ [NTC2-(St2-P2)]*C4
Important: the offset action obtained when C19=4 results from
the combination of the summer and winter offset.
The diagram below shows an example of continuous offset where
C4 is given both positive and negative values. If C4 is positive,
St1 increases when NTC2>St2 and decreases when NTC2<St2.
Viceversa, if C4 is negative, St1 decreases when NTC2>St2 and
increases when NTC2<St2.
Fig.24
Fig.24/a

 Loading...
Loading...