6
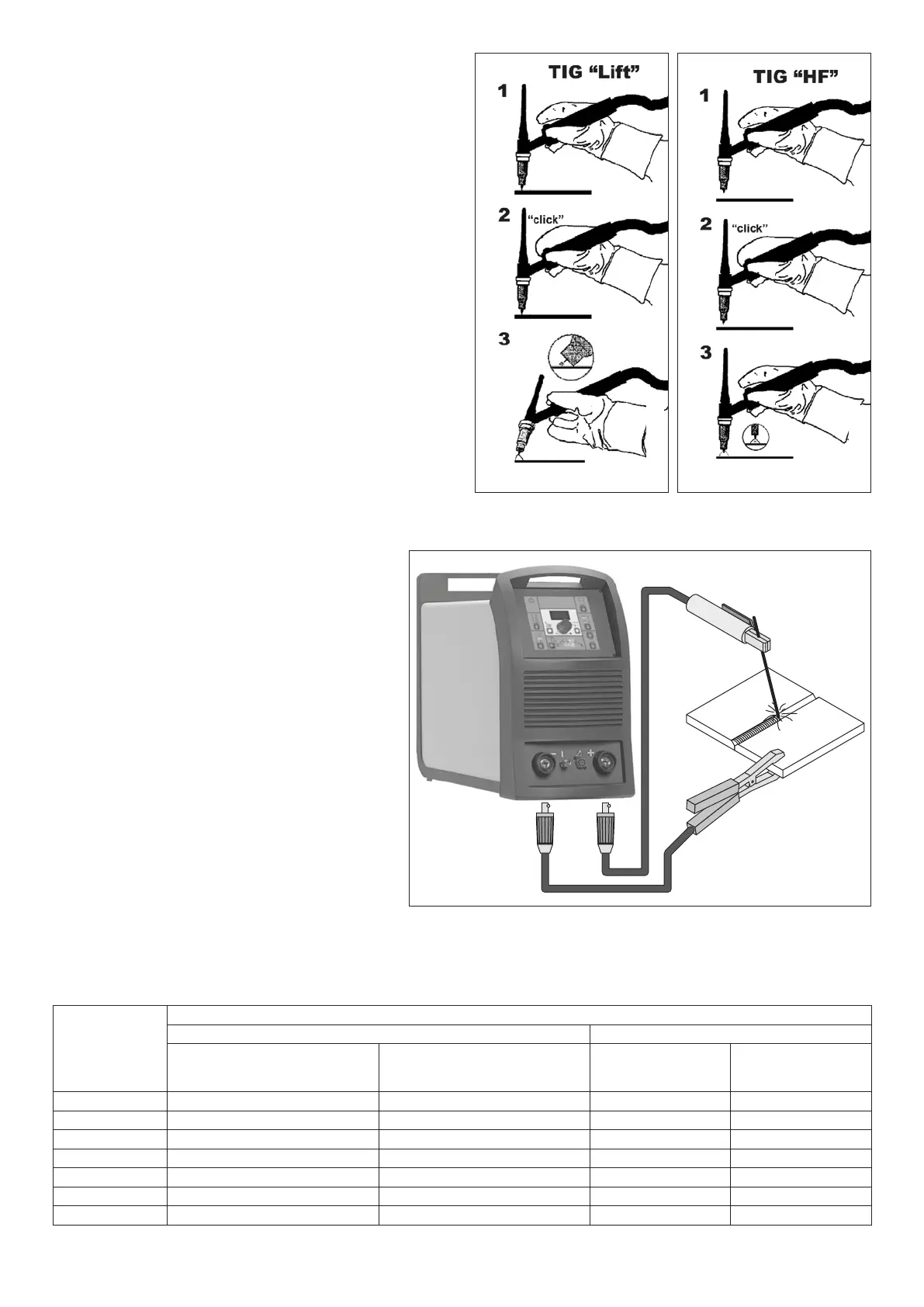
TIG WELDING WITH “Lift” TYPE STRIKING
4a) Open the gas cylinder and flow regulator.
5a) Put the electrode at the point at which welding is to begin,
put the TIG torch at an angle so that the edge of the gas
nozzle is not on top of the piece to be welded, keeping con-
tact between the point of the electrode and the piece to be
welded (Fig. E-1).
6a) Press the torch button.
7a) The “Lift” function strikes the arc when the TIG torch elec-
trode comes into contact with the workpiece and is then
removed (Fig. E-2)
8a) Carry out TIG welding (Fig. E-3).
To end welding:
•
Lift the torch slowly, at a certain point the welding current
decreases, and then stop.
•
The welding machine follows an automatic down slope
along with extinguishing of the arc.
9a) When finished welding remember to shut off the gas cylin-
der.
TIG WELDING WITH HIGH FREQUENCY STRIKING (HF)
4b) Open the gas cylinder and flow regulator.
5b) Put the electrode at the point at which welding is to begin,
put the TIG torch at an angle so that the edge of the gas
nozzle is not on top of the piece to be welded, keeping a
2-3 mm gap between the point of the electrode and the
piece to be welded (Fig. F-1).
6b) Press the torch button.
7b) The voltaic arc strikes even without contact between the
TIG torch electrode and the workpiece (Fig. F-2).
8b) To continue welding put the torch back in its normal posi-
tion (Fig. F-3).
IMPORTANT: The high frequency switches off auto-
matically after switching on.
PART TO BE WELDED
The part to be welded must always be connected to
ground in order to reduce electromagnetic emission.
Much attention must be afforded so that the ground
connection of the part to be welded does not increase
the risk of accident to the user or the risk of damage
to other electric equipment. When it is necessary to
connect the part to be welded to ground, you should
make a direct connection between the part and the
ground shaft. In those countries in which such a con-
nection is not allowed, connect the part to be welded
to ground using suitable capacitors, in compliance
with the national regulations.
WELDING PARAMETERS
Table 3 shows the currents to use with the respective
electrodes for TIG AC and DC welding. This input is
not absolute but is for your guidance only; read the
electrode manufacturers’ instructions for a specific
choice. The diameter of the electrode to use is direct-
ly proportional to the current being used for welding.
2000HA73
2000HA72
FIG. E FIG. F
FIG. G
2000H809
Table 3
Ø ELECTRODE
(mm)
ELECTRODE TYPE - Current adjustment field (A)
TIG DC TIG AC
Tungsten
Ce 1%
Grey
Tungsten
Rare ground 2%
Turchoise
Tungsten
Pure
Green
Tungsten
Rare ground 2%
Turchoise
1 10-50 10-50 - -
1,6 50-80 50-80 30-60 30-60
2,4 80-150 80-150 60-120 60-120
3,2 150-250 150-250 80-160 80-160
4 200-400 200-400 100-240 100-240
4,8 - - 200-300 200-300
6,4 - - 275-400 275-400
 Loading...
Loading...