0-5492 6-7 STICK (MMAW) Welding
A. Butt Welds
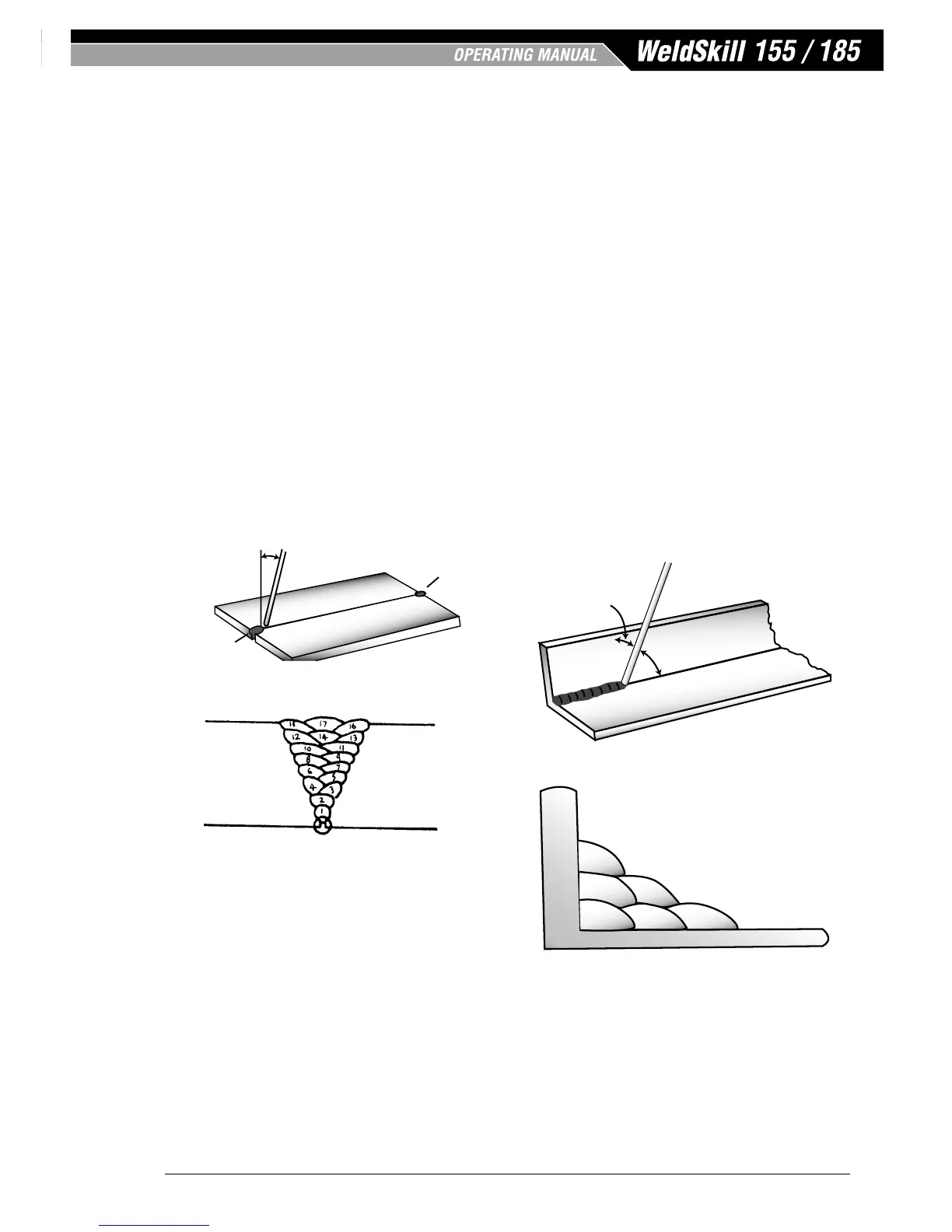
Set up two plates with their edges parallel, as shown in
Figure 6-12, allowing 1.6mm to 2.4mm gap between
them and tack weld at both ends. This is to prevent
contraction stresses from the cooling weld metal
pulling the plates out of alignment. Plates thicker
than 6.0mm should have their mating edges bevelled
to form a 70° to 90° included angle. This allows full
penetration of the weld metal to the root. Using a
3.2mm Ferrocraft 21 electrode at 100 amps, deposit
a run of weld metal on the bottom of the joint.
Do not weave the electrode, but maintain a steady
rate of travel along the joint sufficient to produce a
well-formed bead. At first you may notice a tendency
for undercut to form, but keeping the arc length short,
the angle of the electrode at about 20° from vertical,
and the rate of travel not too fast, will help eliminate
this. The electrode needs to be moved along fast
enough to prevent the slag pool from getting ahead
of the arc. To complete the joint in thin plate, turn the
job over, clean the slag out of the back and deposit
a similar weld.
Electrode
Tack Weld
Figure 6-12: Butt weld
Art # A-07698
Figure 6-13: Weld build up sequence
Heavy plate will require several runs to complete the
joint. After completing the first run, chip the slag out
and clean the weld with a wire brush. It is important
to do this to prevent slag being trapped by the second
run. Subsequent runs are then deposited using either
a weave technique or single beads laid down in the
sequence shown in Figure 6-13. The width of weave
should not be more than three times the core wire
diameter of the electrode. When the joint is completely
filled, the back is either machined, ground or gouged
out to remove slag which may be trapped in the root,
and to prepare a suitable joint for depositing the
backing run. If a backing bar is used, it is not usually
necessary to remove this, since it serves a similar
purpose to the backing run in securing proper fusion
at the root of the weld.
B. Fillet Welds
These are welds of approximately triangular cross-
section made by depositing metal in the corner of
two faces meeting at right angles. Refer to Figure 6-3.
A piece of angle iron is a suitable specimen with which
to begin, or two lengths of strip steel may be tacked
together at right angles. Using a 3.2mm Ferrocraft 21
electrode at 100 amps, position angle iron with one
leg horizontal and the other vertical. This is known
as a horizontal-vertical (HV) fillet. Strike the arc and
immediately bring the electrode to a position perpen-
dicular to the line of the fillet and about 45° from the
vertical. Some electrodes require to be sloped about
20° away from the perpendicular position to prevent
slag from running ahead of the weld. Refer to Figure
6-14. Do not attempt to build up much larger than
6.4mm width with a 3.2mm electrode, otherwise
the weld metal tends to sag towards the base, and
undercut forms on the vertical leg. Multi-runs can be
made as shown in Figure 6-15. Weaving in HV fillet
welds is undesirable.
 Loading...
Loading...











