Basic Principles 51
Cat. No. 01023094
Appendix B Basic Principles
Reverse Osmosis
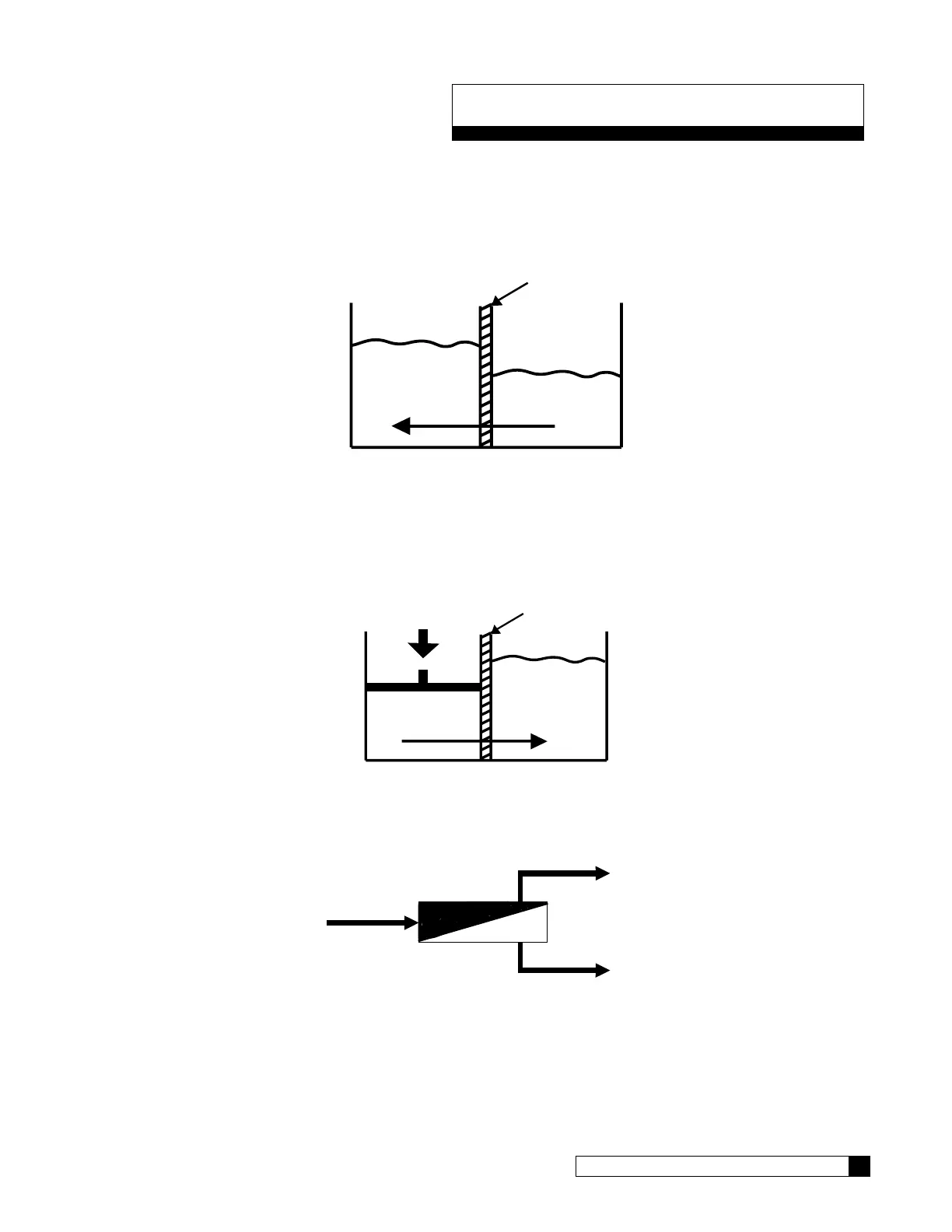
In order to understand reverse osmosis, we must first define osmosis. Osmosis is the passage of a liquid through a
semi-permeable membrane. A semi-permeable membrane is a membrane which allows one component of a solution to
pass through it and not the others. In osmosis, there is a tendency for a liquid to go from an area of less concentration to
an area of more concentration through a semi-permeable membrane. Figure 33 shows the osmotic process.
Membrane
Dilute
Solution
Passage of
Water
Concentrated
Solution
Figure 33. Osmotic process.
If pressure is applied to the concentrated solution, reverse osmosis will take place. The pressure causes a flow through
the semi-permeable membrane into the dilute solution. The semi-permeable membrane acts as a barrier to ions and does
not allow them to pass through into the dilute solution. When applied to water, this means that the product water has a
reduced total dissolved solids content as a result of the passage of water molecules through the membrane while the
mineral ions are rejected. See Figure 34.
Membrane
Dilute
Solution
Passage of
Water
Concentrated
Solution
Pressure
Figure 34. Effect of pressure on reverse osmosis.
Rejection and Recovery
Feed water entering the system is split into two streams, a product stream and a concentrate stream. See Figure 35.
Feed
Product
Concentrate
Figure 35. Feed water product stream and concentrate stream.
During the process of reverse osmosis, some of the water has its dissolved solids content reduced by approximately 99%.
This high quality product water is sent to service.
The rest of the feed water contains the dissolved solids removed from the product water, in addition to the dissolved solids
already present in the feed water. This concentrate water is sent to drain.
The amount of total dissolved solids rejected by the system is expressed as a percentage. A 90% rejection means that
90% of the dissolved solids have been removed from the feed water by the system. To calculate the percent rejection, use
the following equation:
 Loading...
Loading...