Quick reference guide | Atlan SW 2.0n 37
Principles of operation
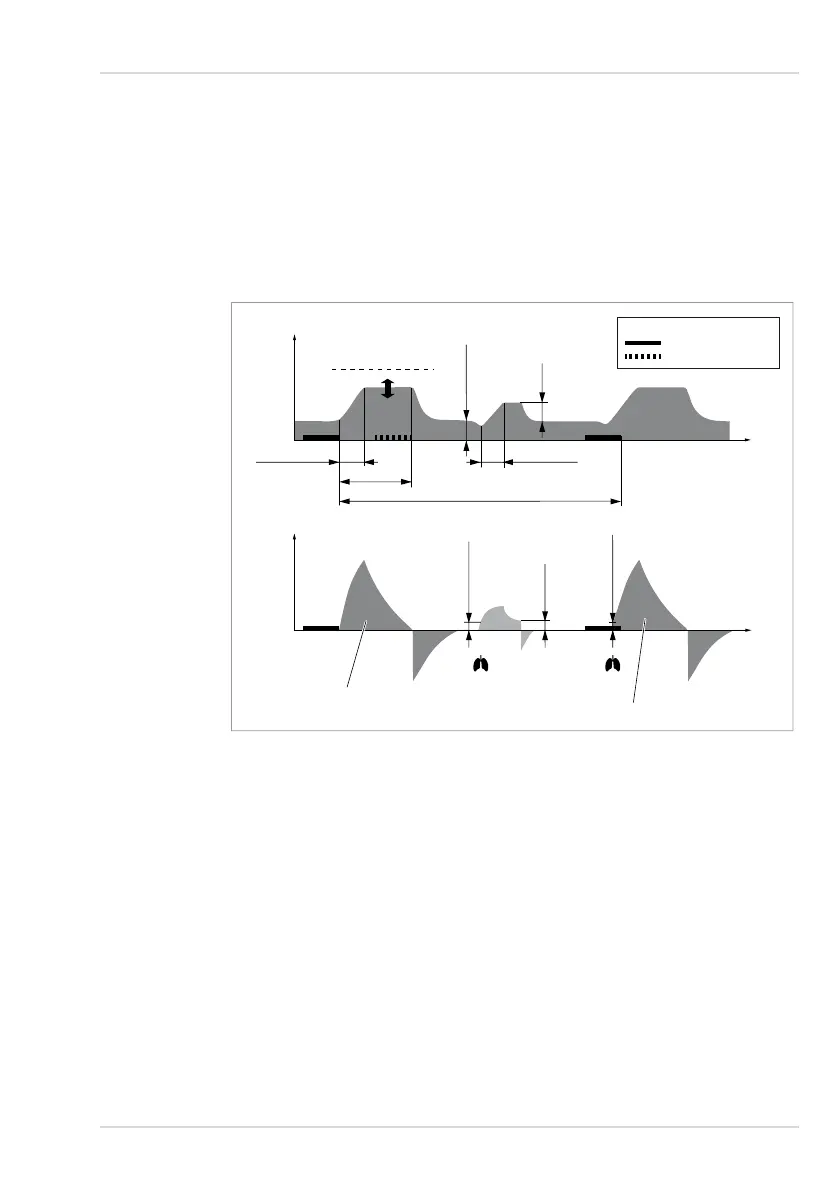
In VC - SIMV, the patient can breathe spontaneously at any time, while the number of
mandatory breaths is predefined. When synchronization is switched on, the breaths are
adapted to the spontaneous breathing of the patient. If inspiratory effort by the patient is
detected during the inspiratory trigger window, a patient-triggered breath will be initiated.
9.1.4.5 VC - SIMV / PS
This mode is similar to VC - SIMV, except that the patient's spontaneous breathing at the
PEEP level during the expiratory phase is pressure-supported with ∆Psupp when outside
the trigger window.
9.1.4.6 VC - AF
For volume-controlled mandatory breaths with AutoFlow, the set tidal volume VT is applied
with the lowest required pressure. The pressure patterns and flow patterns of the
mechanical inspiratory breaths correspond to those of pressure-controlled ventilation.
Due to the patient's inspiratory effort or compliance changes in the lungs, the tidal volume in
an individual breath may deviate from the set tidal volume VT. However, averaged over time
a tidal volume corresponding to the set volume VT is applied.
If no mechanical ventilation has previously taken place, a volume-controlled test breath with
constant inspiratory flow is performed first when starting a ventilation mode with AutoFlow in
order to estimate the lung parameters. The inspiratory pressure required at the start is
determined from this test breath. Each additional breath-related readjustment of the
inspiratory pressure is limited to ±3 hPa (cmH
2O). The pressure difference (inspiratory
pressure - PEEP) is at least 5 hPa (cmH
2O) and the upper inspiratory pressure limit is set by
Pmax. If the set value for VT is reduced, the inspiratory pressure will be reduced by a
greater amount if necessary.
36290
7ULJJHUZLQGRZ
LQVS
7LPH
7LPH
0DFKLQHWULJJHUHGEUHDWK
3DWLHQWWULJJHUHGEUHDWK
H[S
Flow
Paw
Pmax
PEEP
Ti
1/RR
∆Psupp
Insp term
Trigger
SlopeSlope
Trigger
 Loading...
Loading...