48
1. DESCRIZIONE DEI COMPONENTI
GBGB
1. INTRODUCTION TO THE PRODUCT
1.3 Air conditioner composition
Air conditioners are “Split System” type with air to air heat exchange
They are composed of two separate units:
- “indoor unit” to be placed inside the room which has ti be air conditioned
- “outdoor unit” to be placed outside the room which has to be air
conditioned
All functions of the air conditioner are activated by an infrared remote
control
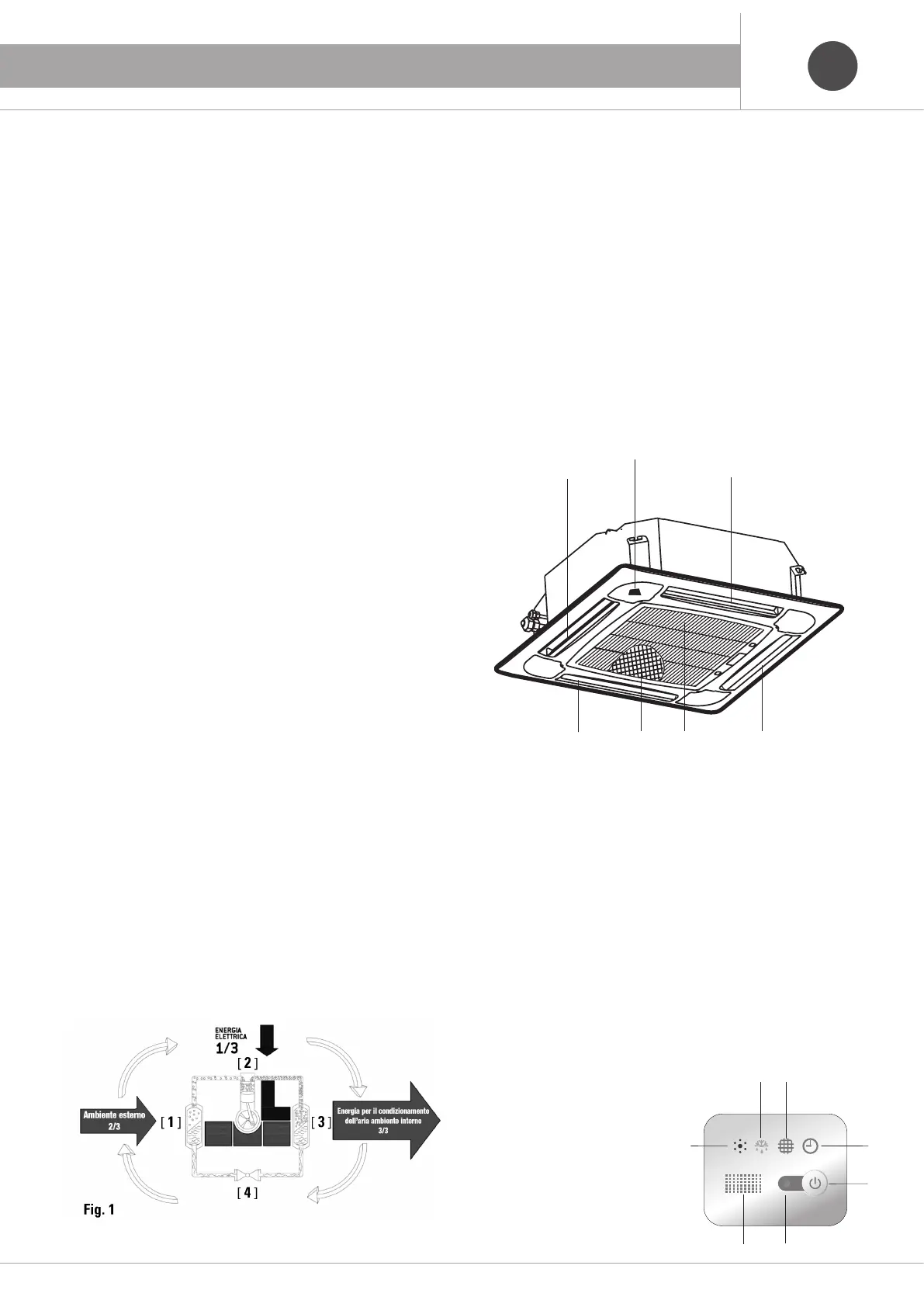
1.4 Indoor Unit
Air inlet grill
Air outlet grill
Horizontal deflector, air flow direction is automatic (Swing)
Air filter (inside the air inlet grill)
Control panel
1.5 Buttons and lights of the indoor unit
1 Operation indicator (red)
Lights up when the unit is in operation.
It is always off if the unit is in SLEEP mode.
2 Emergency button
To reset the filter cleaning indicator. To turn off the unit
Pressing for 5 sec. when the unit is turned off it will turn
on cooling mode.
3 Timer indicator (green). Turned on if the timer is active,
otherwise off.
4 Filter cleaning indicator (yellow)
5 Defrost indicator (green)
It lights up during defrosting, it lights off when defrost is completed
6 Buzzer Sounds when the unit receives the signal by remote control
7 Infrared signal receiver
5
4
6
2
3
7
SET TEMP
ROOM
TEMP
C
AUTO
NO
.
TIMER ON
TIMER OFF
SET TIMER
A
ON/OFF
MODE FAN
SLEEP
SUPER
SMART
IFEELDIMMER
TIMER ONTIMER OFF CLOCK
ON
OFF
SWING
SWING
ON
OFF
MODE
SMART
QUIET
DIMMER
ECONOMY
FEEL
SUPER
FAN SPEED
CLOCK
TIMER ON
TIMER OFF
SLEEP
TEMP.
TEMP.
确定
1.1 Introduction to conditioning
Air conditioner function is to create perfect temperature and humidity
conditions in the rooms they are installed, optimal conditions are able to
satisfy human exigencies, in one word “comfort”.
Working principle is to use refrigerant gas status changes (liquid/vapour)
which is included in the indoor refrigeration circuit, to subtract heat from
one room and move it to another one.
1.2 Refrigeration circuit
RefrigAAeration circuit can be exemplified as follow (Fig.1)
1) Evaporation
Room air is pushed from a fan through a heat exchanger called evaporator
(indoor unit in Cooling mode)
Refrigerant gas, at low pressure and temperature, evaporate by absorb-
ing heat from the air which is consequently cooled (and dehumidified)
2) Compression
Refrigerant in vapour form goes through a compressor. Compressor
causes an increased refrigerant pressure which becomes very hot
3) Condensation
Room air is pushed from a fan through a second heat exchanger called
condenser (indoor unit in Heating mode). Refrigerant gas, at high pressure
and temperature, condensate giving heat to the air which is consequently
heated.
4) Expansion
Refrigerant in liquid form passes through a throttling way called expan-
sion valve. Expansion valve causes a refrigerant pressure lowering which
becomes very cool.
Once again at point 1 and the cycle repeats.
Air conditioners allow to use the energy of the outdoor air to heat the indoor
room and vice versa
This allows to use about:
2/3 renewable and free energy of the air
1/3 electric energy to make the air conditioner work
If a photovoltaic system is installed you will air-condition the house at cost
and environmental impact equal to zero.
 Loading...
Loading...










