ESAB CUTMASTER 120
INTRODUCTION Manual 0-5380
2T-2
F. Torch Ratings
Manual Torch Ratings
Ambient
Temperature
104° F
40° C
Duty Cycle
100% @ 100 Amps @ 400 scfh
Maximum Current
120 Amps
Voltage (V
peak
)
500V
Arc Striking Voltage
7kV
Mechanized Torch Ratings
Ambient
Temperature
104° F
40° C
Duty Cycle
100% @ 100 Amps @ 400 scfh
Maximum Current
120 Amps
Voltage (V
peak
)
500V
Arc Striking Voltage
7kV
G. Gas Requirements
Manual and Mechanized Torch Gas
Specifications
Gas (Plasma and Secondary)
Compressed Air
Operating Pressure
Refer to NOTE
60-95psi
4.1-6.5bar
Maximum Input Pressure
125psi/8.6bar
Gas Flow (Cutting and
Gouging)
300 - 500 scfh
142 - 235 lpm
!
WARNING
This torch is not to be used with oxygen
(O
2
).
NOTE!
Operating pressure varies with torch
model, operating amperage, and torch
leads length. Refer to gas pressure settings
charts for each model.
H. Direct Contact Hazard
Forstandofftiptherecommendedstandoffis3/16
inches / 4.7 mm.
2T.04 Options And Accessories
Foroptionsandaccessories,seesection6.
2T.05 Introduction to Plasma
A. Plasma Gas Flow
Plasma is a gas which has been heated to an
extremely high temperature and ionized so that it
becomes electrically conductive. The plasma arc
cutting and gouging processes use this plasma
to transfer an electrical arc to the workpiece. The
metal to be cut or removed is melted by the heat of
the arc and then blown away.
While the goal of plasma arc cutting is separation of
the material, plasma arc gouging is used to remove
metals to a controlled depth and width.
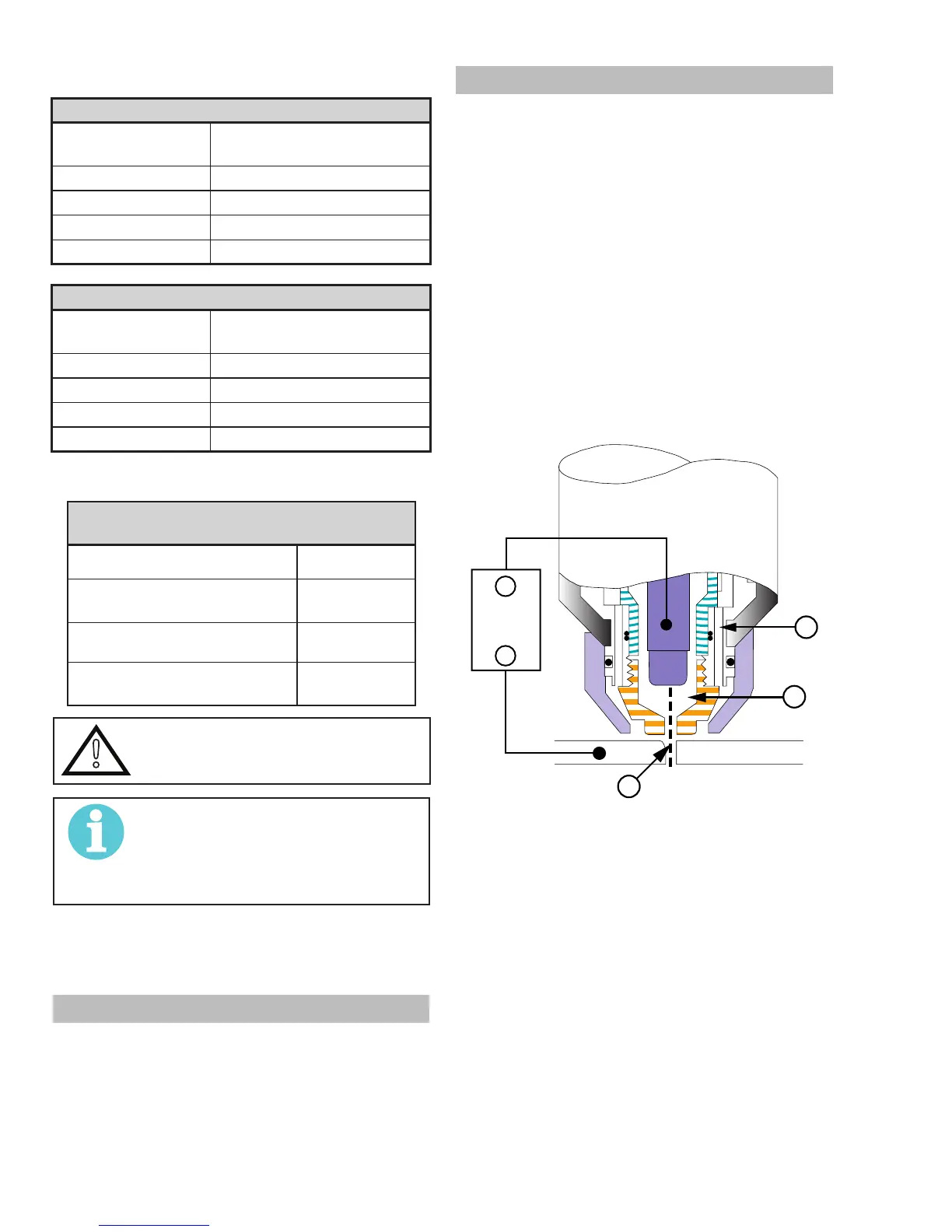
In a Plasma Cutting Torch a cool gas enters Zone
B, where a pilot arc between the electrode and the
torch tip heats and ionizes the gas. The main cut-
ting arc then transfers to the workpiece through the
column of plasma gas in Zone C.
A-00002
Workpiece
Power
Supply
+
_
C
B
A
Typical Torch Head Detail
By forcing the plasma gas and electric arc through
a small orifice, the torch delivers a high concentra-
tion of heat to a small area. The stiff, constricted
plasma arc is shown in Zone C. Direct current (DC)
straight polarity is used for plasma cutting, as shown
in the illustration.
Zone A channels a secondary gas that cools the
torch. This gas also assists the high velocity plasma
gas in blowing the molten metal out of the cut al-
lowing for a fast, slag - free cut.
 Loading...
Loading...