Page 30 of 35
11.1 DETECTOR
All conventional detectors (smoke, heat and
multicriterion) have the same base. These
detectors have a double led indicator at high
visibility (360°) and a low height.
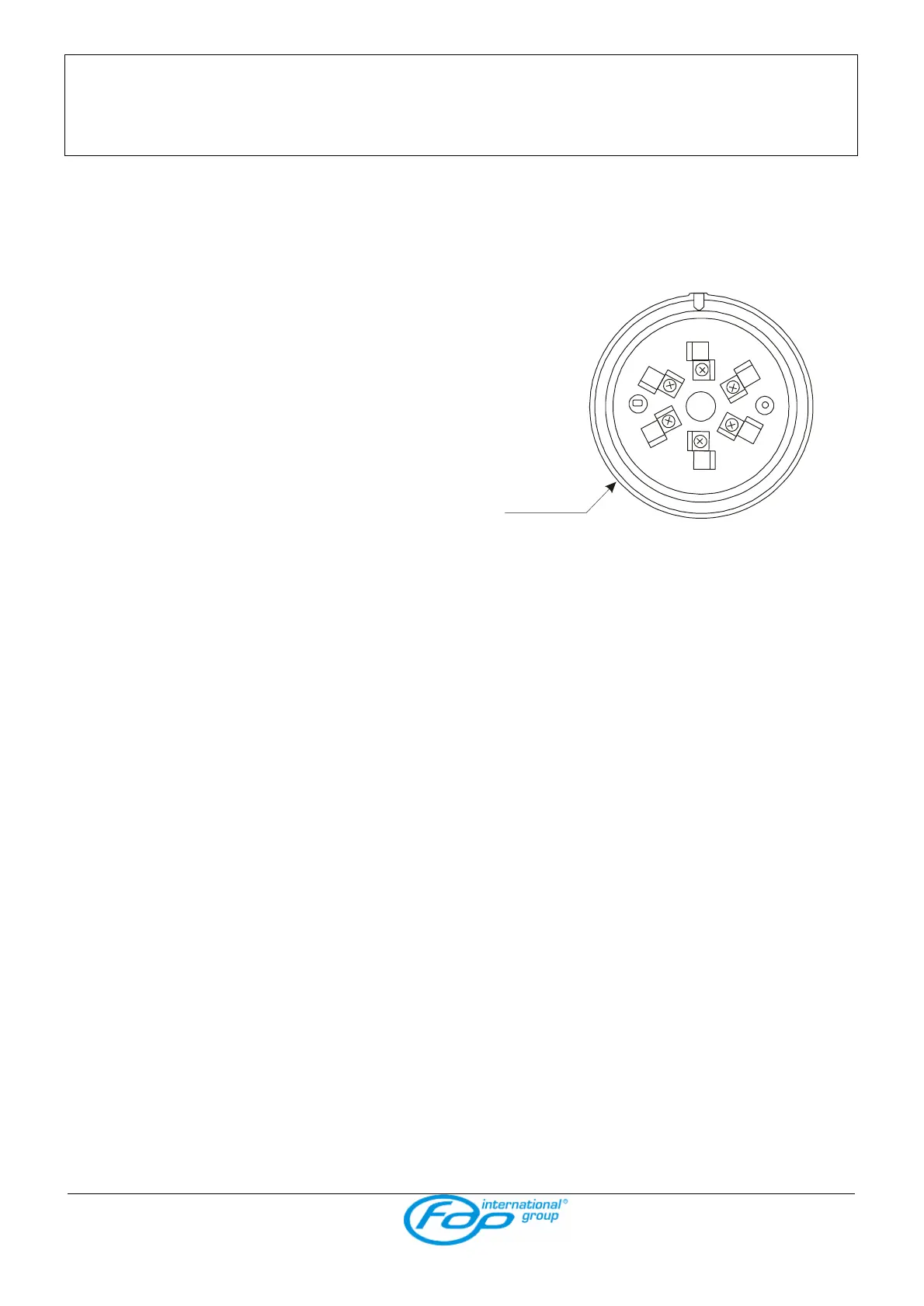
CLIPS DESCRIPTION OF THE BASE
Reed
1 / + + input line.
2 / R not connected.
3 / R not connected.
4 / SCR negative output for outside door repeater.
5 / - - line.
6 / + + output line.
11.1.1 Smoke detector
The smoke detector reacts to the presence of elements caused by the combustion (visible
smoke). The working principle is based on the light dispersion technique (Tyndall effect).
11.1.2 Heat detector
The heat detector has been designed to activate itself when the heat exceeds a previously
fixed level. It is available a heat detector with rate-of rise function; this detector has been
designed to activate itself the speed with which this increment is produced is high, even though
the scheduled level has not been exceeded.
11.1.3 Multicriterion detector
The smoke/heat multicriterion detector reacts to the presence of elements caused by the
combustion (visible smoke) in regards to the smoke detection. The working principle is based
on the light dispersion technique (Tyndall effect). For the detection of the heat, it has been
designed to activate itself when the heat exceeds a certain previously fixed level or when the
speed with which this increment is produced is high, even though the programmed level has
not been exceeded.
PART 11
POINTS DESCRIPTION AND UTILIZATION
 Loading...
Loading...