6
8. Working Principles
The working principle of the electromagnetic unit is based on the Faraday law of
electromagnetic induction. When the conductor moves in the magnetic field, it will
generate induced EMF on both sides of the conductor in the orthogonal direction of
the magnetic field direction and the motion direction. The EMF is directly proportional
to the motion speed of the conductor and the magnetic induction intensity.
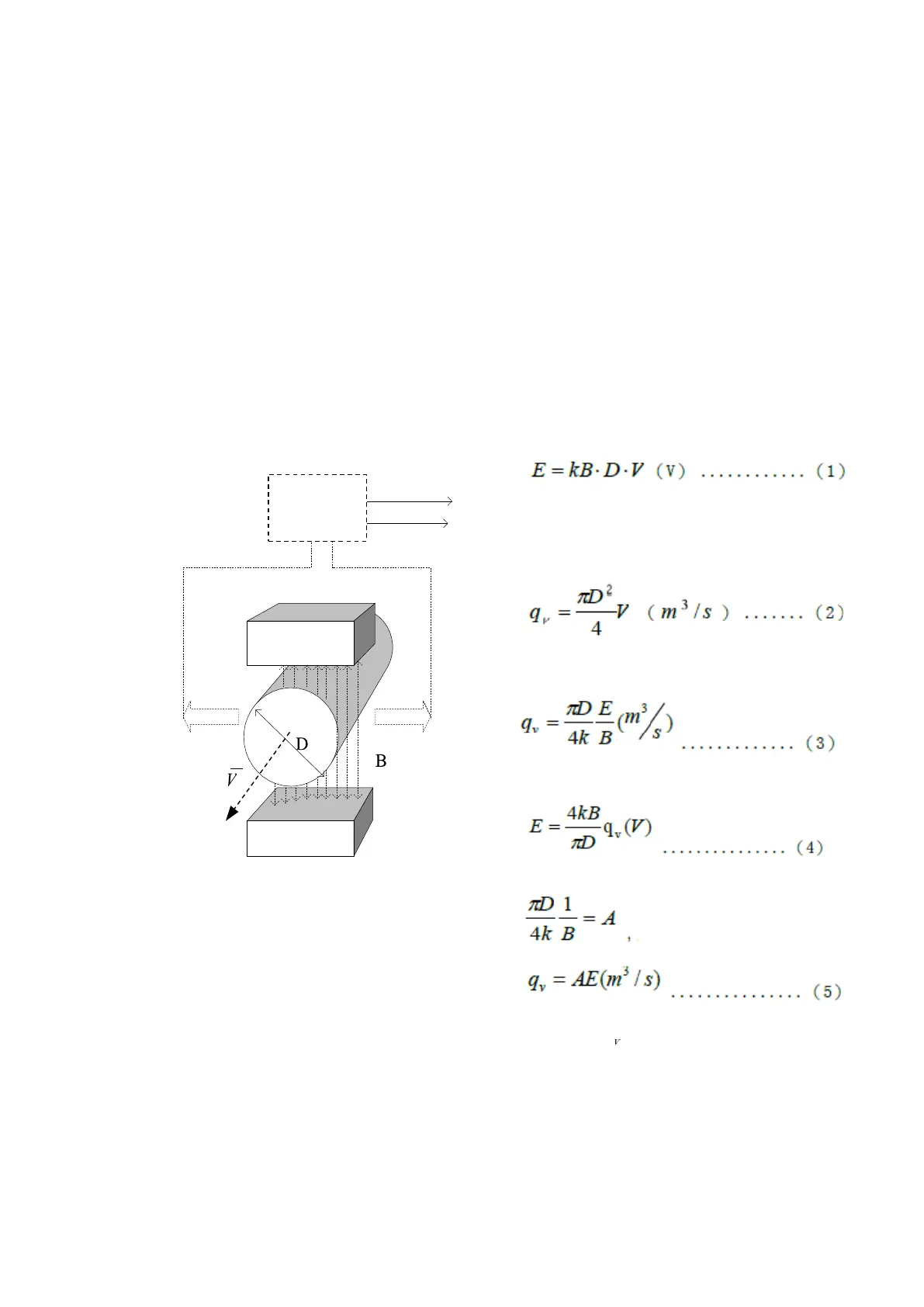
As shown in <Figure 1>, the conducting fluidic passes through the insulating tube with
the internal diameter of D(m) at the average flowing speed V(m/s) that is equipped
with a pair of measuring electrodes. Moreover, the tube is in a magnetic field with
uniform magnetic induction intensity of B (T). In this case, the electrodes will induce
the EMF (E) at the orthogonal direction of the magnetic field and the flowing direction.
According to the law of electromagnetic induction, E can be written as Equation (1):
Wherein, k is the proportional coefficient.
The volume flow can be written as
From Equation (1) and (2), we can get:
Thus, EMF can be represented as
:
When B is a constant in Equation(3)
Equation(3) can be modified as:
It can be concluded that the flow qv is directly
proportional to the EMF E.
 Loading...
Loading...