Architecture and strategies Virtualization
U41855-J-Z125-3-76 63
Dokuschablonen 19x24 Version 7.4de für FrameMaker V7.x vom 09.02.2010 © cognitas GmbH 2001-2010
19. March 2018 Stand 18:25.47 Pfad: P:\FTS-BS\Server\SE-Server\SE-Doku\1303912_BuV_062\BuV_e\buv.k02
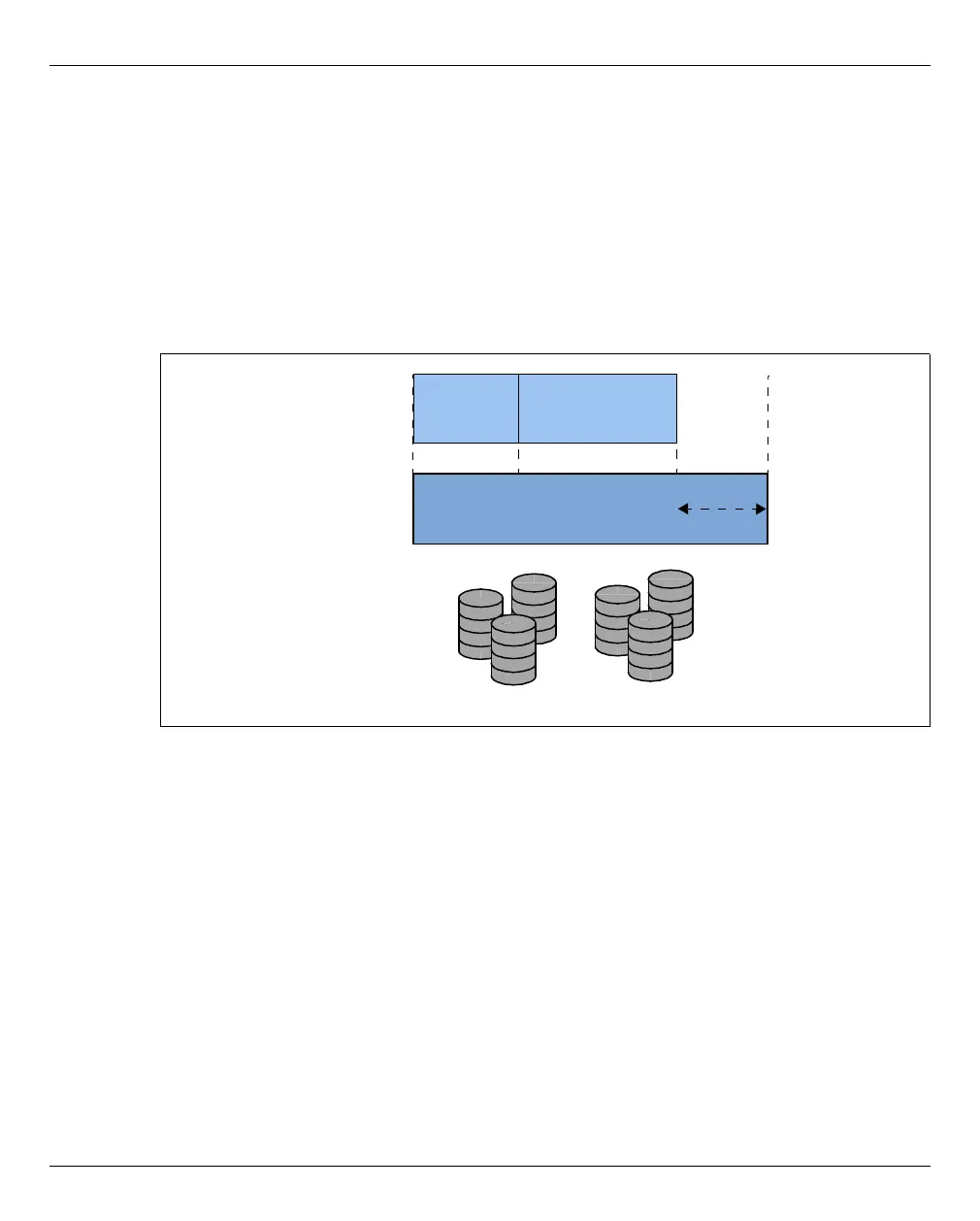
Disk pools and virtual disks
The physical disks of the connected disk storage peripherals can be assigned to so-called
disk pools and form a linear storage space. SAS-RAID systems (e.g. ETERNUS JX40) and
external FC disks are supported.
A virtual disk is a section of a disk pool. The virtual disk is seen as a uniform and contiguous
disk by the XenVM which uses it (in figure 9, for example, as device xvda; the
corresponding device in a fully virtualized system would be hda), see also the figure below
with the abstraction levels.
Figure 11: Virtual disks - abstraction level of disk usage
External FC disks can be connected to more than one host, which permits switching, i.e.
alternating use of these disks.
For information on tasks in the XenVM device management see section “Managing XenVM
devices on Server Unit x86” on page 188.
Installation sources
ISO images of CDs/DVDs and installation configuration files which can be used to automate
installation are referred to as installation sources. The ISO images provided as installation
sources are employed primarily for system installation, but can, for instance, also be used
to install applications or to provide data for the guest systems.
The installation sources are managed in a local library with 80 GB of storage space.
disk02disk01
Free
poolx
Disk Pool
Physical Disks
Virtual Disks
 Loading...
Loading...











