30
CHAPTER1 Basic Functions
1.17.2 Referring to C/C++ Variables
C/C++ variables can be specified using the same descriptions as in the source program
written in C/C++.
■ Specifying C/C++ Variables
C/C++ variables can be specified using the same descriptions as in the source program. The address of C/
C++ variables should be preceded by the ampersand symbol "&". Some examples are shown in the Table
1.17-1 .
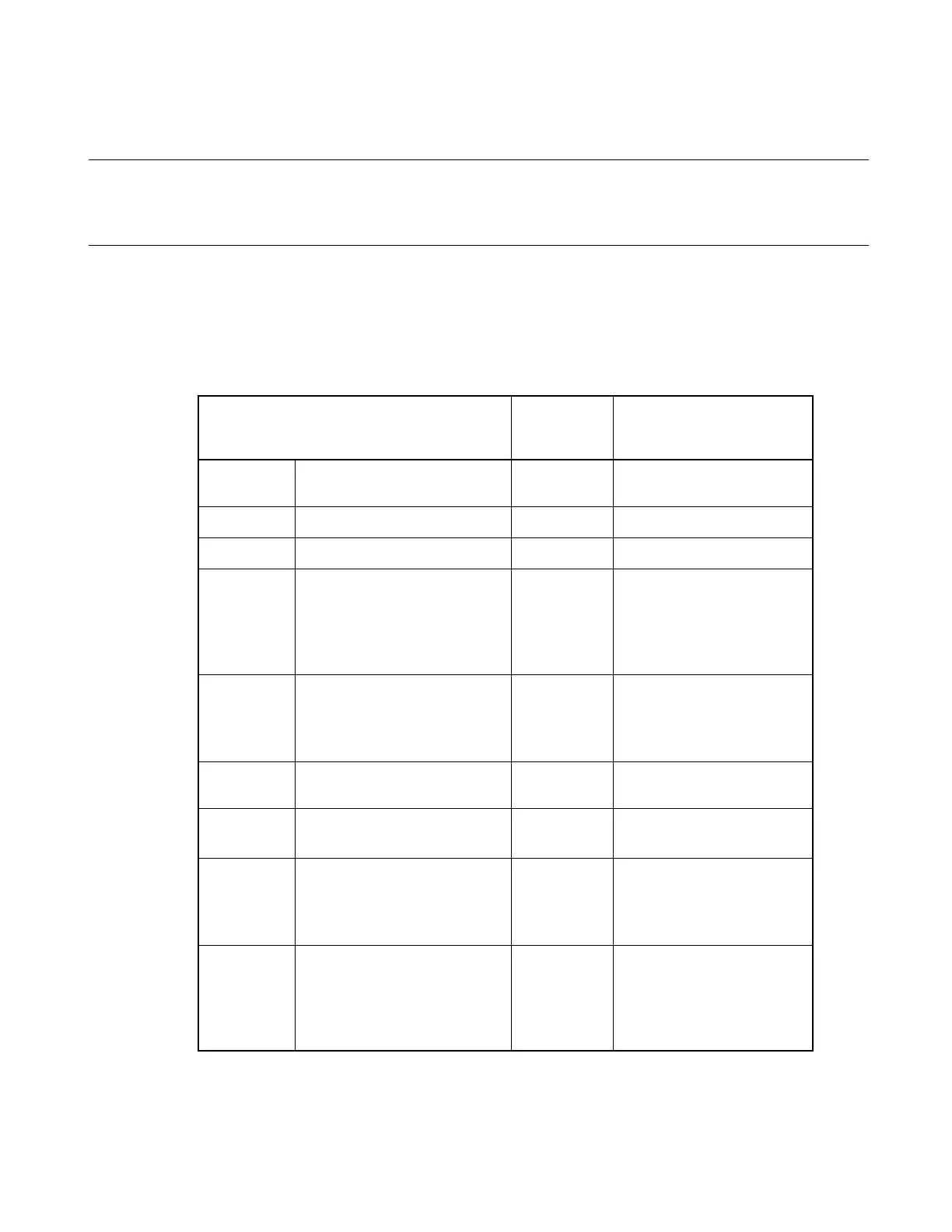
Table 1.17-1 Examples of Specifying Variables
Example of Variables
Example of
Specifying
Variables
Semantics
Regular
Variable
int data;
data Value of data
Pointer
char *p;
*p Value pointed to by p
Array
char a[5];
a[1] Value of second element of a
Structure
struct stag{
char c;
int ;
struct stag st;
struct stag *stp;
st, c
stp->c
Value of member c of st
Value of member c of the
structure to which stp points
Union
union utag{
char c;
int i;
}uni;
uni.i Value of member i of uni
Address of
variable
int data;
&data Address of data
Reference
type
inti i;
int &ri = i;
ri Same as i
Class
class X{
static int i;
}cls;
int X::i;
cls.i
X::i
Value of member i of class X
Same as cls.i
Member
pointer
class
class X{
short cs;
}clo;
short X::* ps=&X::cs;
X*clp=&clo;
clo.*ps
clp->*ps
Same as clo.cs
Same as clp->cs
 Loading...
Loading...