44
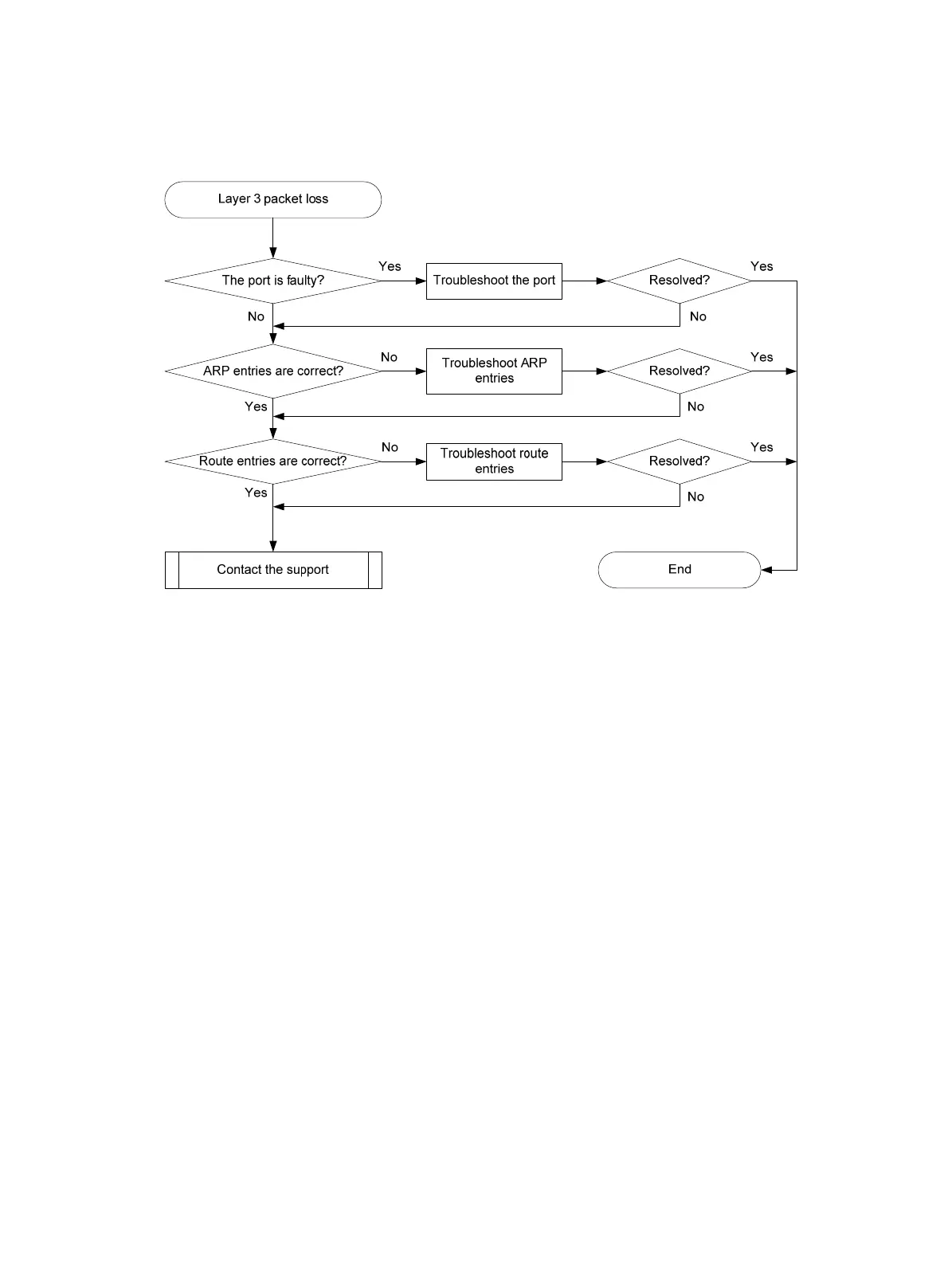
Troubleshooting flowchart
Figure 21 Troubleshooting Layer 3 forwarding failure
Solution
To resolve the issue:
1. Verify that the port is not faulty (due to hardware or configuration issues).
If the port is faulty, follow the solution in "Layer 2 forwarding failure"
to troubleshoot the issue.
2. Verify that the ARP entry for the gateway is correct:
a. Execute the display arp command to verify that the ARP entry for the gateway is correct.
If the switch has not learned the APR entry, execute the arp static command to
configure a static ARP entry. If an incorrect ARP entry exists, execute the debugging arp
packet command to locate the issue.
b. Execute the display mac-address command to verify that the output interfaces in the
MAC address entries and ARP entry are the same.
If the output interfaces are not the same, execute the reset arp command to clear the
ARP entries. Then the switch can learn ARP entries again.
3. Verify that route entries are correct:
a. Execute the display ip routing-table command to verify that route entries are
correct.
If incorrect route entries exist, troubleshoot the protocol that learns the route entries.
b. Execute the display fib command to verify that the output interfaces in the FIB entries
and route entries are the same.
If the output interfaces are not the same, execute the reset command to clear the route
entries. Then the switch can learn route entries again.
4. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.

 Loading...
Loading...