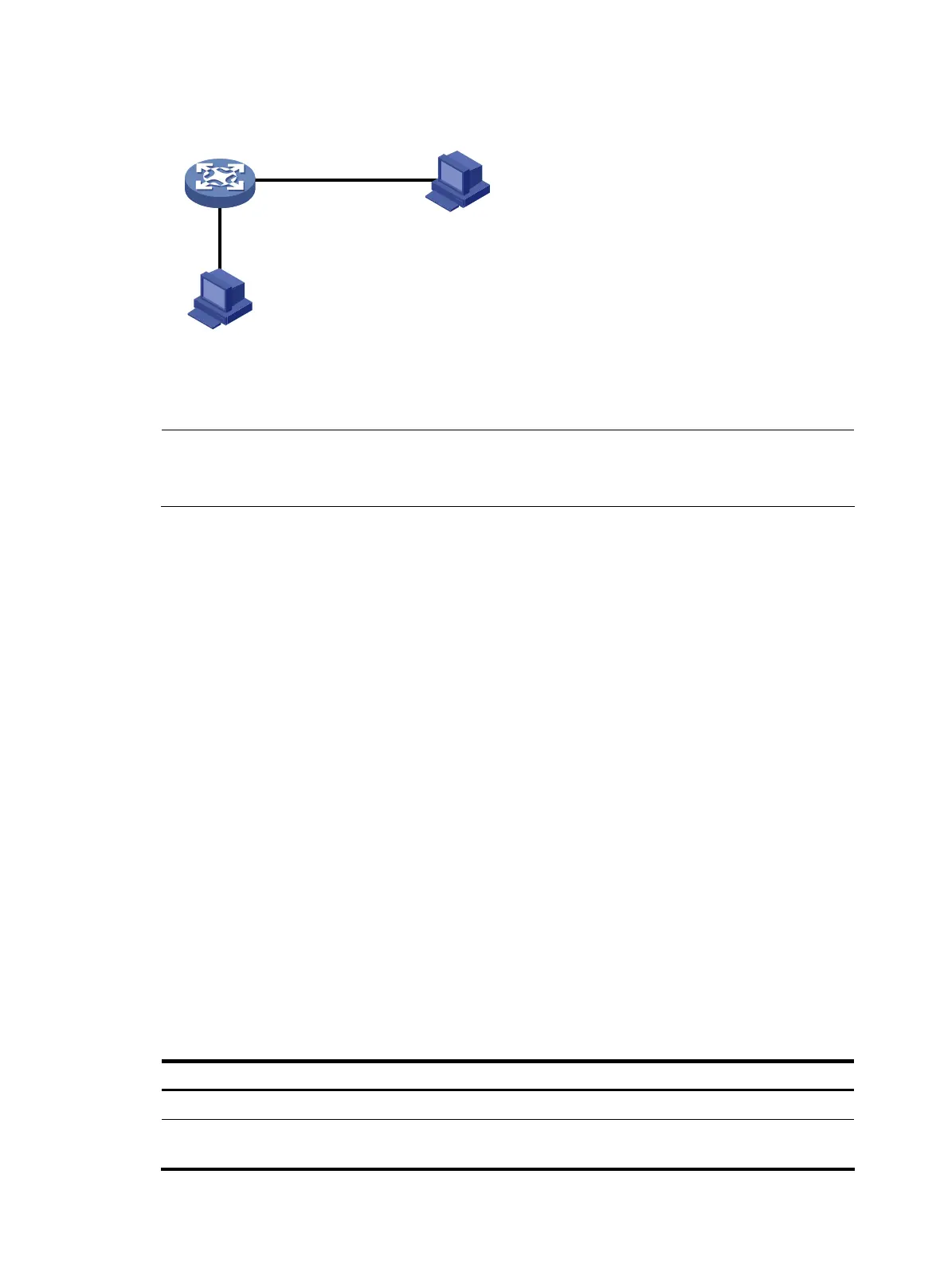
Figure 36 Network diagram for SNMP logging
Terminal
Agent
NMS
Console
1.1.1.2/24
1.1.1.1/24
Configuration procedure
NOTE:
This example assumes that you have configured all required SNMP settings for the NMS and the agent
(“SNMPv1/SNMPv2c configuration example” and “SNMPv3 configuration example”).
# Enable logging display on the terminal. (This function is enabled by default. Skip this step if you are
using the default.)
<Sysname> terminal monitor
<Sysname> terminal logging
# Enable the information center to output the system information with the severity level equal to or higher
than informational to the console port.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] info-center source snmp channel console log level informational
# Enable logging SNMP GET and SET operations.
[Sysname] snmp-agent log get-operation
[Sysname] snmp-agent log set-operation
# Verify the configuration.
• Use the NMS to get a MIB variable from the agent. The following is a sample log message
displayed on the configuration terminal:
%Jan 1 02:49:40:566 2006 Sysname SNMP/6/GET:
seqNO = <10> srcIP = <1.1.1.2> op = <get> node = <sysName(1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0)> value=<>
• Use the NMS to set a MIB variable on the agent. The following is a sample log message displayed
on the configuration terminal:
%Jan 1 02:59:42:576 2006 Sysname SNMP/6/SET:
seqNO = <11> srcIP = <1.1.1.2> op = <set> errorIndex = <0> errorStatus =<noError> node
= <sysName(1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0)> value = <Sysname>
Table 2 Description of SNMP log message fields
Field Description
Jan 1 02:49:40:566 2006 Time when the SNMP log was generated.
seqNO
Serial number automatically assigned to the SNMP log,
starting from 0.
93
 Loading...
Loading...