Selecting a data migration method
The data migration method that you select must provide the best compromise between efciency and
impact on the system users. The selected method provides a simple but robust method that minimizes
user impact.
Most methods of data migration affect the everyday operation of a computer system. When data is
moved, the data must be in a certain state, and typically requires that updates or changes cease while the
movement occurs. Depending on the amount of data that you are moving and your migration method,
data might be unavailable for an extended period, perhaps several hours. The following factors might
contribute to the migration time:
• Creating new logical volumes or le systems
• Modifying conguration les
• Receiving integrity checks
Consider the following items to determine the best method for your data migration:
• Management software provides simple robust methods that you can use during production without
disturbing users.
• The AIX logical volume manager (LVM) provides methods that you can use at any time without
disrupting user access to the data. You might notice a small performance degradation, but this is
preferable to shutting down databases or requiring users to log off the system.
Notes:
– AIX and HP-UX 11.xx ship with logical volume management (LVM) software as part of the base
operating system. LVM provides complete control over all disks and le systems that exist on an AIX
system. HP-UX has similar volume management software.
– Sun Microsystems has a basic volume management product that is called Solstice, which is available
for the Solaris systems.
– Linux systems also use the LVM.
• Methods that use backup and restore procedures have the most impact on the system usage. These
procedures require that databases and le systems are in quiescent states to ensure a valid snapshot of
the data.
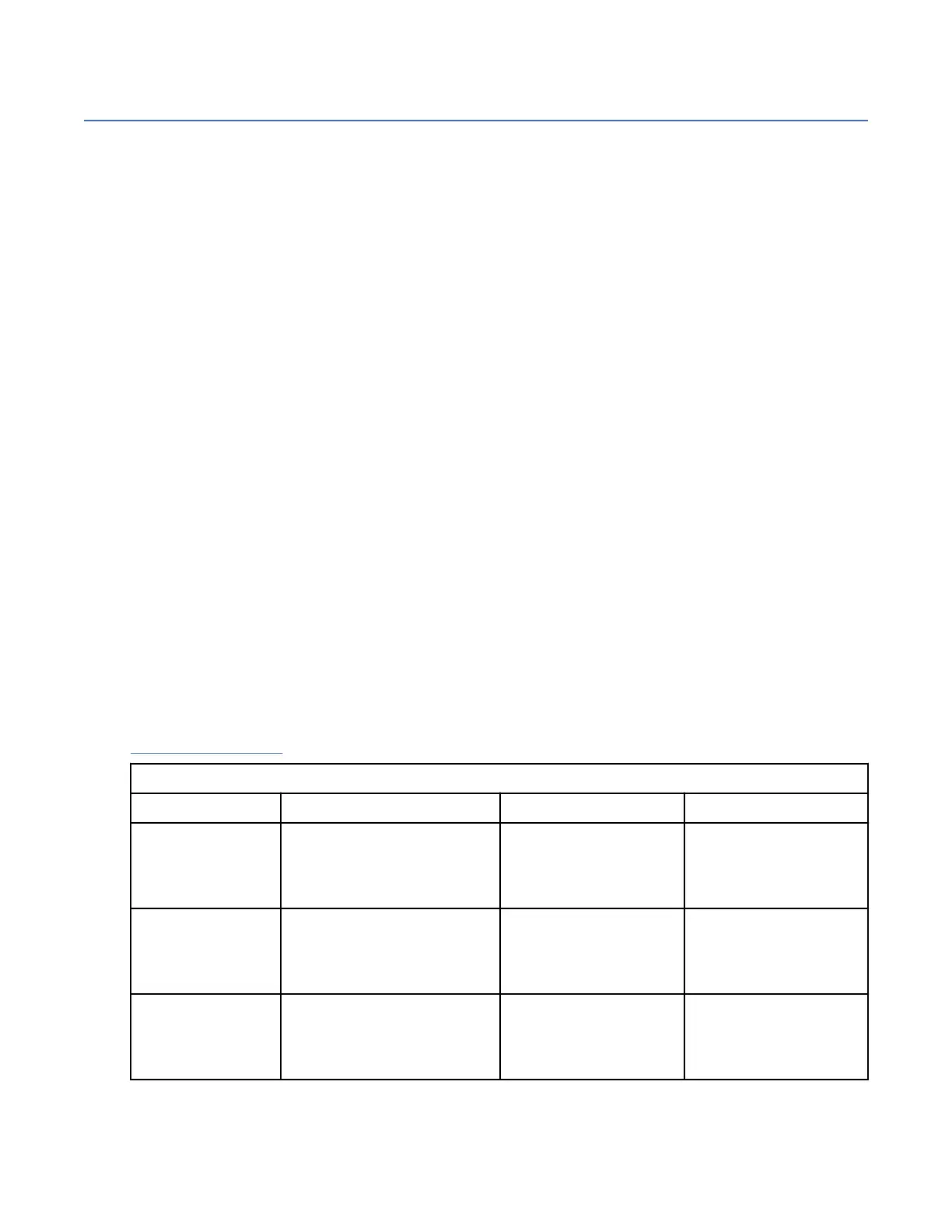
Table 60 on page 112 compares data migration options and lists advantages and disadvantages of each.
Table 60. Comparison of data migration options
Type Example Advantages Disadvantages
OS / LVM Mirroring Logical Volume Managers,
(LVM) Veritas Volume
Manager (VxVM), Windows
Disk Administrator
Little or no application
service disruption
Potential application
delays
UNIX or Windows
Commands
cpio, cplv, dd, tar, backup
restore; copy, scopy, xcopy,
drag and drop
Common, easy to use,
tested
Length of service
interruption varies;
scripting prone to errors
and more testing
Remote Copy Synchronous Mirror (Metro
Mirror); Asynchronous
Mirroring (Global Mirror and
Global Copy)
Operating system
independent
Like storage device
types needed
112 IBM DS8900F: DS8900F Introduction and Planning Guide
 Loading...
Loading...











