Technical Reference
73
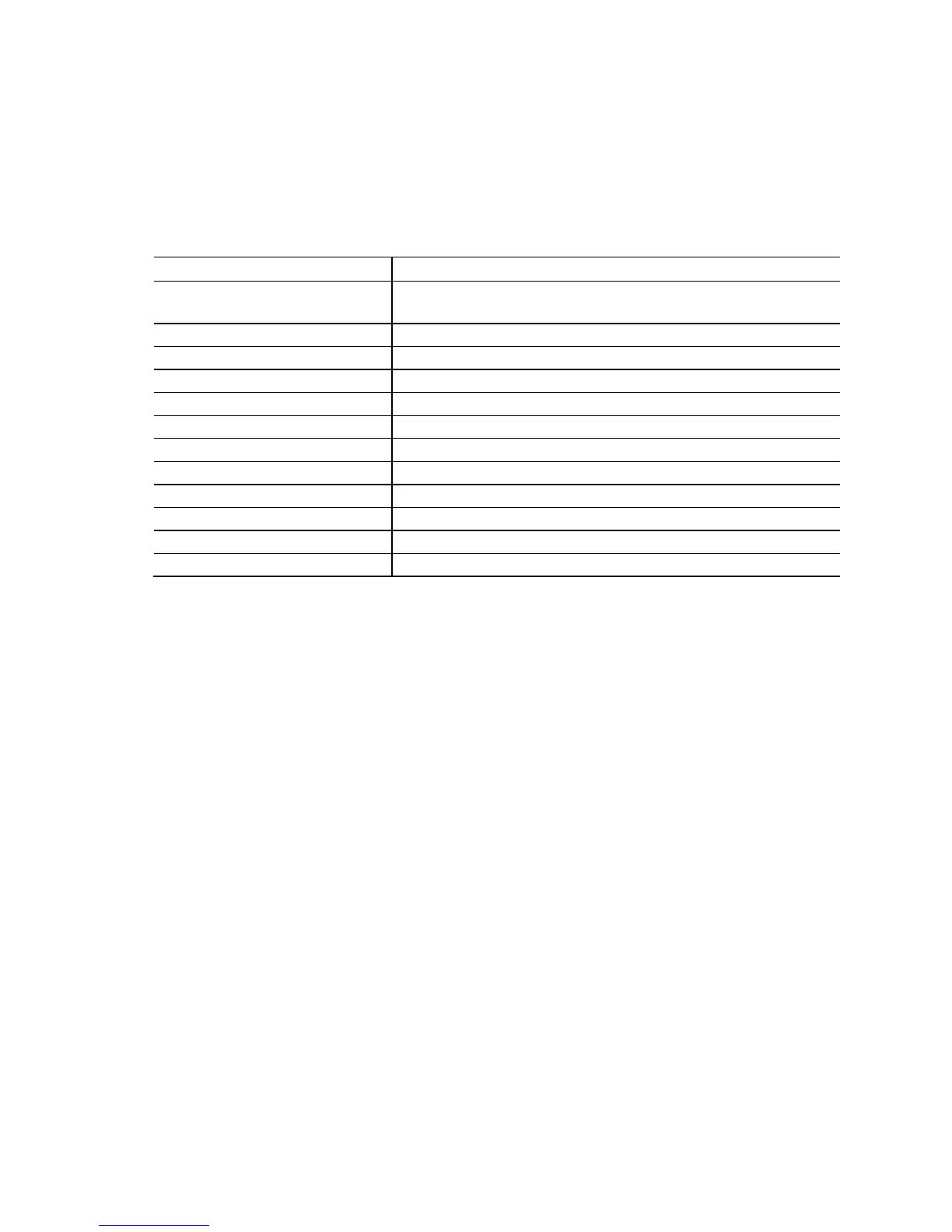
Table 41 provides maximum case temperatures for the components that are sensitive
to thermal changes. The operating temperature, current load, or operating frequency
could affect case temperatures. Maximum case temperatures are important when
considering proper airflow to cool the board.
Table 41. Thermal Considerations for Various Components and Subsystems
Component Maximum Case Temperature
Processor For processor case temperature, see processor datasheets and
processor specification updates
Intel NM10 Express Chipset 115
o
C
Voltage regulator subsystem 85
o
C
Serial port transceivers 85
o
C
mSATA/PCIe multiplexer 85
o
C
SuperIO device 85
o
C
Audio codec device 85
o
C
LAN subsystem 85
o
C
eDP/LVDS subsystem 85
o
C
DC-to-DC subsystem 85
o
C
USB subsystem 85
o
C
SO-DIMMs (typical) 85
o
C
2.7.1 Chassis Design Guideline
The pin fin heatsink design used on this board will be able to dissipate up to 6.5 W of
processor power in most fanless chassis. This board is targeted for 1-3 liters volumetric
or larger in slim desktop or All-in-One configurations, vertically or horizontally oriented
thin mini-ITX chassis
For best thermal performance, it is recommended to have a system fan providing
reasonable airflow directly over all the major components on the board. The pin fin
heatsink is designed to have the best thermal performance when airflow direction is
parallel to the heatsink fins. It is highly recommended that cables and chassis
hardware do not block the direction of the airflow towards the processor, memory or
other components.
The processor on the board will generate the highest amount of heat, leading to high
ambient temperature within the chassis. If available, the system fan should be located
near the board region in order to effectively regulate airflow (see Figure 24). A system
fan located further away from the board region, i.e., at the optical disk drive or hard
disk drive region, will be less effective in controlling the local ambient temperature.
Regardless of where the system fan is located, maximum inner chassis temperature
must not exceed the maximum operating temperature as defined in the environmental
specifications in Section 2.9. Chassis inlet vents should also provide adequate openings
for airflow to pass through. By using the built-in pin fin heatsink, most chassis with a
system fan should have inner chassis temperature safely below the specified limit.

 Loading...
Loading...