48
The switch also performs the following actions on the port that received the IGMP leave message: If the port
receives any IGMP membership report in response to the group-specific query before the aging timer expires, the
switch considers that some host attached to the port is receiving or expecting to receive multicast data from that
multicast group and will reset the aging timer on the port.
If the port receives no IGMP membership report in response to the group-specific query before its aging timer
expires, the switch considers that no hosts attached to the port are still members of that multicast group address and
thus removes the multicast forwarding entry that the port corresponds to from the forwarding table when the aging
timer expires.
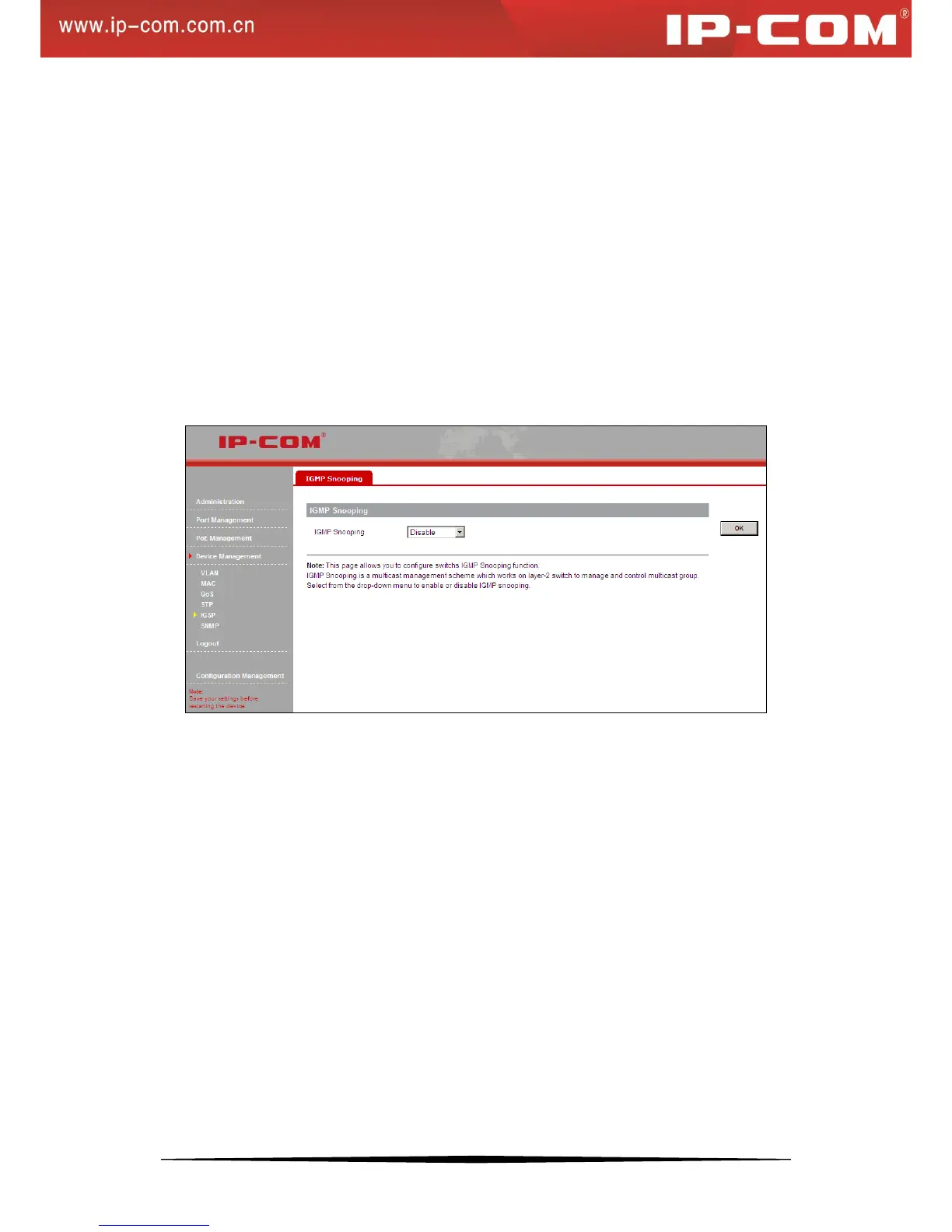
2. IGMP Snooping Configurations
Click Device Management >IGMP > IGMP Snooping to enter the screen below.
To enable the IGMP Snooping feature, simply select Enable and then click OK.
3.5.6 SNMP
1. SNMP Overview
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) designed specifically for
managing and monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management stations to read and modify the
settings of gateways, routers, switches, and other network devices. Use SNMP to configure system features for
proper operation, monitor performance and detect potential problems in the switch, switch group or network.
SNMP, using polling scheme, is suitable for use in small sized network environment demanding high speed and
low cost. SNMP, implemented through the connectionless UDP, can seamlessly interoperate with multiple devices.
SNMP Work Mechanism
The SNMP framework comprises NMS and Agent:
NMS—Network Management Station NMS, is a station that runs the SNMP client software to monitor and manage
the SNMP-capable devices in the network.
 Loading...
Loading...