be measured also generating current; however, with this
connection it is also possible to test the excitation curve.
The following table explains the AC voltage output to be used as a
function of CT parameters.
Given:
. VA = VA rating;
. IS = secondary current;
. KN = overload factor,
compute:
VSM = VA * KN / IS
And then VSM/2, that is the maximum test voltage, so that we
keep away from saturation and the related errors. Note that at
the saturation there is usually 1 V per turn; more rarely 0.5 V per
turn.
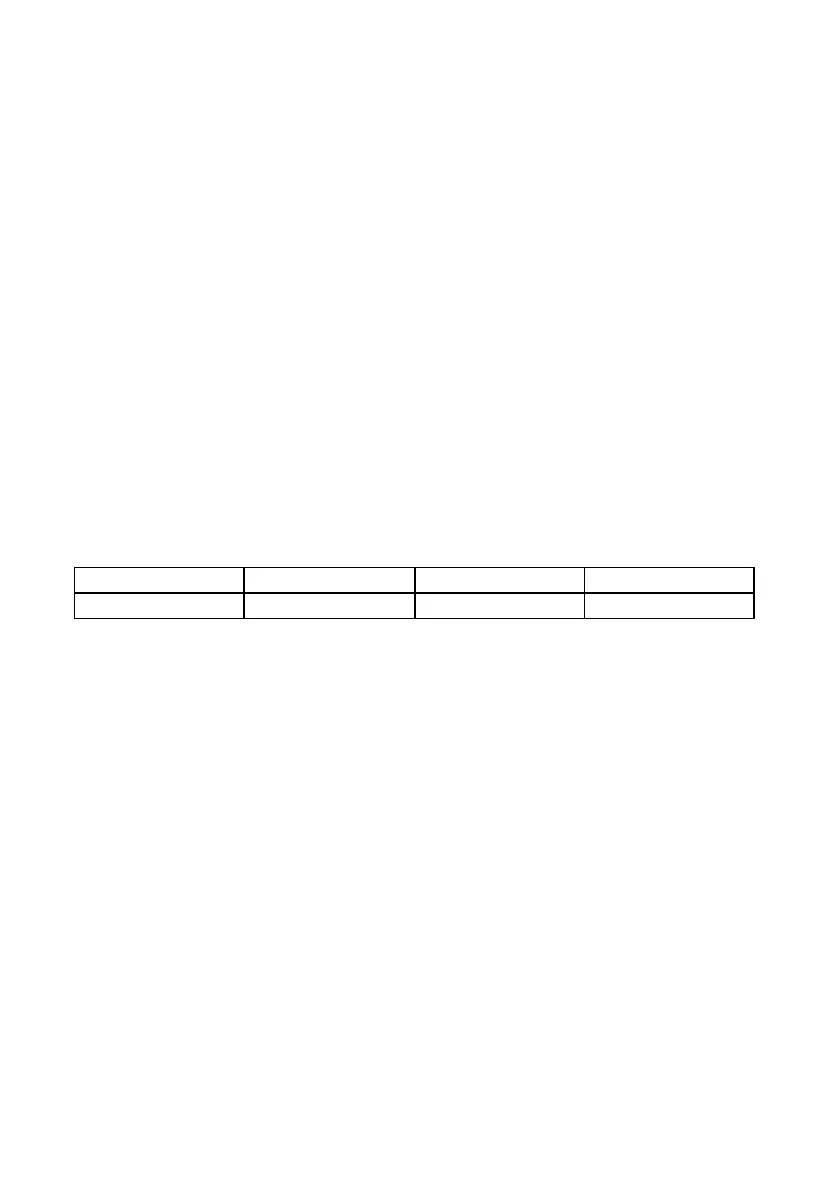
The test voltage range is the following.
VSM/2 < 80 V 80 TO 220 V > 220 V
V RANGE 90 V 250 V 3000 V
The voltage input range is also selected as a function of the test
voltage and of the CT ratio.
Given:
. KCT = CT ratio;
. VP = voltage at primary,
Then, compute:
VP = VSM / (2 * KCT)
If VP > 10 V, then connect the CT’s primary to the 600 V
measurement input, else connect it to the 10 V measurement
input.
The connection diagram is the following.
 Loading...
Loading...